[Chart] Visual Programmability: A Guide for Code-as-Thought in Chart Understanding
[Chart] Visual Programmability: A Guide for Code-as-Thought in Chart Understanding
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.09286
- github: https://github.com/Aphelios-Tang/Code-as-Thought
- archived (인용수: 0호l, 25-09-23 기준)
- downstream task: Chart Understanding
1. Motivation
-
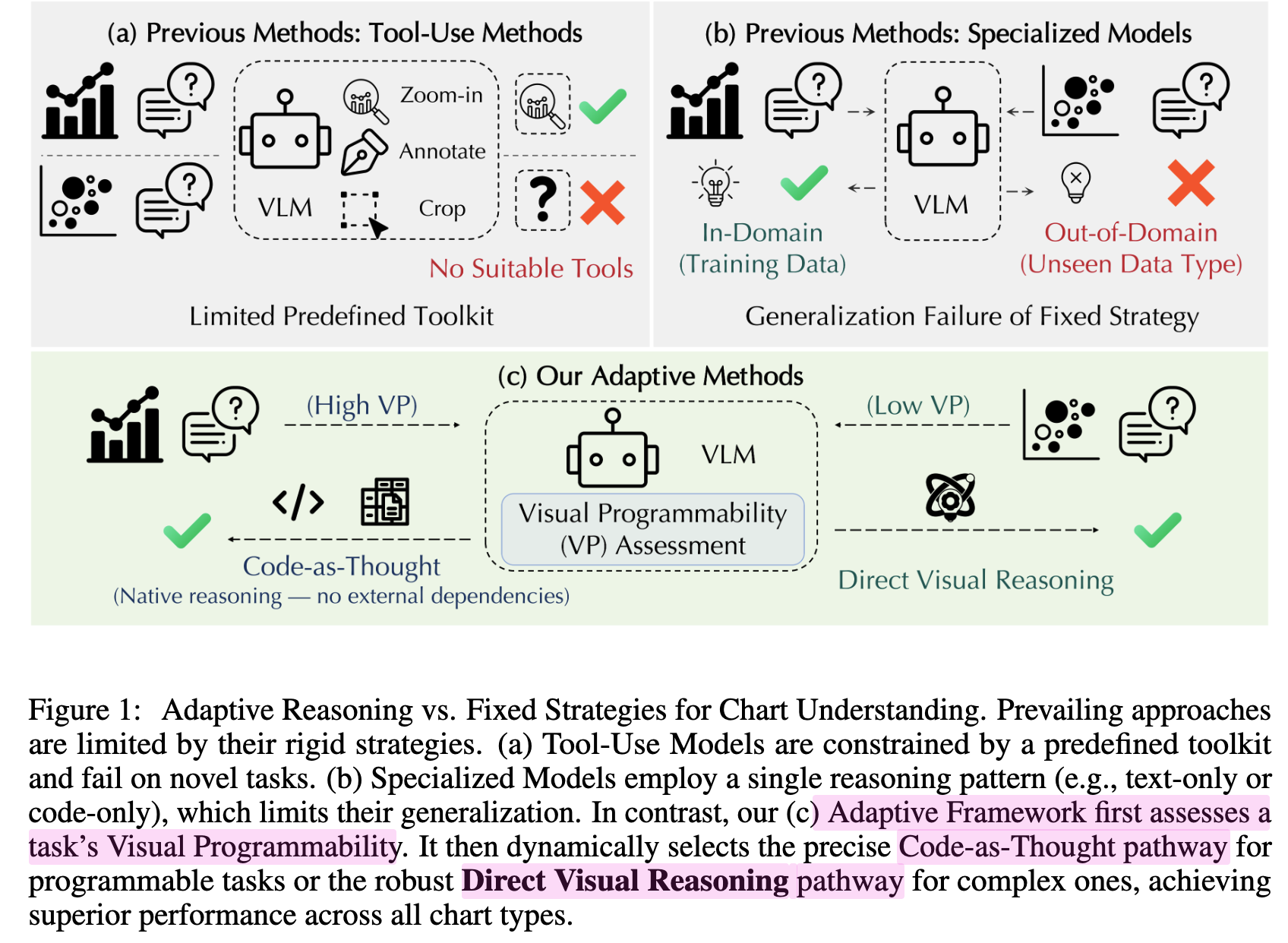
Chart Understanding은 두가지 방식이 존재하며 각각 제약사항이 존재함
-
Pre-defined Toolkit (a)
- 사전 정의된 기능 외에 능력을 요구할 경우 취약함
$\to$ 더 flexible & universal한 tool인 code를 도입
-
finetuning (b)
- SFT로 학습하면 OOD에 대해 성능 하락이 발생함
- CoT 기반의 RL로 학습하기에 중간 thinking step을 검증하기가 어려움
- 1개의 (Monotonic) reasoning style은 전체 chart type에 대해 optimal하지 않음
$\to$ 주어진 Chart, query에 따라 dynamic하게 natural CoT reasoning & code-based reasoning (CaT) 중 1개를 판단하는 dual reasoning 방안을 제안해보자!
-
2. Contribution
-
새로운 chart task에 적합한 code-based reasoning 방법인 visual programmability를 제안함
-
최적의 reasoning path (code / vision)를 adaptive하게 선별하는 adaptive framework를 제안함
-
dual reward system: factual accuracy & strategic flexibility
-
code-only (CaT) 방식은 아래 예시 (a)에서 reasoning 후 예측 시 성능이 향상됨
-
code-only (CaT) 방식은 아래 예시 (b)에서 지속적으로 틀린 reasoning을 예측 $\to$ direct visual analysis(CoT)가 더 효과적
-
아래 예시 (c)처럼 query에 따라 CaT 방식이 좋은 경우 / CoT 방식이 좋은 경우도 있음
ex. CaT가 좋은 예시: “How many distinct data series are plotted?”
ex. CoT가 좋은 예시: “What is the approximate value of the orange line (h/a = 1000) when d = 7?”
-
-
-
outstanding performance & generalization
3. Visual Programmability
-
Code-as-Thought가 Chart Understanding에서 Silver-Bullet인가?
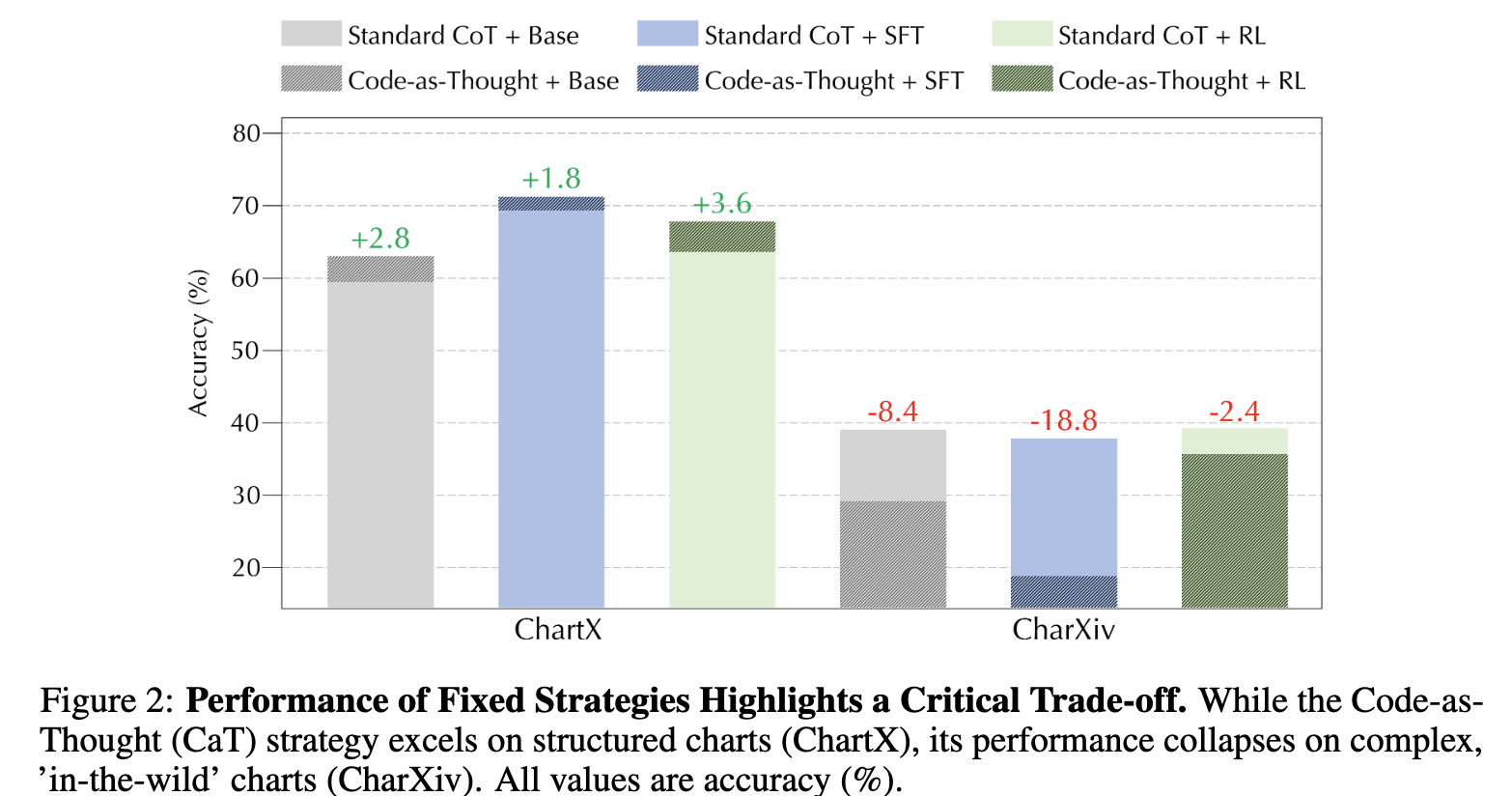
- ChartX: High programability 데이터셋으로 구성된 경우, CoT보다 성능이 향상됨
- ChartXiv: Low programmability데이터셋으로 구성된 경우, CoT보다 열등함
$\to$ No!
-
모델의 능력치의 문제가 아니라 전략을 선택 적용하는 문제임 $\to$ 최적의 전략은 task-dependent함 (Fig.4(c) 참고)
Adaptive Code-Based Reasoning Framework
-
overview
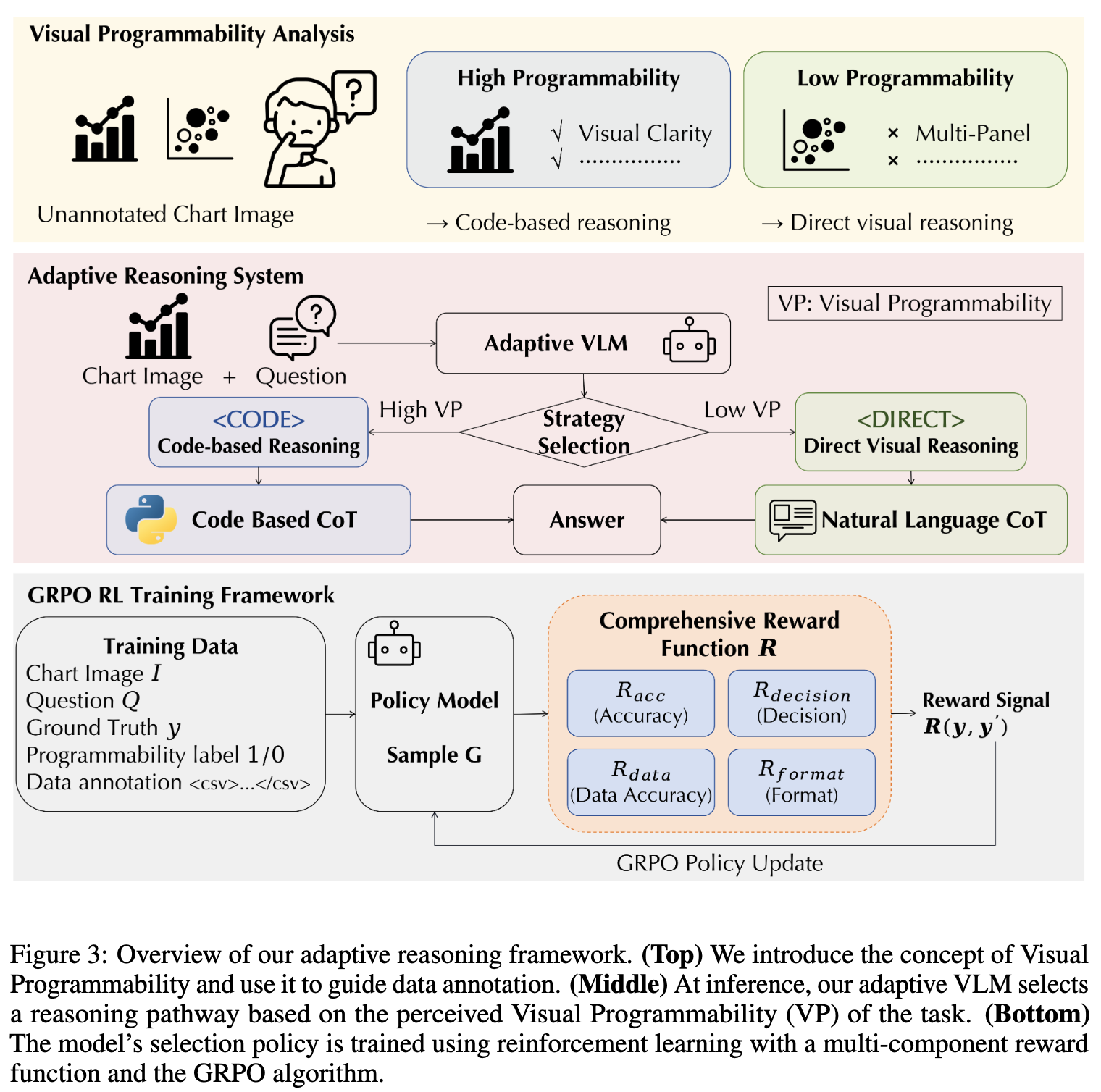
3.1 Visual Programmability: Understanding the Boundaries of Code
-
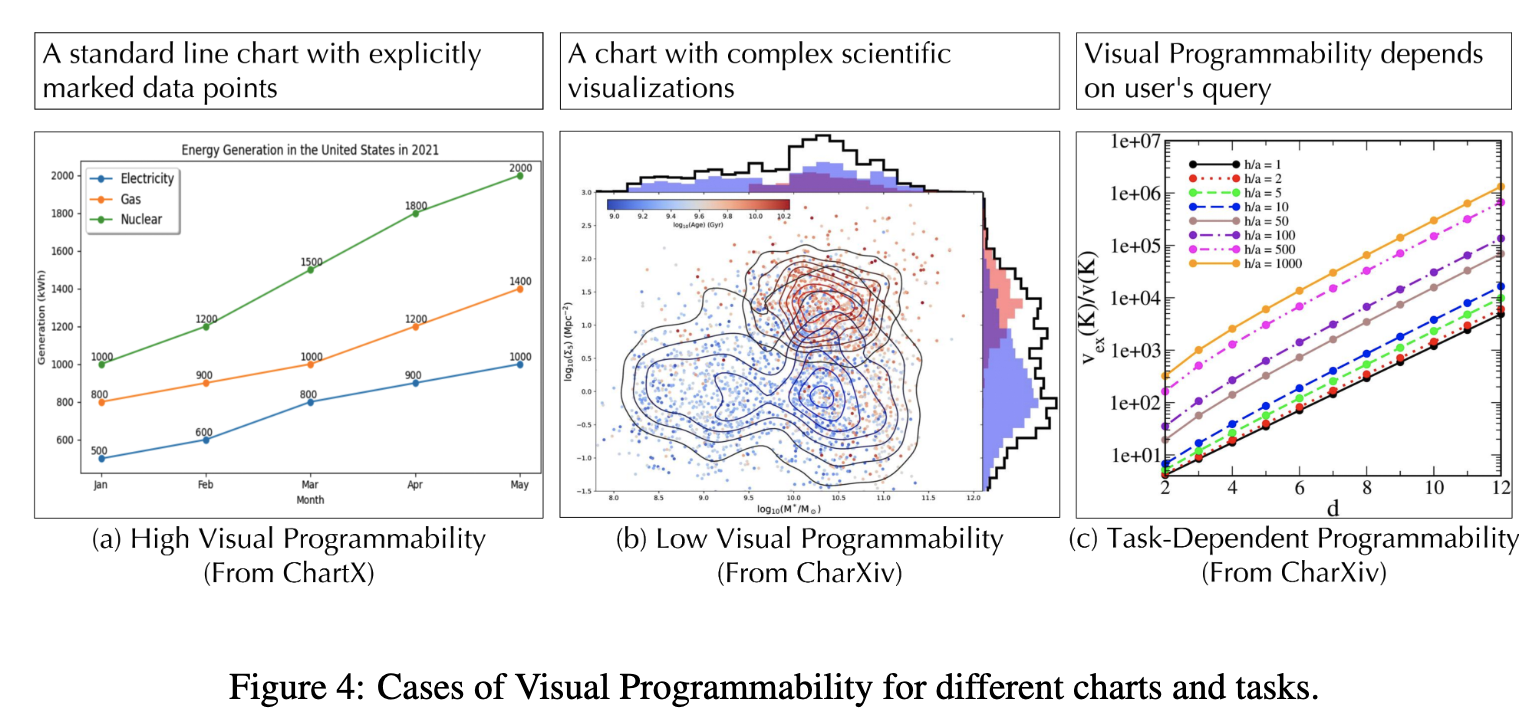
Visual Programmability?
- task(query)에 종속된 속성으로, learnable하며, chart-question pair를 code로 reasoning가능한지 판별함
- chart의 구조적 명료성 (strutural clarity), 시각적 복잡성 (visual complexity), 그리고 본연의 query에 영향을 받음
-
High vs Low Programmability

-
High programmability: (a)
-
Low programmability: (b)
-
query에 따라 High or Low: (c)
ex. High programmability: “How many distinct data series are plotted?”
ex. Low programmability: “What is the approximate value of the orange line (h/a = 1000) when d = 7?”
-
3.2 Adaptive Reasoning Mechanism
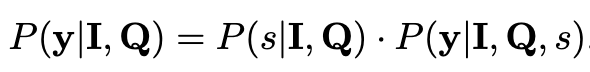
- $y$: complete response
- $I$: Image
- $Q$: Query
- $s$: selected strategy token $\in {
,\}$ - Code based Path (
): chart를 parse하기 위한 코드를 작성 (ex. DataFrame)하여 answer를 계산 - Direct Path(
): natural language COT기반으로 전반적인 visual perception을 수행.
- Code based Path (
3.3 Training via Reinforcement Learning
-
outcome-based reward를 적용
-
GRPO
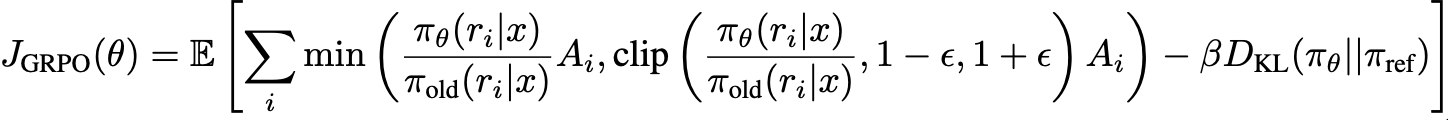
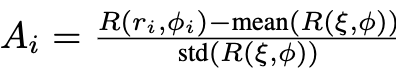
- $\pi_{old}$: previous version policy
- $\pi_{\theta}$: current version policy
- $\pi_{ref}$: sft된 policy
-
reward

-
accuracy reward: 최종 정답과 일치하면 1.0, 아니면 0.0
-
decision reward
- strategy를 올바르게 선택 + 정답이 올바르면 full reward
- strategy는 올바른데 + 정답이 틀리면 partial reward
- strategy가 틀리면 0.0
-
data accuracy reward
-
Code-path일 경우만 적용하여 hallunication을 해결하고자 도입
-
code로 생성한 DataFrame과 csv ground-truth 정답으로부터 추출한 table의 값을 비교 (row 갯수, column 갯수, value일치여부 종합적으로 평가)
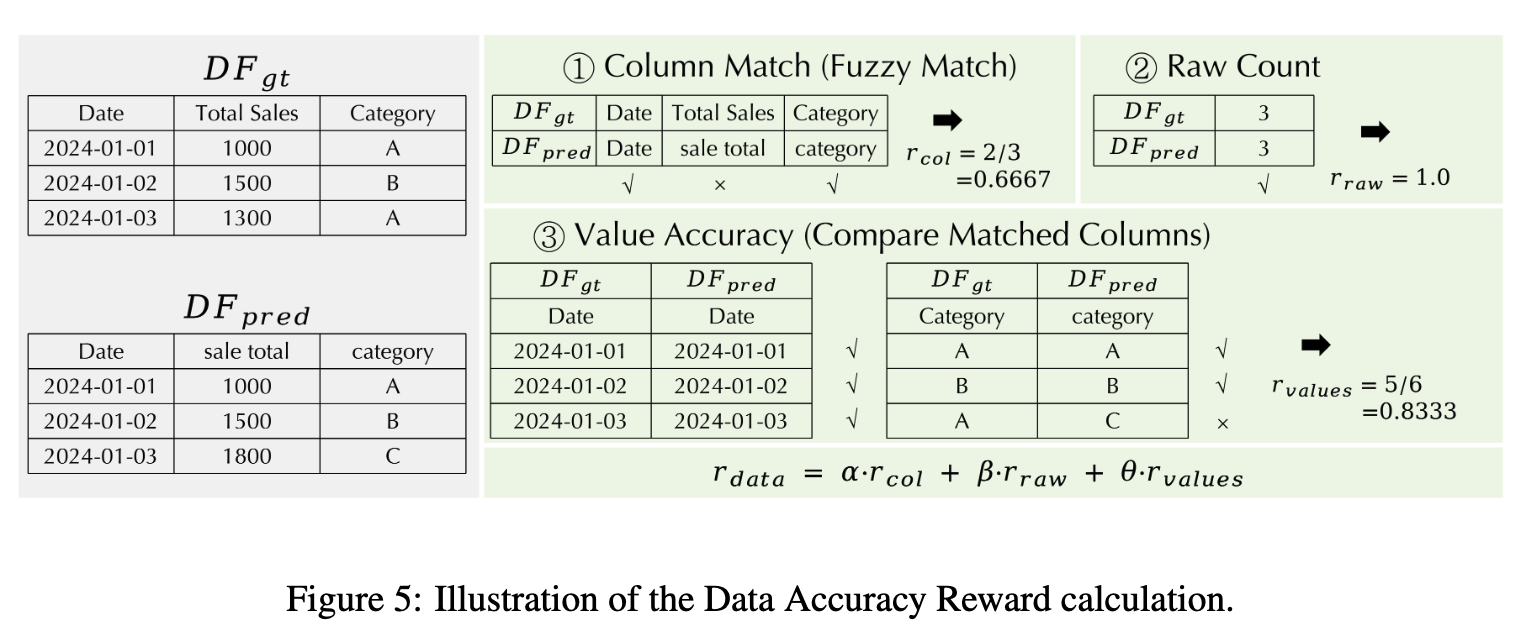
-
알고리즘

-
-
-
format reward
- 정답이 \boxed{} 형태로 출력되면 1.0, 아니면 0.0
-
4. Experiments
- Data
- Training
- CaT: ChartMimic dataset (4.8K)
- CoT: Gemini-2.5-Flash로 생성한 question-answer pairs
- Evaluation
- ChartX: high-programmability dataset
- ChartBench
- ChartQA
- CharXiv: low-programmability dataset (과학수업 자료, etc)
- Training
- Model
- Qwen2.5-VL-7B
-
정량적 결과
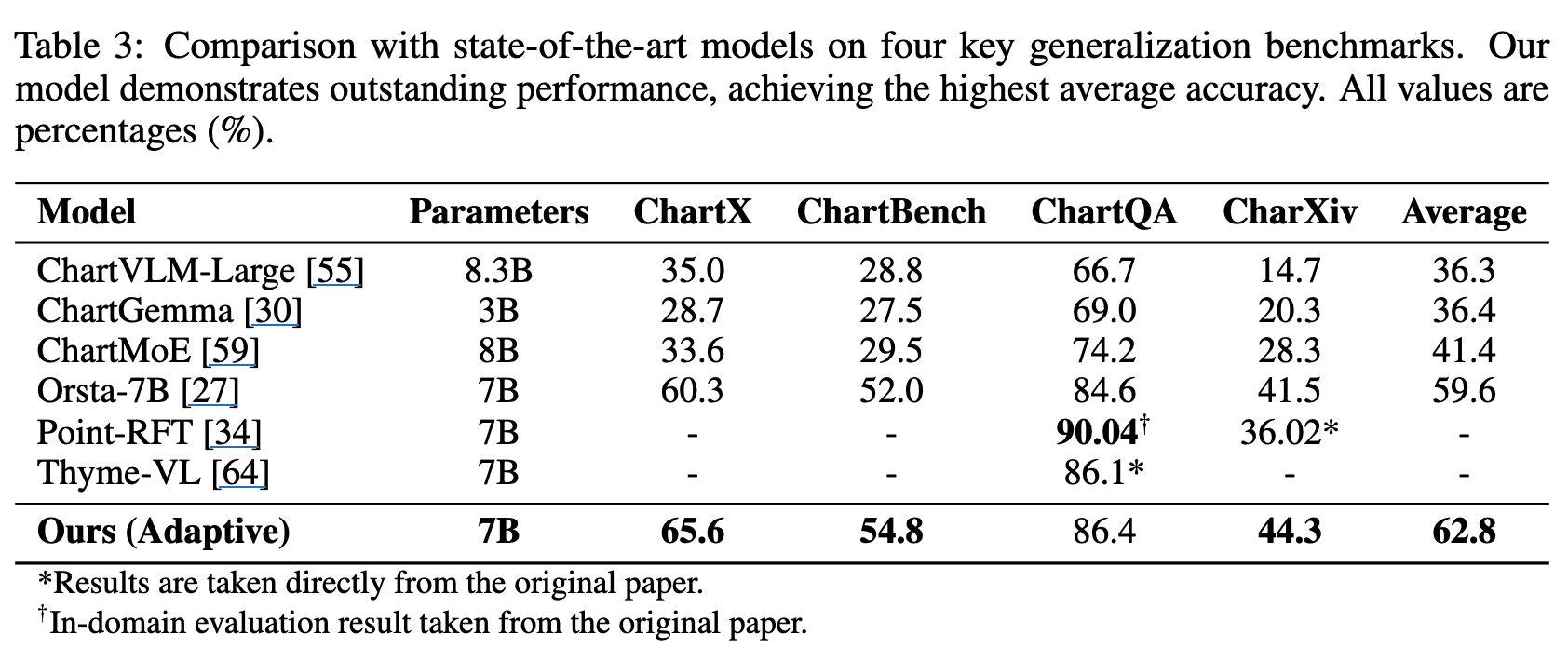
-
Ablation Study
-
Visual Programmability vs. Fixed Strategy
-
성능 비교
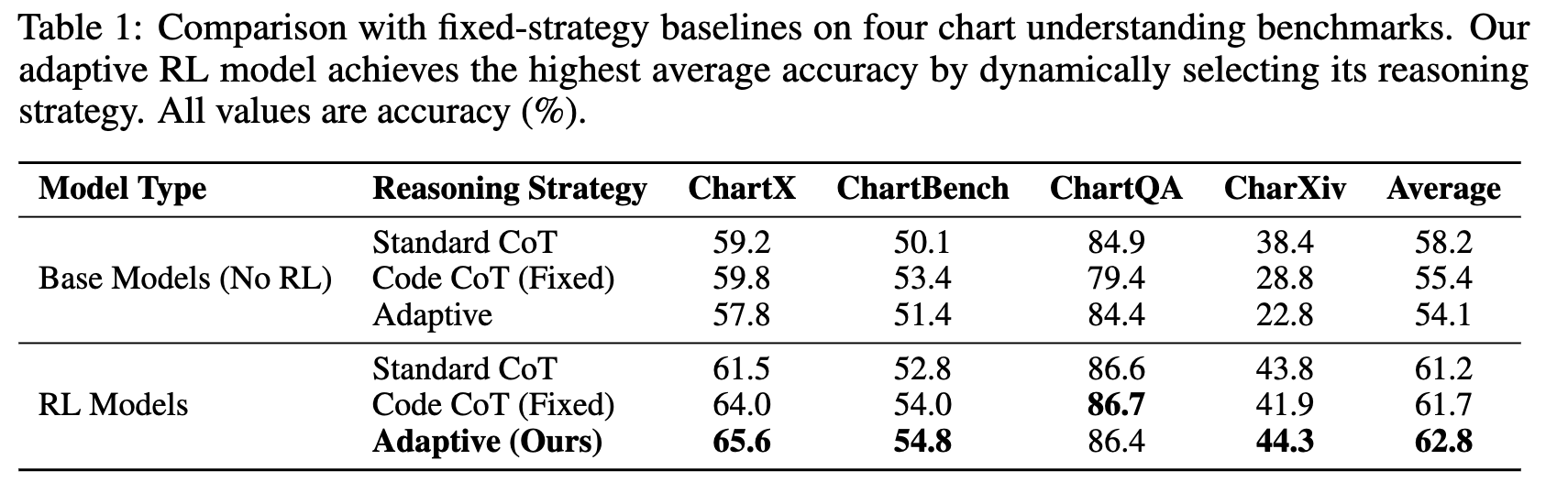
-
Code-as-Thought 사용정도 비교
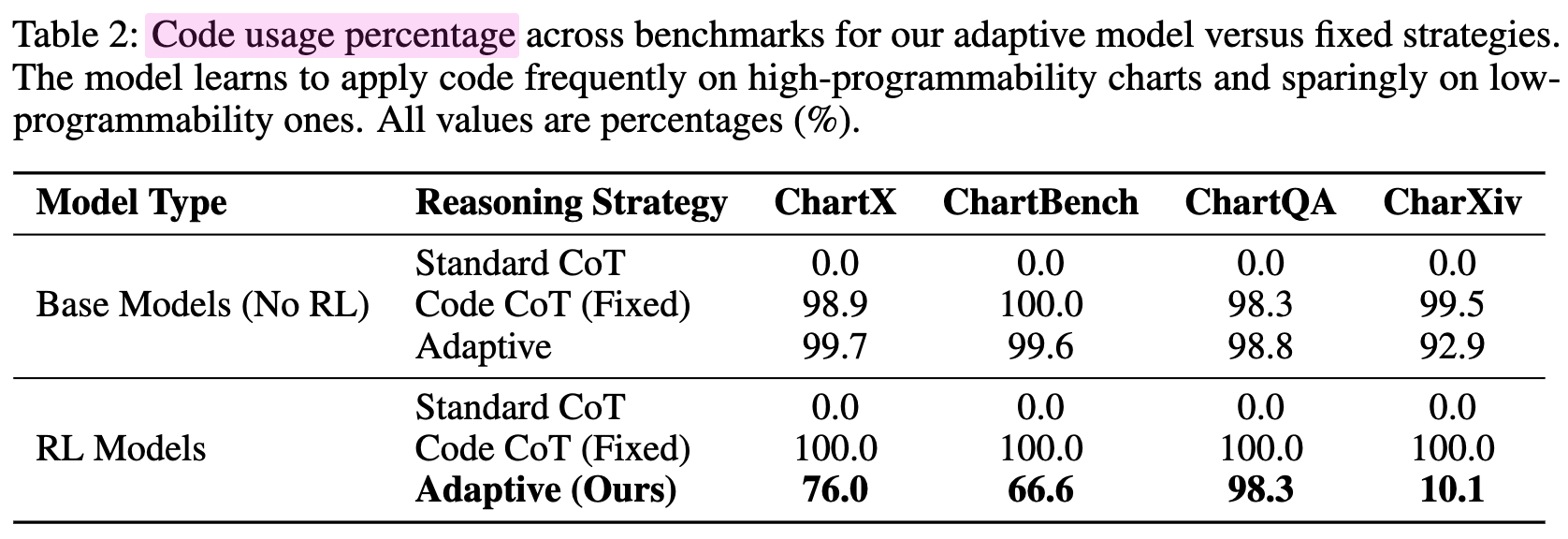
-
-
모델 크기별 성능 분석
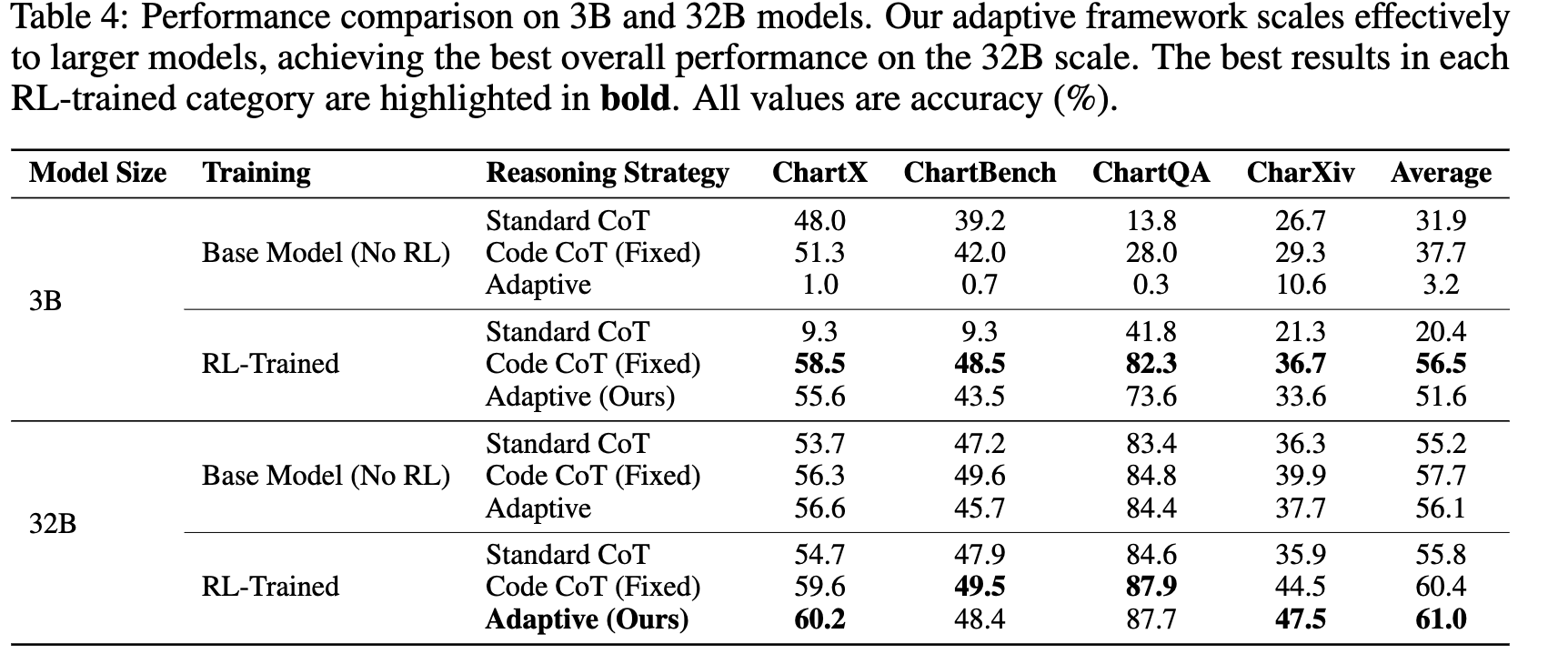
-
-
Reward 별 성능 기여도 분석
-
성능 비교
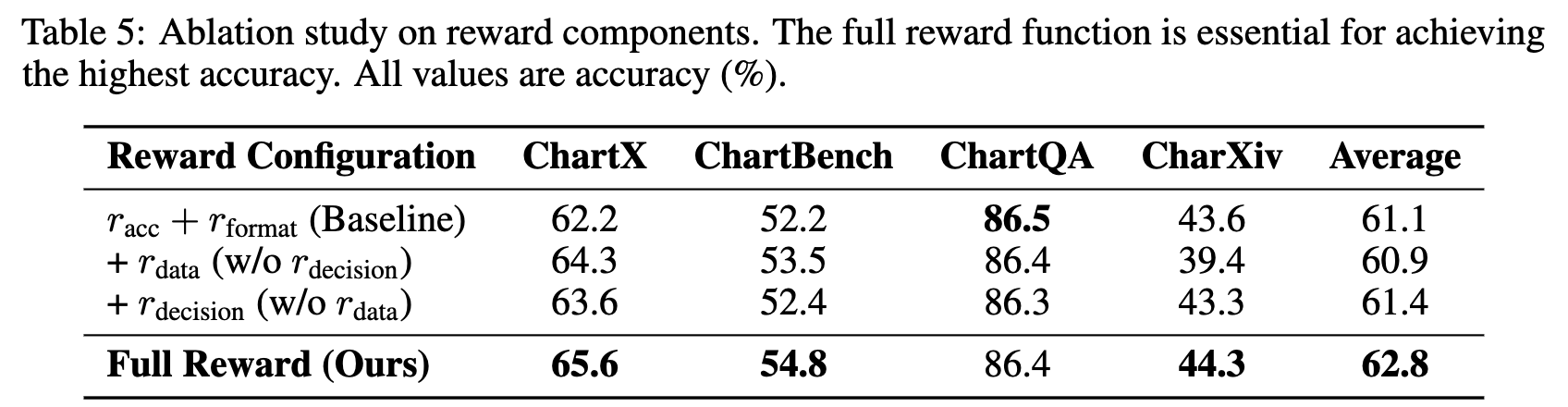
-
Code-as-Thought 사용율
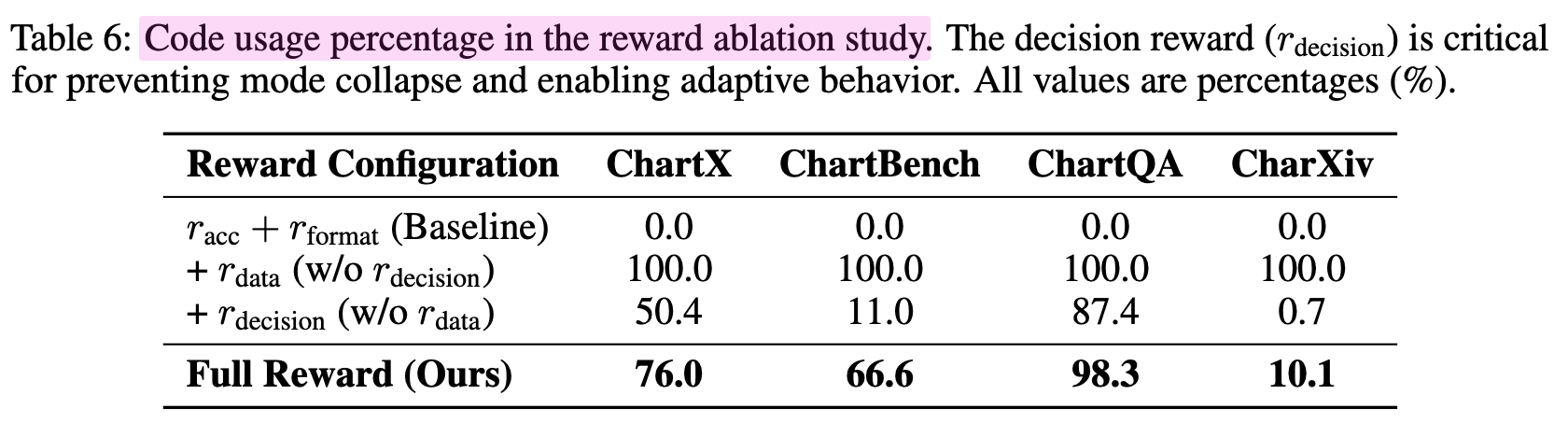
-
-
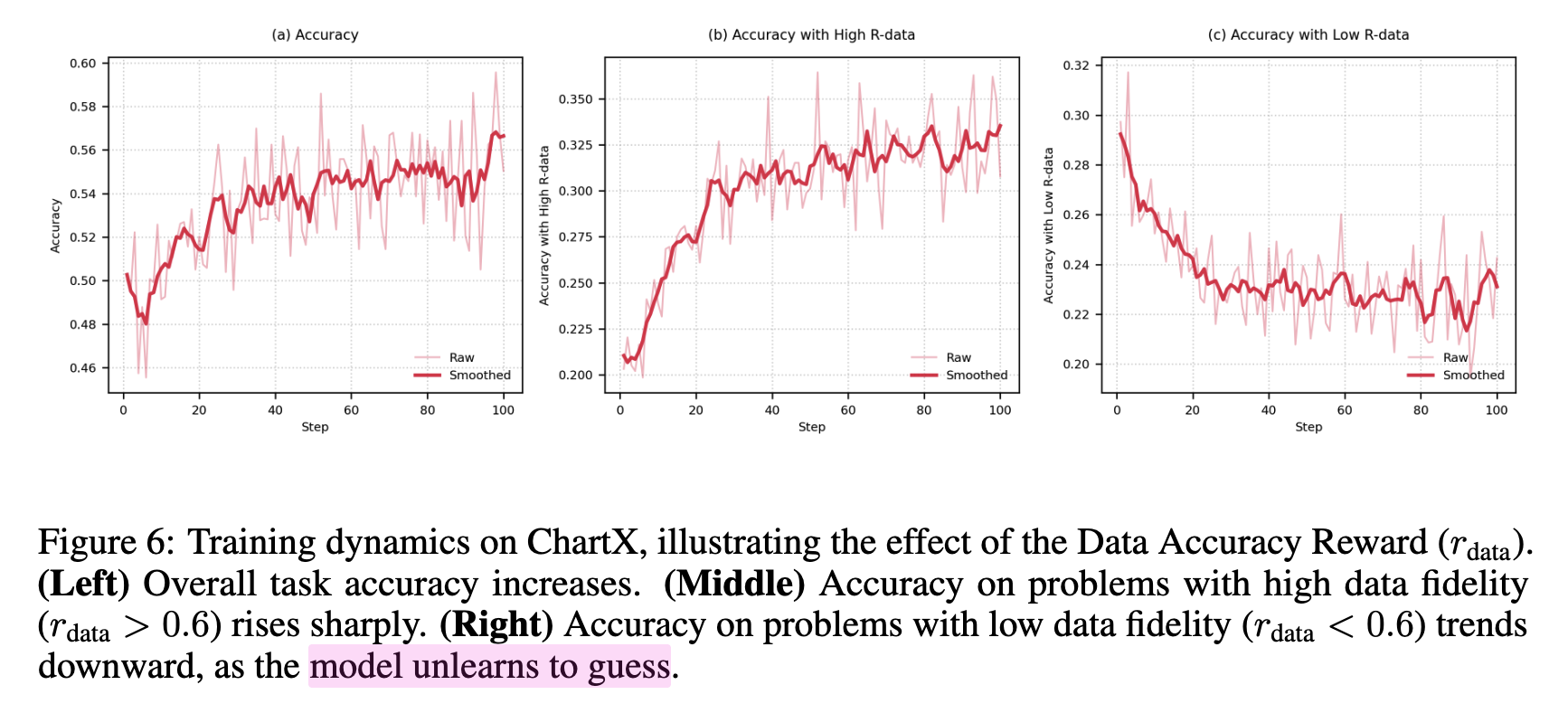
reasoning의 수치적 정확도가 얼마나 중요한지 추가 실험
- 수치 fidelity (정확도) 가 높은 경우, 최종 정답이 맞는 확률이 올라감
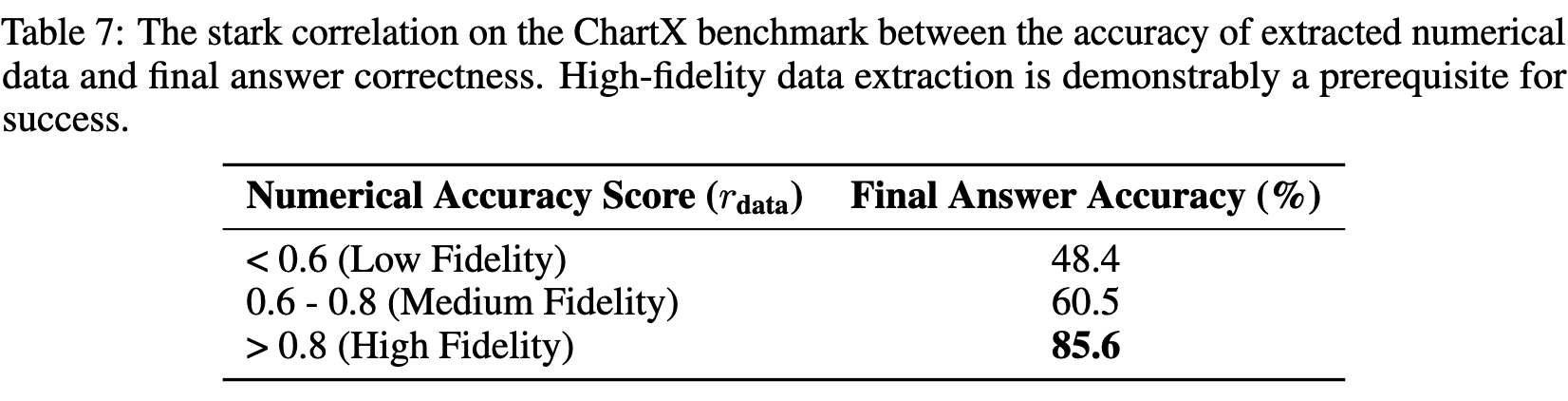
-
data accuracy reward는 수치 정확도가 낮은 경우를 “unlearn”하도록 함 (결과적으로 (a) 전체 accuracy가 상승하므로.)