ShowUI: One Vision-Language-Action Model for GUI Visual Agent
[WebGUI] ShowUI: One Vision-Language-Action Model for GUI Visual Agent
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.17465
- github: https://github.com/showlab/ShowUI
- CVPR 2025 accepted (인용수: 50회, ‘25-06-27 기준)
- downstream task: Web element grounding, Web Navigation
1. Motivation
-
기존에 GUI assist agent는 language-based (ex. HTML, accessibility tree) / closed-source API기반이 많았음 $\to$ 이들은 사람과 같이 UI를 이해하는 능력이 부족함
-
최근 Multimodal agents가 등장했으나, 두 가지 한계가 있음
-
고해상도 (>2K resolution) 이미지에 대한 long-context processing에 비용적 한계
-
Vision-Language-Action을 관리하기 어려움
ex. “scroll”은 website는 2가지 방향, mobile은 4가지 방향
“Return” on website == “Press home” on mobile
-
다양한 training data
-
element grounding
-
navigation
$\to$ 어떻게 효율적으로 사용할지에 대한 연구가 부족함
-
-
2. Contribution
-
Vision-Language-Action model인 ShowUI agent를 제안함
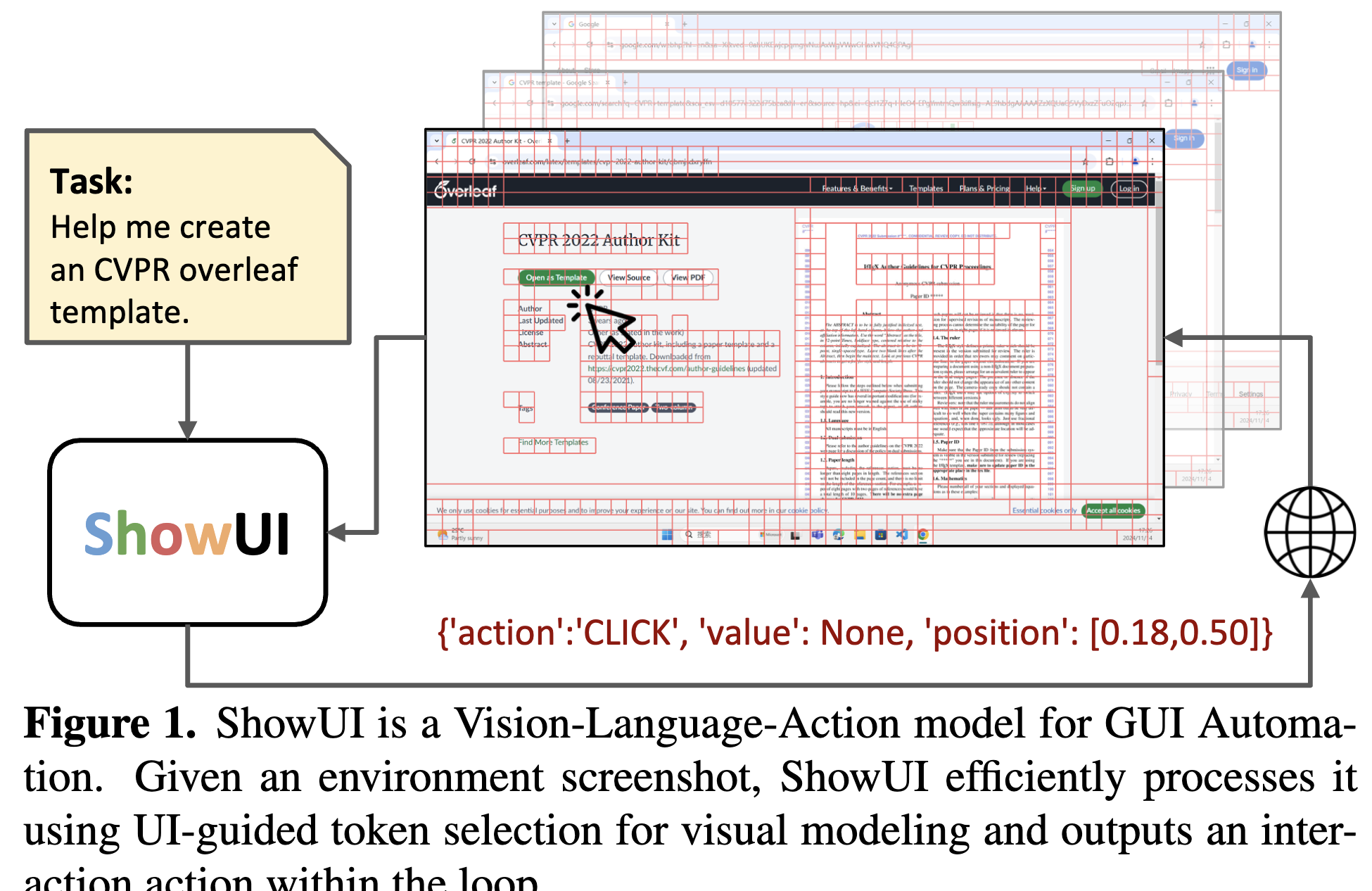
- UI-Guided Visual Token Selection: Screenshot을 UI connected graph로 모델링하여 redundunt한 관계를 이용함으로써, 해당 정보가 self-attention block에서 중복 token의 선별 기준이됨 $\to$ 계산량 줄이고(33%), 성능은 향상(1.4배 향상)
- Interleaved Vision-Language-Action Streaming: GUI navigation을 위해서 필수인 action과 screenshot, 그리고 query간의 interleaved한 이해를 위하여 action space에 대한 document 제공, vision token length와 action의 balance를 위해 multi-turn action과 text query를 pairing하는 방법을 제안함
- Small-scale High quality GUI Interaction-following dataset: data type별 imbalance 해소를 위한 resampling 전략과 정밀한 데이터 정제를 통해 256K data를 제안
-
해당 데이터 기반 2B lightweight model로 zero-shot screenshot grounding에서 75.1% accuarcy
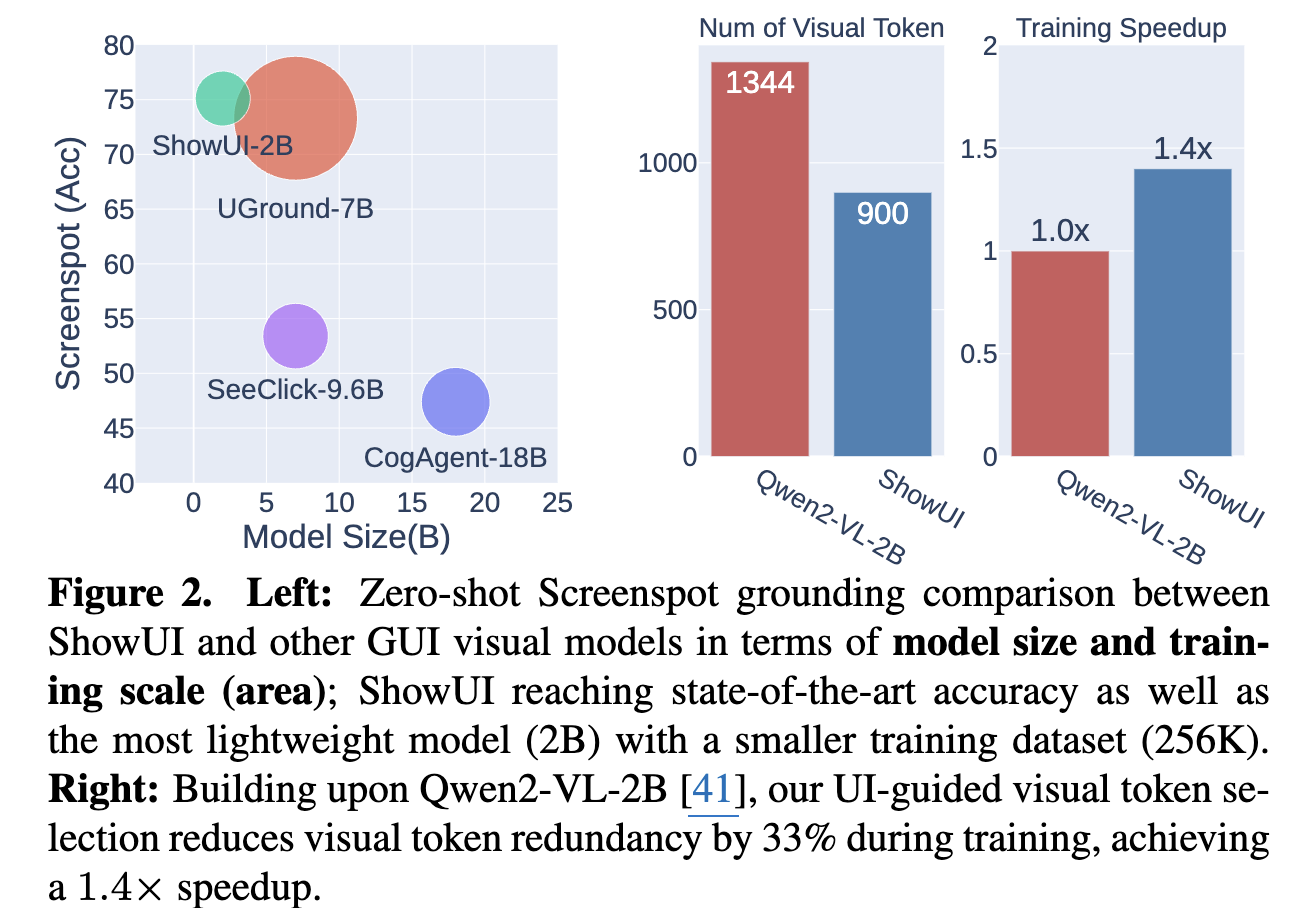
-
Web, Mobile, ,online 환경의 navigation에서도 GUI agent의 효과가 있음을 밝힘
3. ShowUI
-
Overall Architecture
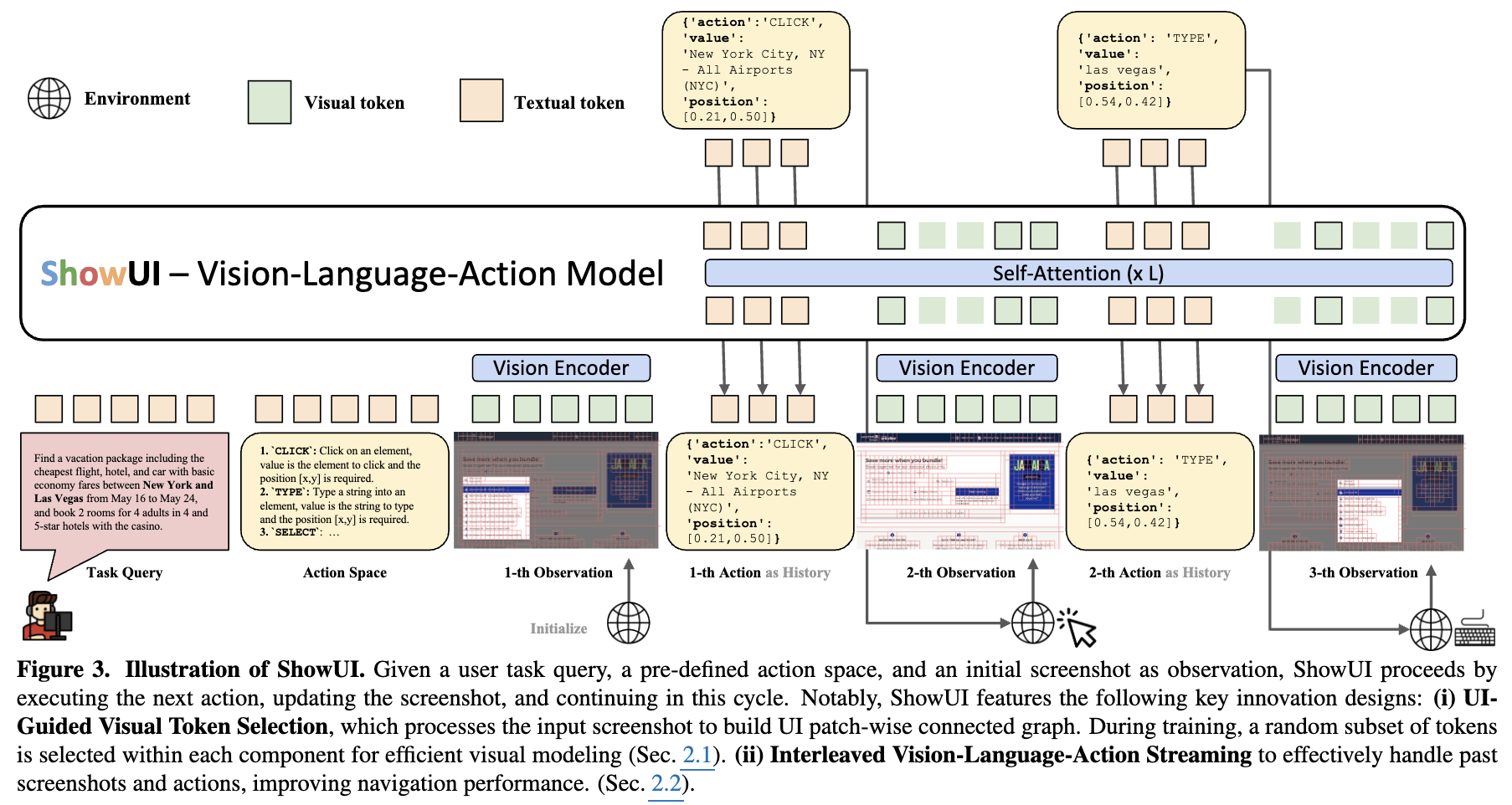
3.1 UI-Guided Visual Token Selection
-
UI screenshot이 natural vision과 무엇이 다른가?
- 내재적으로 구조화되어 있음 (html format)
- readability와 usability를 위주로 설계되어 있음 $\to$ 빈 공간에 상대적으로 정보가 적고, text & icon에 전달할 정보가 가득함
-
UI Connected Graph 구축
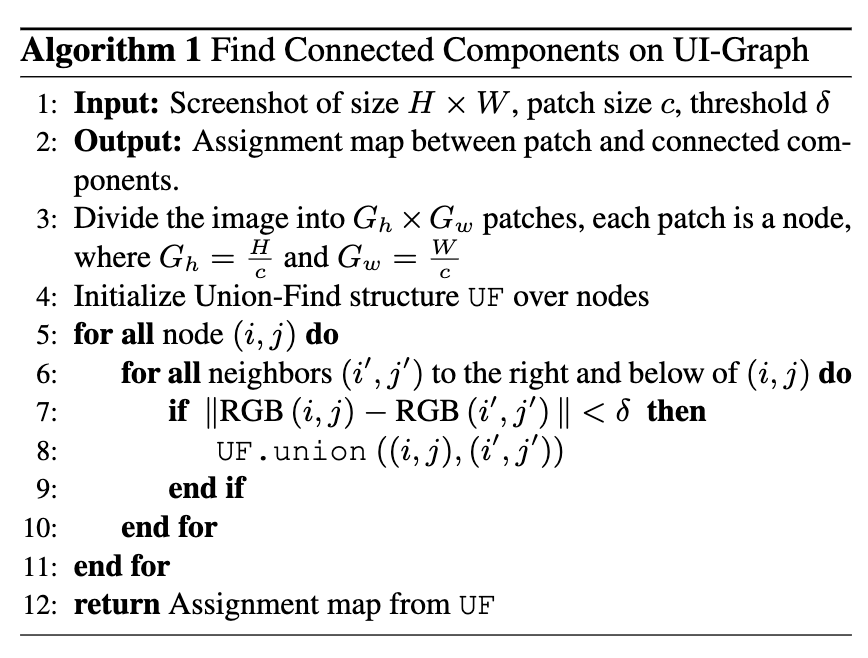
-
Union-Find method: 각 image patch를 node로 보고, RGB 값을 기준으로 작은 threshold값보다 차이가 적게 나면 redundunt한 patch끼리 grouping함
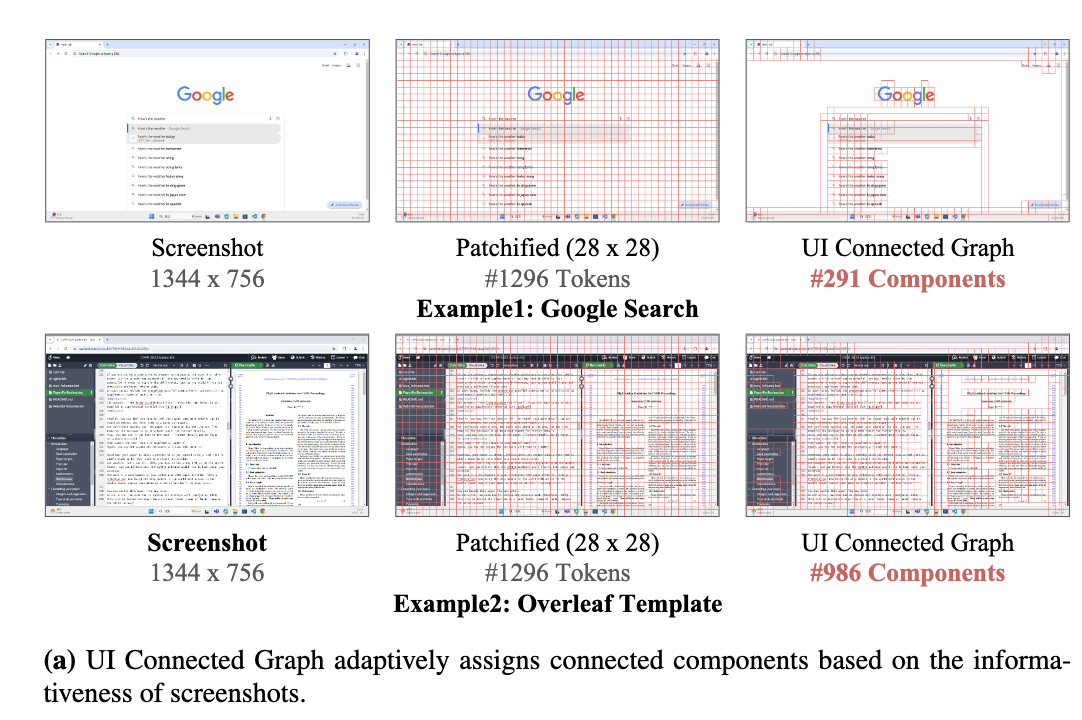
-
Device별 Union-Find 결과
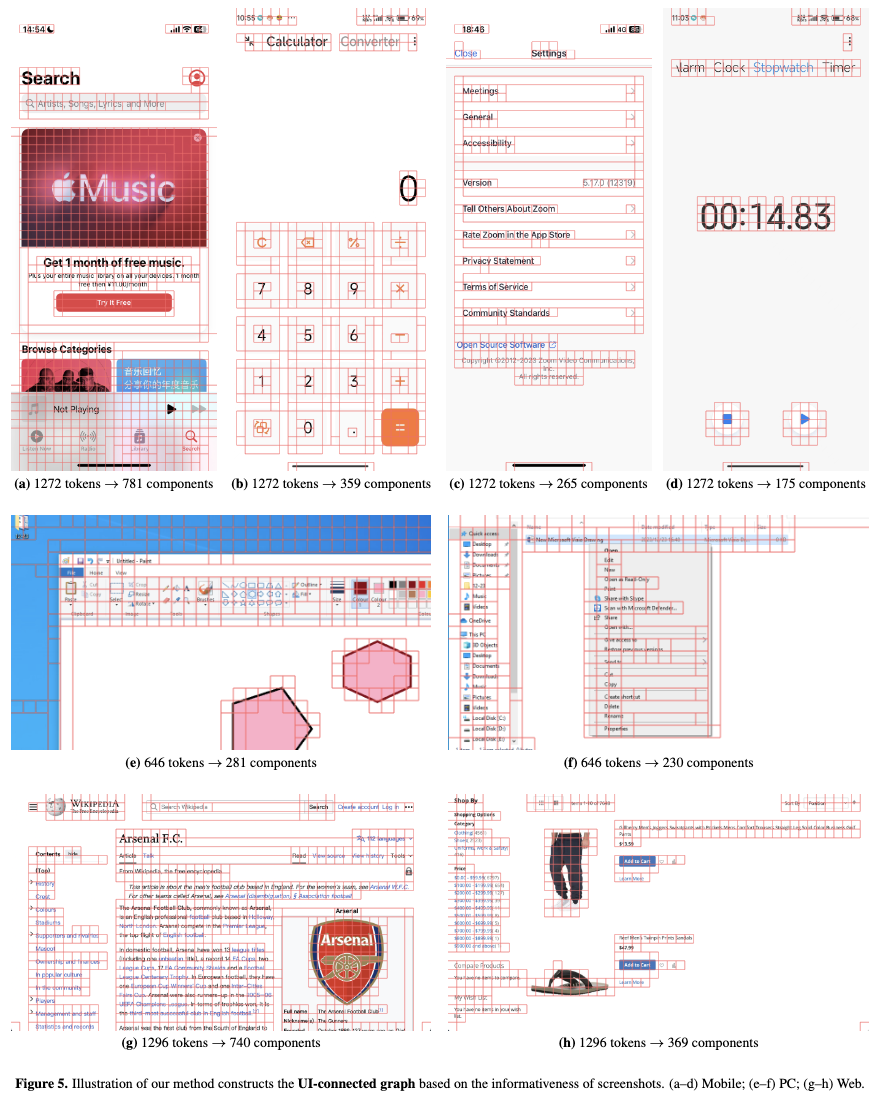
-
-
Token Merging v.s. Token Selection
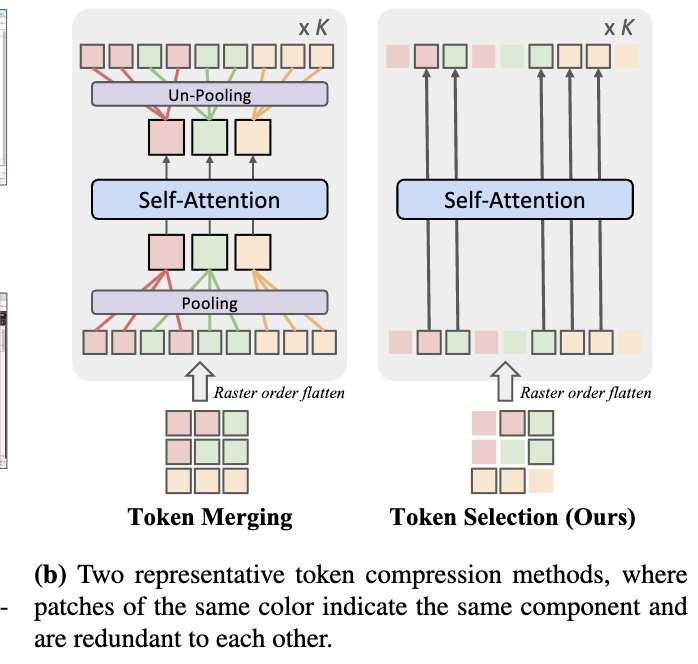
- Token Merging을 쓰면 positional information lose가 필연적으로 발생함
- Token Selection은 random portion으로 같은 group 내 patch를 skip하고, selection된 patch는 원본의 positional information을 보존함
3.2 Interleaved VLA Streaming
-
Action이 natural text와 무엇이 다른가?
-
query가 주어진 상황에서 next action의 type과 action parameter를 예측.
-
device별로 다른 action space
-
같은 기능인데 다른 action name인 경우
(e.g. [CLICK] in web / [PRESS HOME] in mobile)
-
같은 action name인데 parameter가 다른 경우
(e.g. [SCROLL] in web에서는 up&down 2개 뿐 / mobile에서는 up&down&left&right 4개)
-
-
JSON format으로 구조화
(i.e., {‘action’: ‘action type’, ‘value’: ‘element’, ‘position’: [x,y]})
-
action에 대한 README를 system prompt에 주입하여 암기하지 않고, 해당 prompt를 참고하도록 model을 훈련 $\to$ test-time에 새로운 action이 나오더라도, 재학습 없이 system prompt만 바꾸면 되도록.
-
-
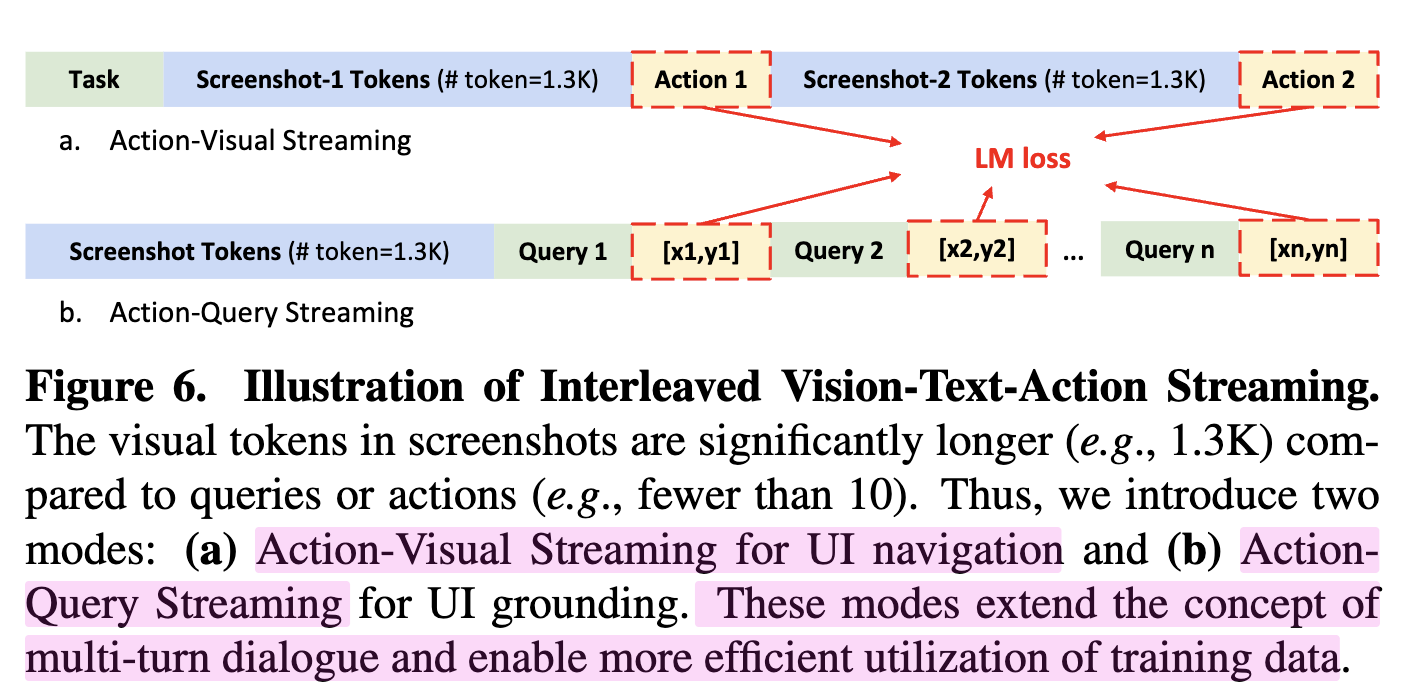
Action with Visual
- 과거의 screenshot history와 action history를 번갈아 capture하며 LM loss로 next action 예측하도록 학습
- web일 경우, 화면전환이 static하므로, screenshot을 masking하는 전략을 통해 학습 효율을 높임
-
Action with Text Query
- 1 step navigation 혹은 element grounding의 경우, one-image에 parallel actions 혹은 multiple elements가 등장함
- query와 answer는 image에 비해 token이 훨씬 적으므로 one-image-one-query는 학습이 비효율적임
- one-image-multi-queries 로 전환하여 학습
3.3 GUI Instruction Tuning
-
다양한 web/mobile benchmark를 선별함
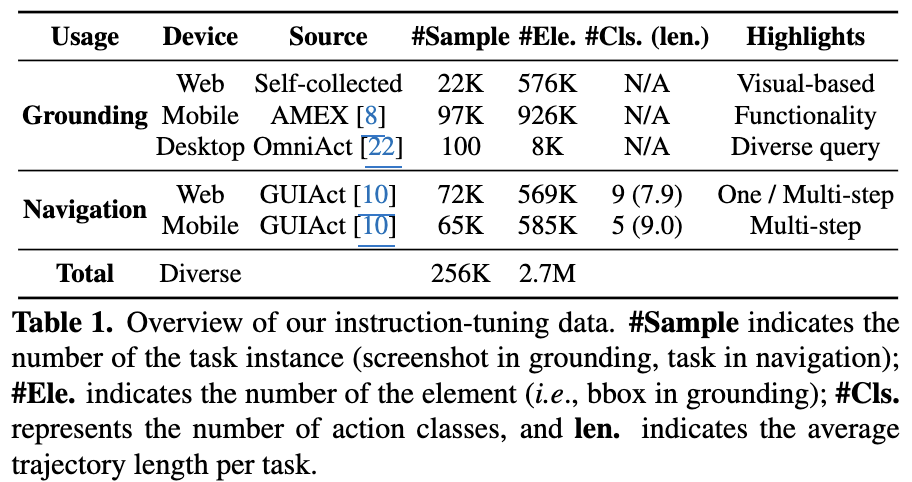
-
Web-visual elements
- static text가 전체 element중 40%를 차지
- VLM의 OCR성능이 좋음에 착안하여 visually rich한 element 중심으로 collect함 $\to$ 22K Web (‘Button’, ‘Checkbox’ 등)
- static text가 전체 element중 40%를 차지
-
Desktop diverse query
-
자동 수집이 어려우므로, web에 비해 상대적으로 desktop data는 귀함
-
OmniAct dataset (2K elements, 100 images) 기반으로 하되, raw element tag (ex. ‘message_ash’) 가 아니라 3가지 meta data를 GPT기반으로 정제함
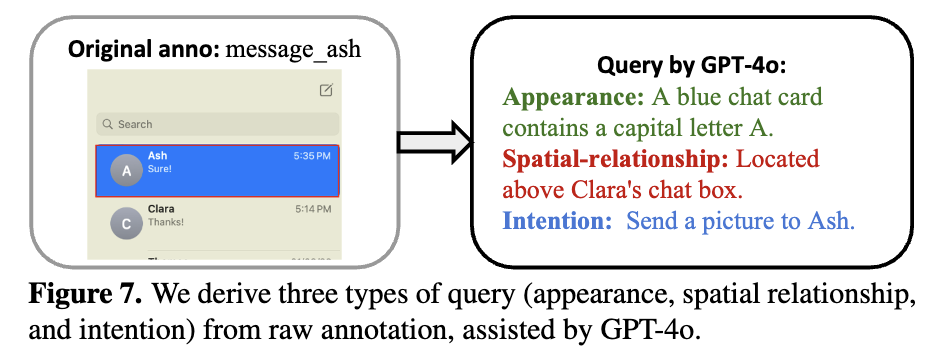
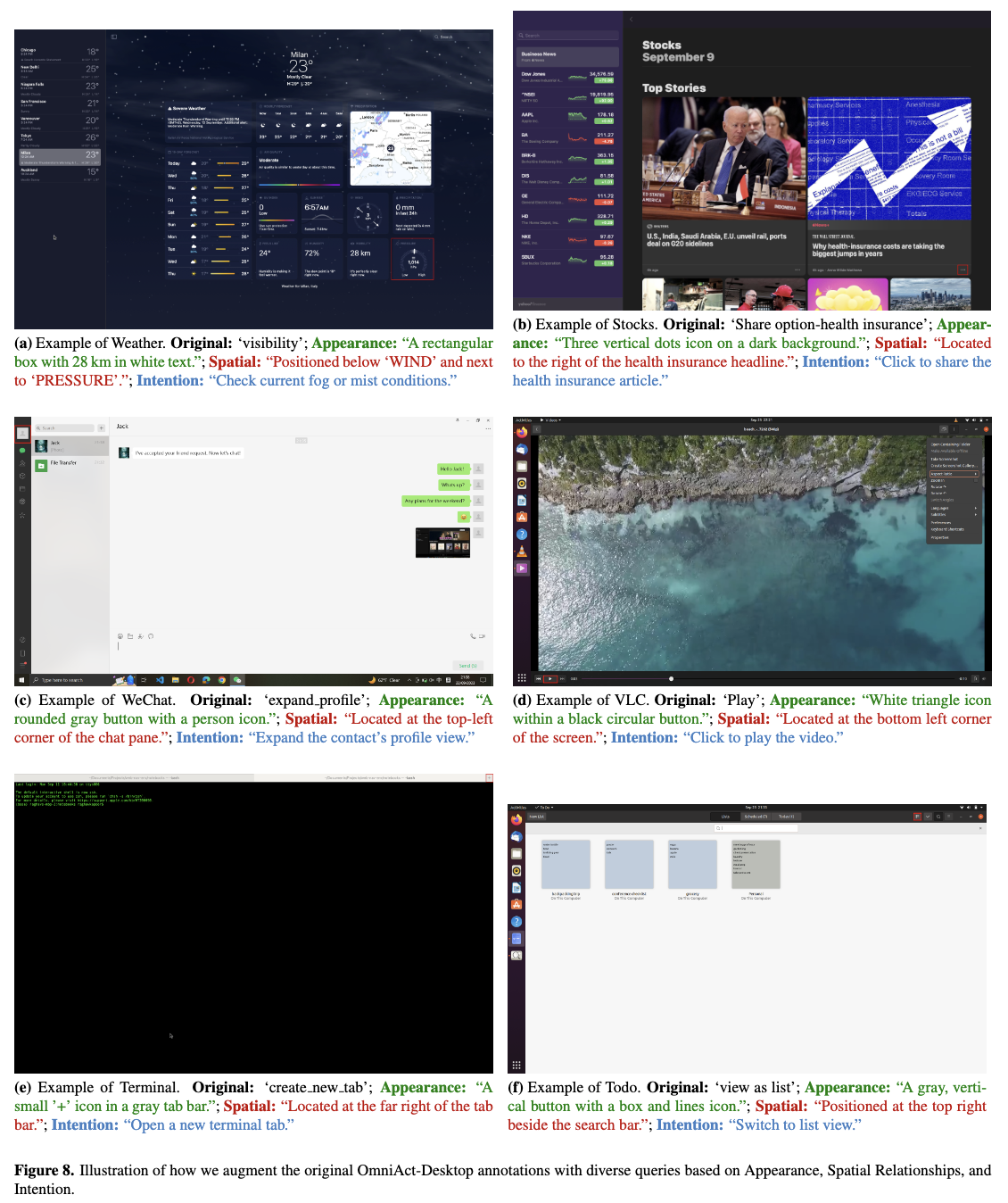
-
-
Mobile Functionality
- AndroidLike에 정의된 description 사용
-
Balance data by Sampling
- 다양한 data (desktop, mobile, web)간에 균일한 sampling하도록 sampling
4. Experiments
- Evaluation Benchmarks
- Grounding: Screenspot
- Navigation
- Web: Mind2Web
- Mobile: AITW
- Online: MiniWob
4.1 Main Results
-
Grounding Tasks
-
정량적 결과
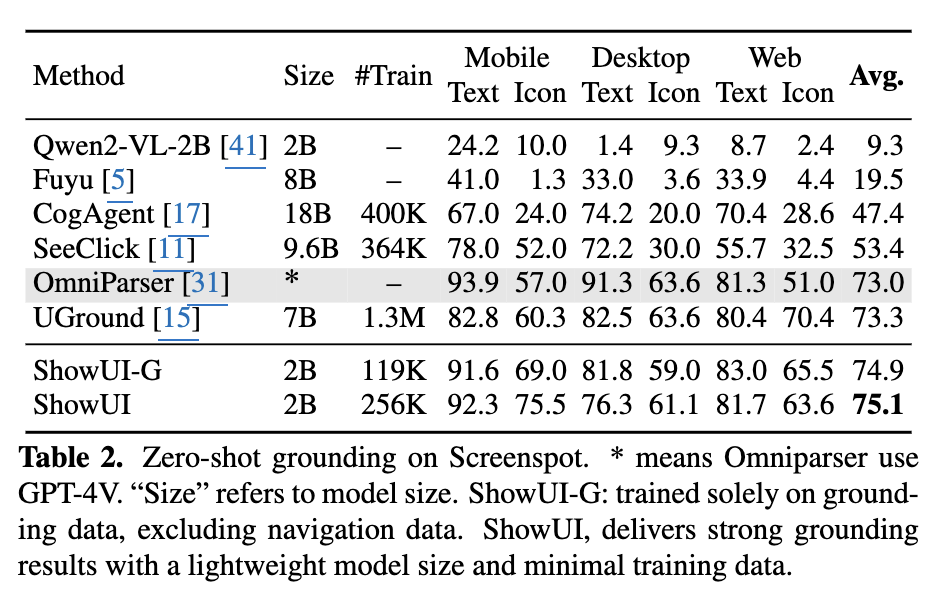
-
정성적 결과
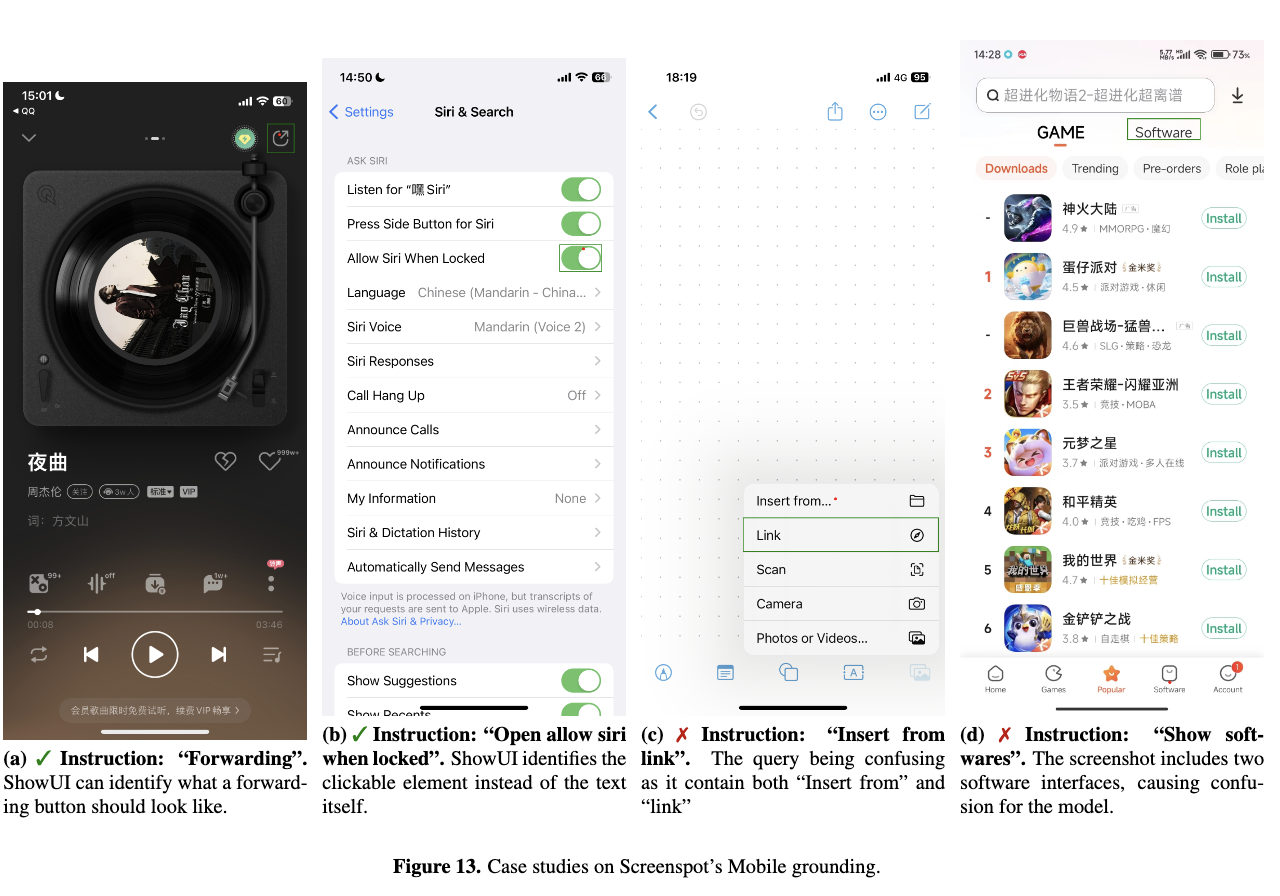
-
-
Navigation Tasks
-
정량적 결과
-
Mobile: AITW
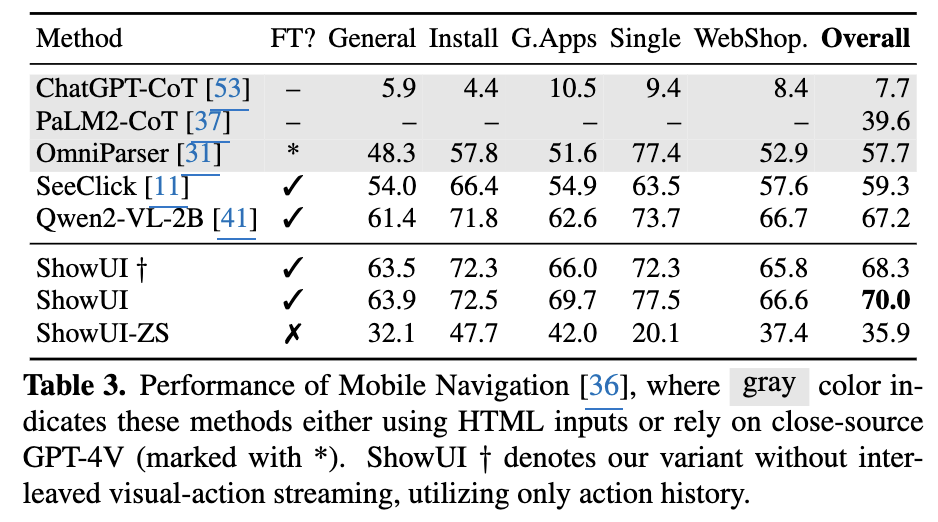
- Visual History를 제거한 (+) 버전 (68.3)보다 ShowUI (70.0) 성능이 좋음 $\to$ Visual screenshot history가 mobile같이 cross platform이 활성한 경우 긍정적으로 작용
-
Website: Mind2Web
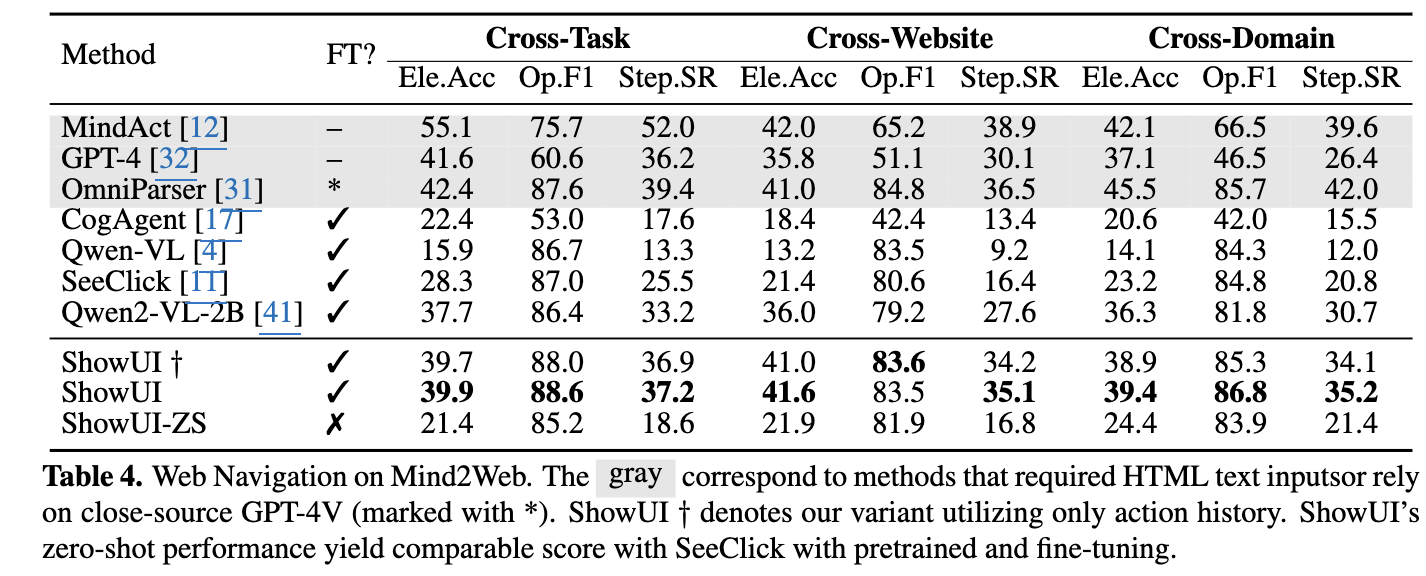
- Mind2Web은 single website / 3개 action space기반이다 보니 visual context가 AITW에 비해 상대적으로 덜 중요 (+1.1% v.s. +1.7%)
- Cross-Task보다 Cross-Website / Cross-Domain이 성능이 떨어짐 $\to$ Text보다 Visual perception이 성능에 bottleneck
-
Online: MiniWob
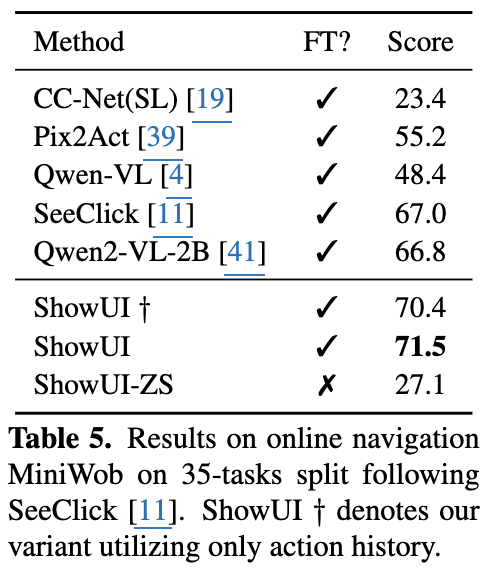
-
-
정성젹 결과
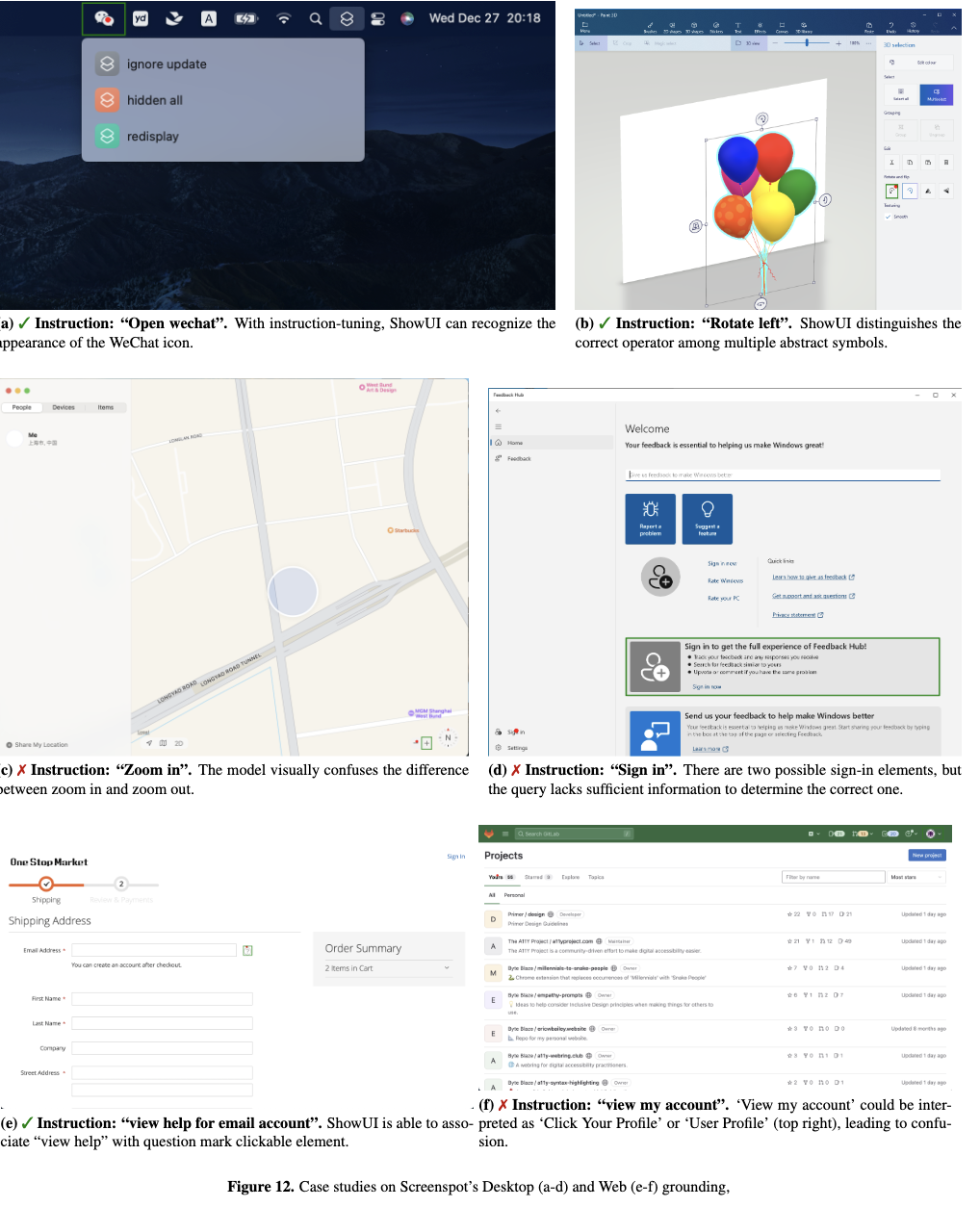
-
4.2 Ablation Studies
-
UI-Guided Token Selection
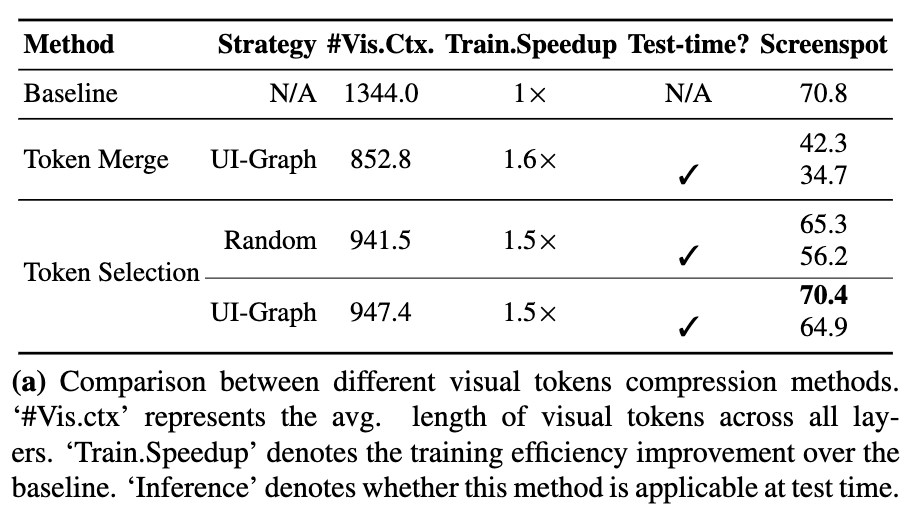
- Token Selection-Random : Random하게 Token을 선택
- Token Selection-UI-Graph: 같은 node내에서만 skip
-
UI-Guided Token Selection을 반영하는 layer별 성능
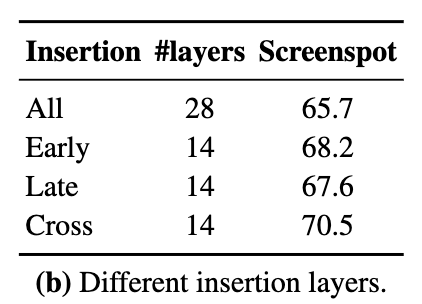
-
UI-Guided Token Selection Ratio별 성능 비교
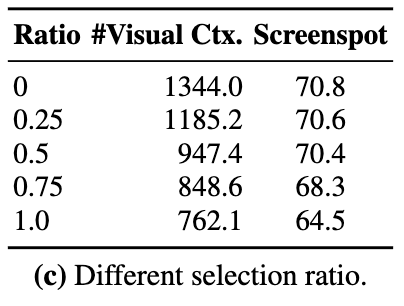
-
Interleaved Streaming
-
Multi-turn streaming 유무에 따른 성능 비교
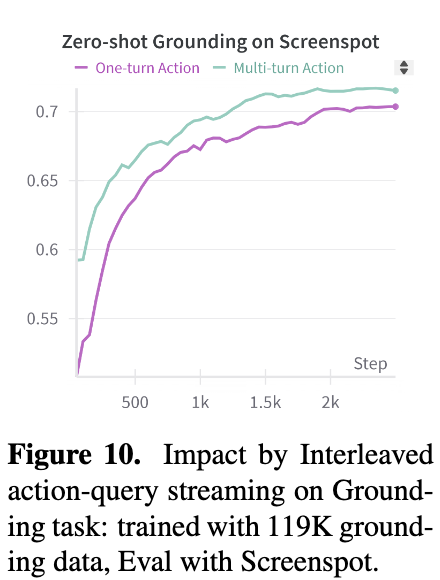
-
Action-Visual Impact
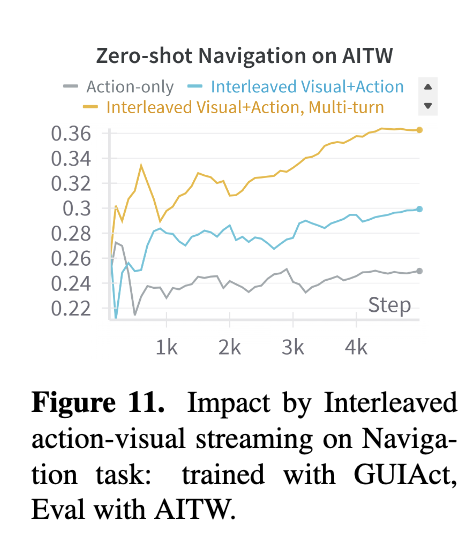
-
-
Training data recipe별 성능 비교
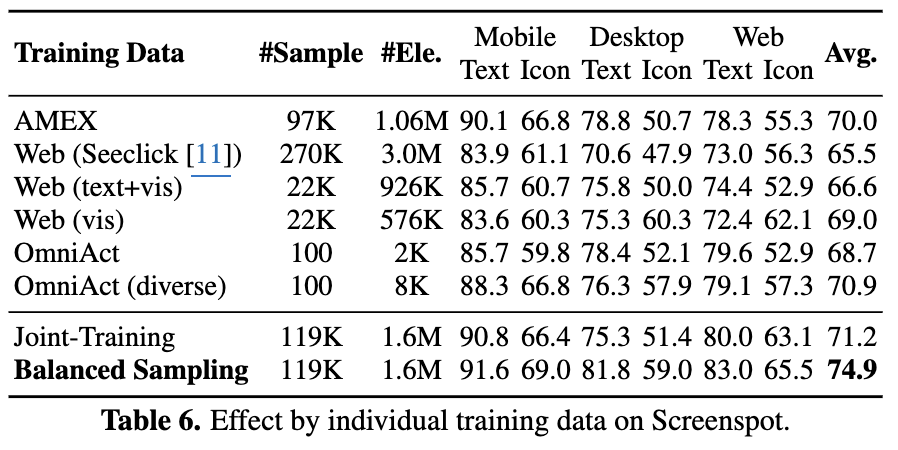
- Quality matters
- line 2 (65.5) vs. line 3 (66.6)
- Visual element가 더 중요
- line 3 (66.6) vs. line 4 (69.0)
- Balanced Sampling이 중요
- line 7 (71.2) vs. line 8 (74.9)
- Quality matters