[SSD][OD] PROTOCON: Pseudo-label Refinement via Online Clustering and Prototypical Consistency for Efficient Semi-supervised Learning
[SSD][OD] PROTOCON: Pseudo-label Refinement via Online Clustering and Prototypical Consistency for Efficient Semi-supervised Learning
- CVPR 2023 논문
- task: SSL for classification
Abstract
- 문제 제시 : Semi-supervised Learning의 고질적 문제 → Label-scarce class에 대해 pseudo label의 quality가 좋지 못해, performance가 줄어든다.
- Label-scarce class : 10개 미만의 label 이미지만 있는 class
- 해결책 :
- Imbalanced class 문제를 풀고자 constrained k-mean clustering 기법을 적용하여 prototype을 class별로 구한다.
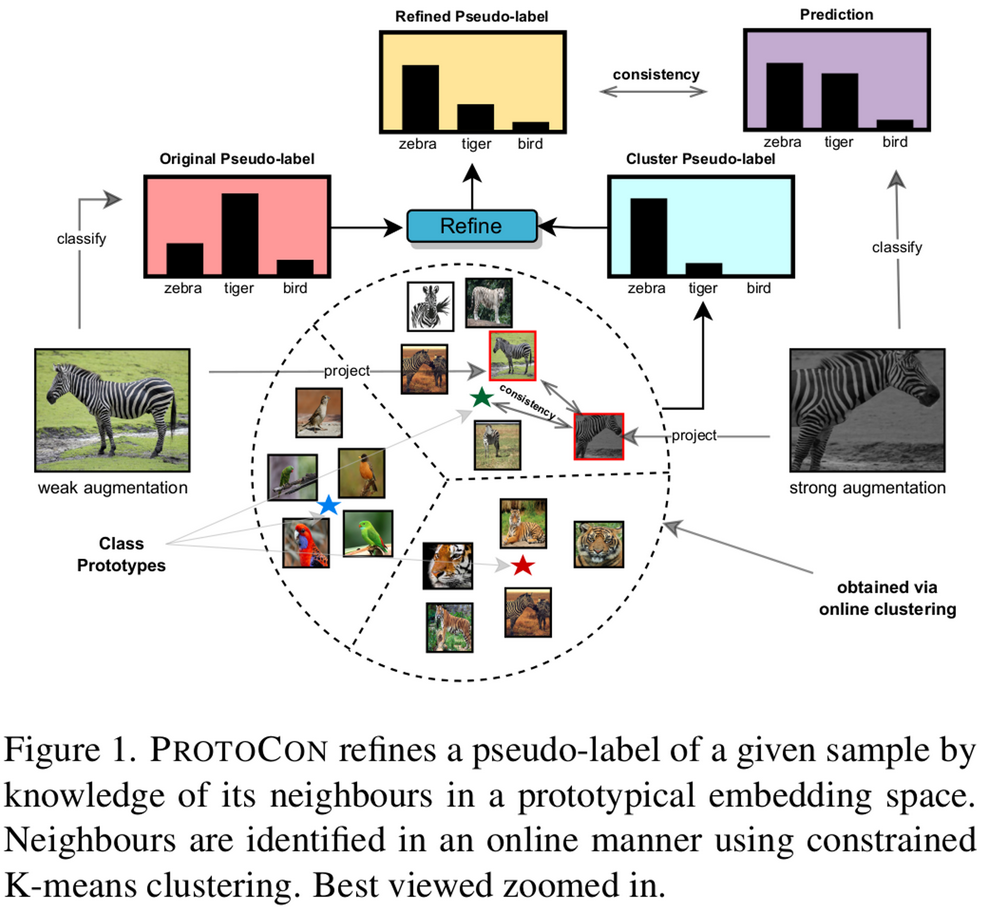
- prototype을 토대로 online으로 pseudo label을 정제한다. (label-refinement)
- label의 history 정보를 prototype에 집약시키므로 image embedding을 저장할 필요 없다. (memory efficient) → 더 큰 dataset에도 적용이 가능함
1. Introduction
- Label-scacre SSL의 underperformance 이슈를 해결하고자 2가지를 제안함
- Label refinement strategy 적용
- two different label의 combination
- model’s classification softmax prediction
- 현재 이미지와 인접한 (nearest neighbor) 이미지들의 projection space softmax prediction
- SSL의 경우 two label의 representation이 다를수록 co-training 효과가 증가한다고 함. (학습할 정보가 많아지기 때문)
- 따라서 classification head와 별도로 prototype를 뽑는 head 를 둠 (projection head)
- Class space의 confirmation-bias를 잡기 위해 prototypical space에서 구한 pseudo-label로 label을 smoothing함 (뒤에서 더 자세히 설명)
- K-mean clustering의 cluster size에 최소값 제약을 두어 imbalanced class 이슈를 해결
- 철학 : 이전 epoch에서 prediction한 전체 history를 (prototype space에) 저장하여 pseudo label 정제에 활용한다!
- nearest neighbor 정보를 이용하여 centriod를 online으로 update한다.
- 뿐만 아니라, memory efficient하게 prototype을 저장하는 방법 제안
- two different label의 combination
- 초기 학습 속도 향상을 위해 self-supervised learning loss 도입
- weak, strong augmented prototype에 대해 D dimension으로 softmax취한 consistency가 같아지게 학습함
- SSL classification benchmark 5개에서 SOTA 달성
2. Related Work
Confidence-based Pseudo-labeling
- fixed threshold → adaptive threshold로 넘어가는 추세
- easy-to-learn class만 잘 학습하는 이슈 해결
- class-based adaptive threshold, instance-based adaptive threshold, average of pseudo-label distribution, etc.
- Pseudo-label refinement
- auxiliary task를 학습하는 projection head를 별도로 두어 weak-supervision 수행
- Language semantics, instance-similarity matching, graph-based contrastive learning, etc
→ 본 논문은 Pseudo-label refinement 방식을 채택
Consistency Regularization
- Fixmatch 인용함. 즉, weak perturbation에 대해 similary pseudo-label을 생성해야 한다는 게 핵심. (Regularization)
Semi-superivision via self-supervision
- Self-supervised Learning 2 concept
- Pretraining 으로 Self-sup.을 사용
- semi-sup과 함께 사용
- 이 경우, image classification의 경우 자기 이미지가 클래스가 되므로, classification task에 상충하는 효과가 발생할 수 있다.
- 하지만, 본 논문은 Classification space가 아닌 별도의 space (Prototype space)에서 self-sup.을 동시에 학습에 활용하여 initial training 속도를 향상시킨다.
3. Approach
Motivation
- label-scarce SSL의 confirmation bias를 해결코자 co-training 기법을 제안함
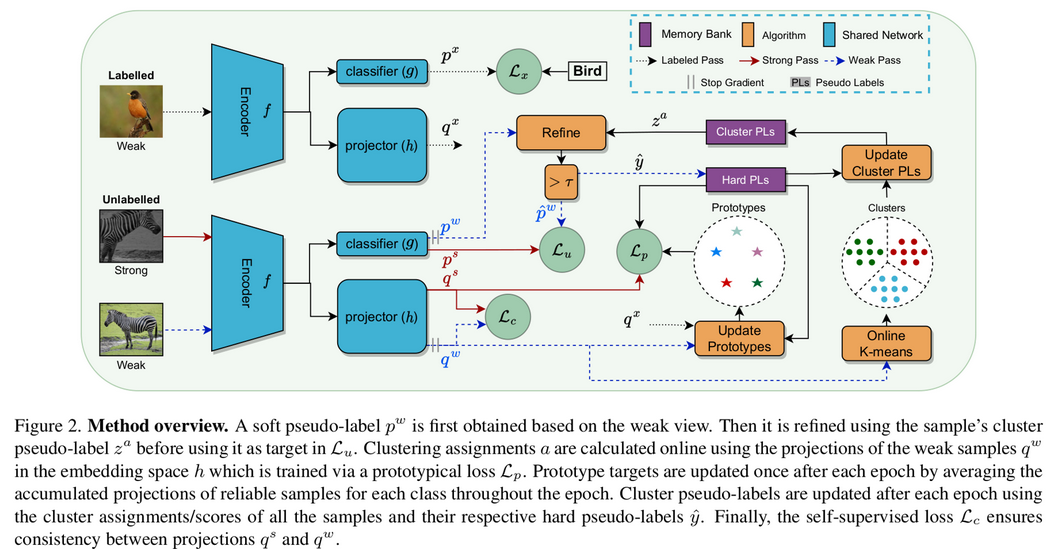
- $\mathbb{p}^w$: classifeer softmax prediction of weak labeled images
- $\mathbb{z}^a$: projection softmax prediction of labeled + reliable unlabeled (weak augmented) images
- $h$: projector (prototype embedding space로 mapping하는 역할)
- $g$: classifer (class embedding space로 mapping하는 역할)
- $f$: Encoder (backbone)
Prototypical Space
-
class prototypes ←→ class labels와 대치되는 개념
-
class prototypes로 모든 labeled image와 reliable unlabeled image들의 두 가지 정보를 memory bank에 저장 ($O(2N)$), $N$: 전체 이미지의 갯수
-
hard pseudo-labels
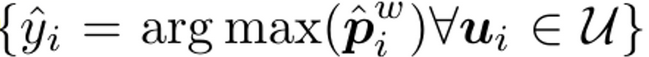
-
reliability indicator
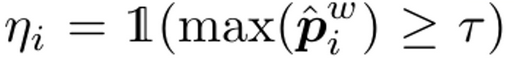
-
-
Prototype for class $c$
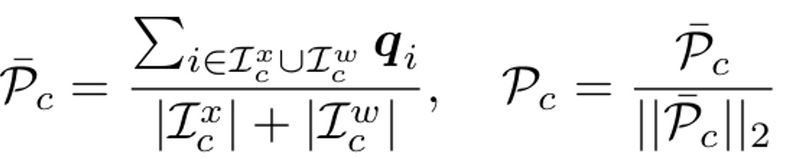

-
Prototypical consistency Loss
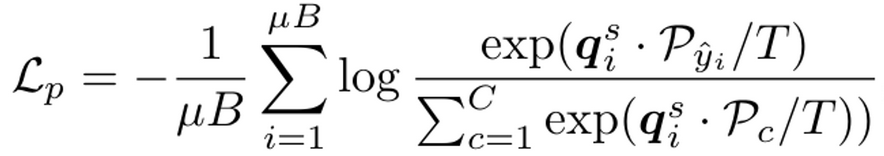
- $\mu$: labeled와 unlabeld의 비율 (1%일 경우, 99)
- $B$: labeled 이미지 갯수
- $\mathbb{q}_i^s$: i번째 strong augmented image의 projection embedding vector
Online Constrained K-means
-
mini-batch 레벨에서 k-means clustering 수행
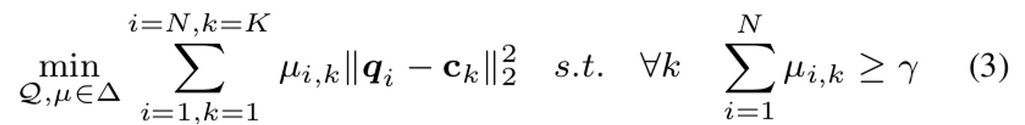
- $\gamma$: lower bound of cluster size
- $\mu_{i,k}$: i번째 unlabeled sample의 k-th cluster (0 or 1)
- $\Delta$: domain of $\mu$
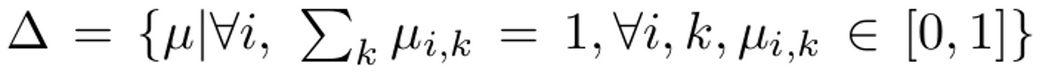
-
3번식을 online으로 풀기 위해서 mini-batch의 sample을 어떤 cluster에 할당할지 정하는 assignment problem으로 바라봄
-
greedy method을 대체하기 위한 alternate solver 방식으로 접근 → dual variables $\rho_k$가 등장!
-
dual variable?
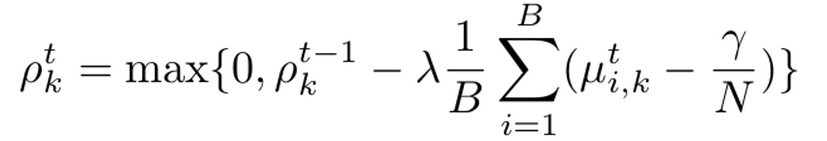
- $\gamma$와의 violation된 값을 기준으로 iterative 하게 update해준 변수
- $\lambda$: dual variable을 update해주는 dual learning rate
-
3번식과 동치
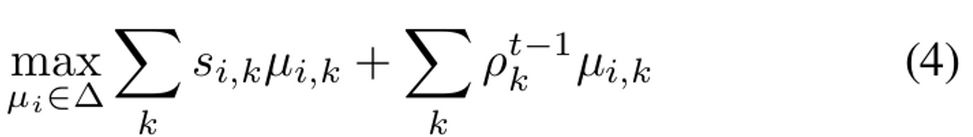
- $s_{i,k}=\mathbb{q}_i^T\mathbb{c}_k$: k번째 cluster centroid와 unlabeled image $\mathbb{u}_i$ sample의 projection embedding간의 similarity
- $\rho_k^{t-1}$: 이전 step (t-1)에서의 k번째 cluster의 dual variable
- $\mu_{i,k}$를 closed-form으로 아래와 같이 대입하면 4번식을 풀 수 있다!
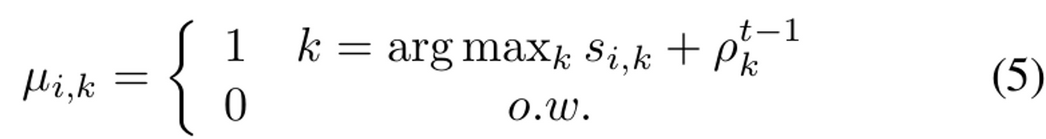
-
update centroids
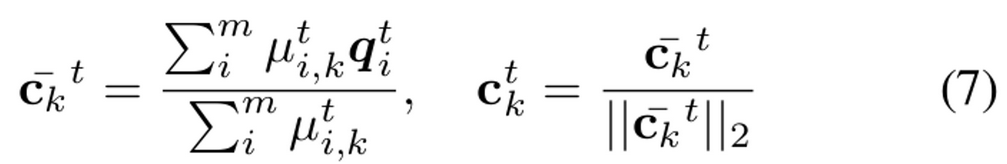
- m: t번째 iteration (mini-batch)까지 바라본 instance의 갯수
-
memory bank
- unlabel instance별로 2개의 추가적인 정보를 저장해야 함 → $O(2N)$이 추가로 필요
-
현재 epoch에서의 cluster assignment ($a(i)={k \mu_{i,k}=1}$) - similarity score ($s_{i,a(i)}$)
-
- unlabel instance별로 2개의 추가적인 정보를 저장해야 함 → $O(2N)$이 추가로 필요
Cluster Pseudo-labels
- memory bank에서 query해서 k번째 cluster의 c class에 대한 softmax prediction (projection head’s prediction)을 구함
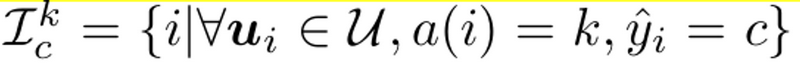
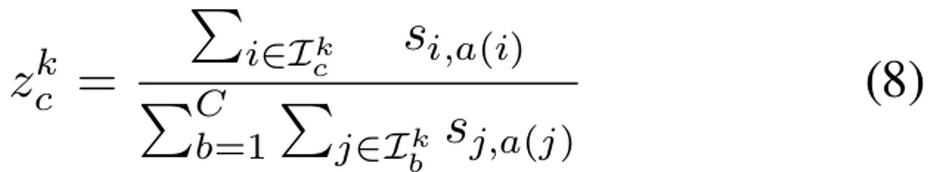
Refining Pseudo-labels
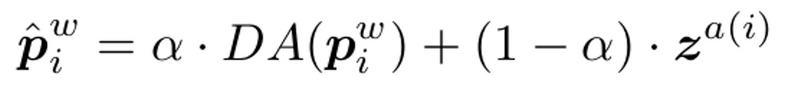
-
$\mathbb{p}^w$: classifier softmax prediction of weak labeled images
-
DA (Domain Alignment) : moving average + Normalize
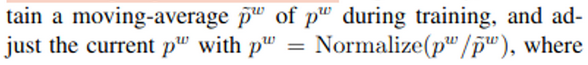
-
-
$\mathbb{z}^a$: 이전 epoch의 prototypical embedding space상에서 분포
Classification Loss
-
Unlabeled Loss
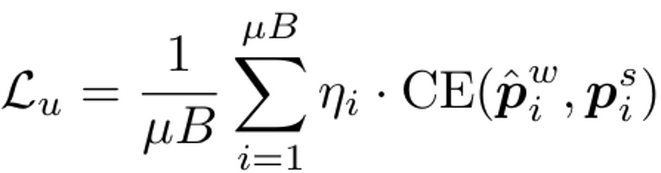
-
Labeled Loss
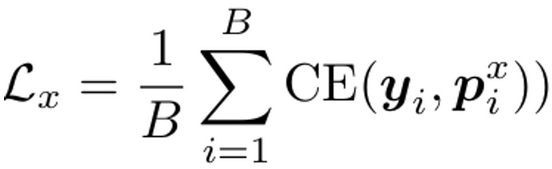
Self-sup. Loss & Final Objectives
-
self-sup. loss
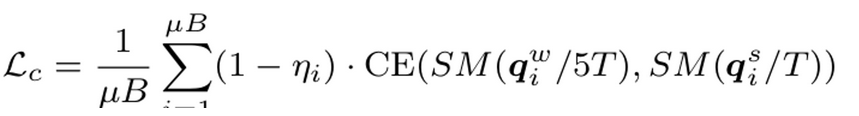
- d 차원의 projection vector $q^w, q^s$에 대해 Softmax를 취한 후 Cross Entrophy Loss를 계산 → consistency 효과
- weak unlabeled sample에 sharpening을 더 줌
-
Total Loss
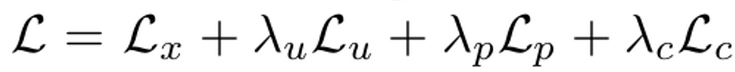
Design Considerations
-
Number of clusters
- cluster당 최소한의 sample 갯수 n을 결정하고, K=N/n으로 결정
- $\gamma$=0.9n으로 고정
→ online으로 KNN (n=4800, 200 for ImageNet & CIFAR)
-
Multi-head Clustering
- Projection head를 여러개 두고, 평균을 취하는 방식은 negligible cost가 듬
- ImageNet처럼 큰 데이터에서는 여러개일 때 효과적이나, 그외엔 1개도 충분
-
Memory analysis
- $O(4N+K\times C)$의 비교적 저렴한 memory cost
- 4N: hard pseudo-label,reliability, cluster assignment, similarity scores
- KC: cluster pseudo-labels
←→ $O(N\times d)$
9.6M vs. 153.6M
- $O(4N+K\times C)$의 비교적 저렴한 memory cost
4. Experiments
Dataset
-
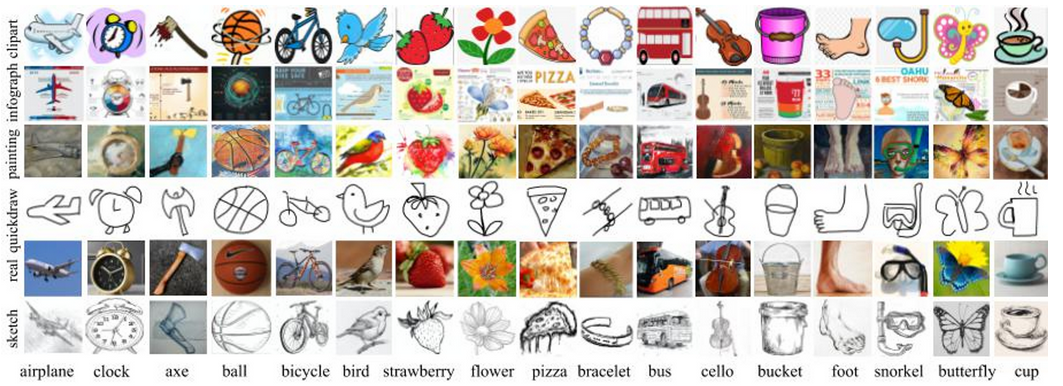
DomainNet (580K, 6 domain, 345 classes)
-
Semi-sup. Classification Task이므로 이 중에 Clipart, Sketch domain에서만 실험 진행
-
-
CIFAR 10 ( total 60K images, 10 classes, 6K for each class) &
CIFAR 100 (60 K images, 100 classes, 600 for each class)

- Mini-ImageNet (60K images, 100 classes, 600 images per each class)
- Image Net (14.2M images, 1,000 classes)
Implementation details
- Encoder : Wide-ResNet-28-2(28-8) or Resnet-50
- Projection head : 2 Layer MLP, d=64 or d = 128
- optimizer : SGD w/ momentum=0.9, weight decay = 0.0005, batch = 64,
- $\tau$=0.95 or 0.7, 1024 epochs
- lr schedule: 0.03 w/ cosine decay
- weak aug ; horizontal flip, strong aug ; RandAugment or SimCLR augmentations for large dataset
- *n :* 250 or 4,800
- dual learning rate $\lambda$=20, mixing ration $\alpha$=0.8, temperature T=0.1
Results
-
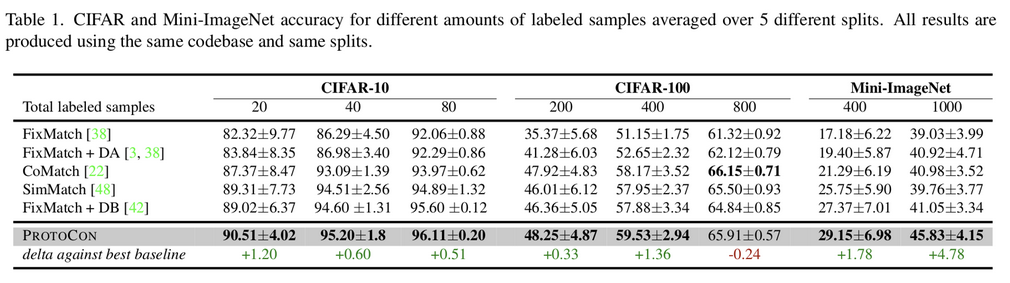
CIFAR 10 & Mini-ImageNet
-
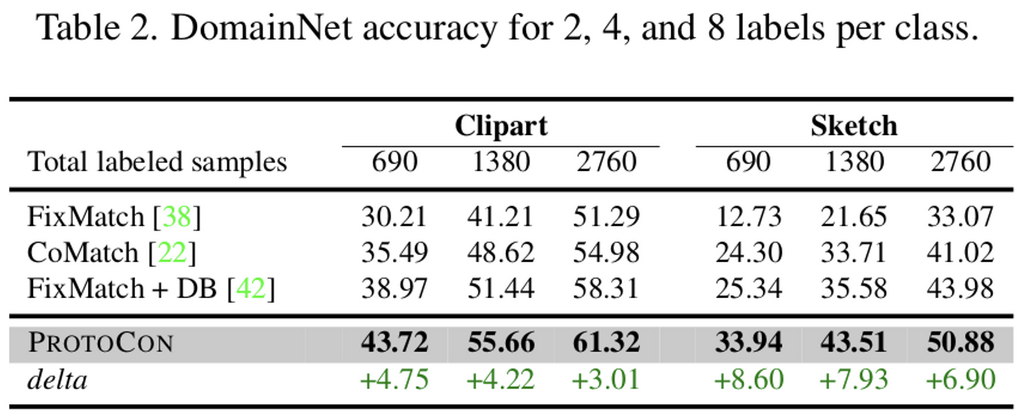
DomainNet
-
DomainNet은 high-level noisy label이 특징인 데이터임
-
특히 DomainNet에서 잘되는 것은 Prototypical refinement가 pseudo-label을 효과적으로 정제한다고 볼 수 있음
-
-
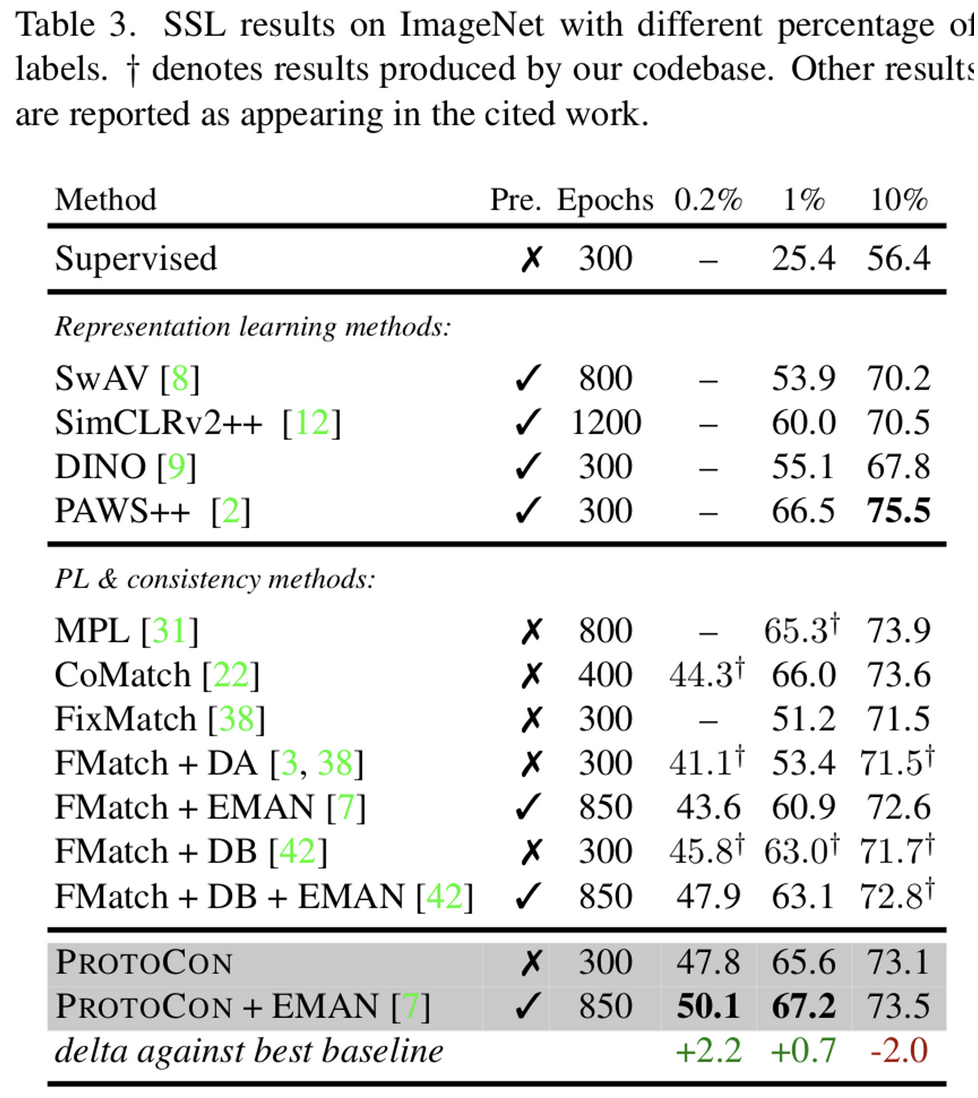
ImageNet
-
Refinement가 어떻게 학습에 도움이 되는가?

-
Classifier PL 의 경우, feature가 강한 이미지들로 대표됨 (좌측)
-
반면, Prototypical Images (가운데)는 bluerry하지만 prototypical(?)한 이미지들로 대표됨
-
즉, 두 head (classification & projection)이 서로 다른 정보를 토대로 classify를 하고 있으로 co-training효과에 시너지가 발생함
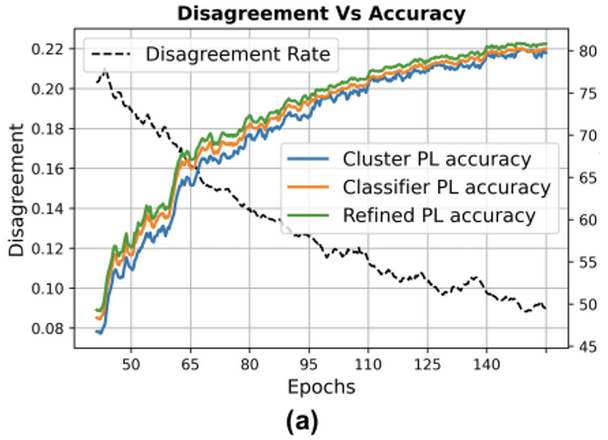
-
-
Self-sup. Learning의 역할
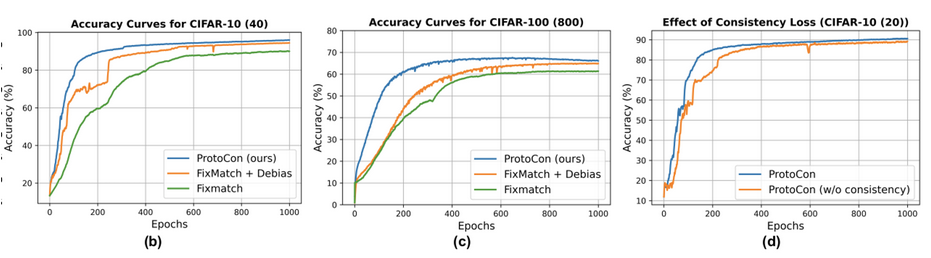
- (b), (c): 초기 model의 prediction이 uncertain할 때, learning을 boosting하기 위해 사용
- (d): 실제 accuracy에 기여하기도 함
- instance-consistency loss로 학습해야 하며, SimCLR에서 말했듯, instance-discrimination loss를 classification loss와 동시에 학습시키면 상충효과로 인해 학습이 안됨
-
Ablation
- $n, \alpha$
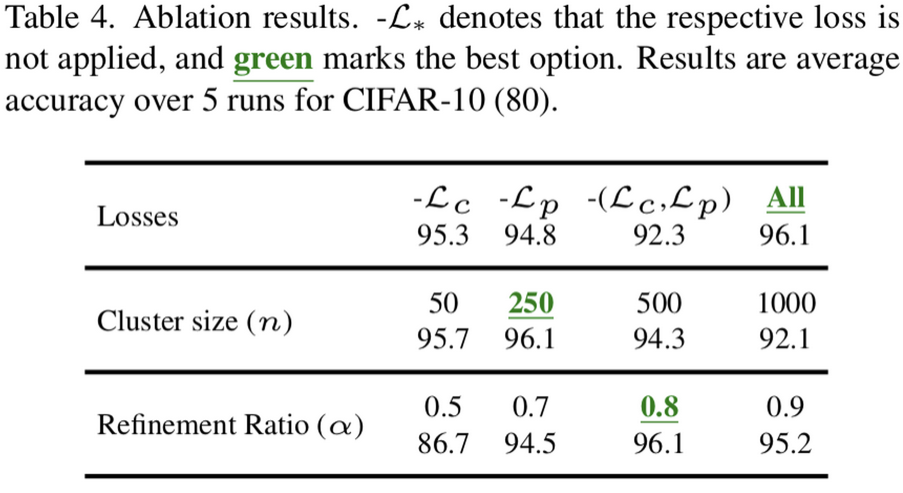
5. Conclusion
- co-training을 통한 pseudo label refinement가 label-scarce SSL task에 도움이 되는 PROTOCON을 제안