OmniParser for Pure Vision Based GUI Agent
[WebAgent] OmniParser: OmniParser for Pure Vision Based GUI Agent
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.00203
- github: https://github.com/microsoft/OmniParser
- archived (인용수: 41회, ‘25-05-29 기준)
- downstream task: Action Grounding (SeeAsign, ScreenSpot), Multi-step GUI Navigation / Task Completion (Mind2Web(Web), AITW(Mobile))
1. Motivation
-
GPT-4V와 같은 VLM의 발전으로, Web UI상에서 기본적인 요소에 대해, coordinate (x, y)를 예측하는 action grounding이 challenging하다.
-
이를 해결하고자 Set-of-Mark (SoM)기법이 제안되었으나, 이 역시 HTML 정보로부터 actionable element를 잘 추출해야 한다.
$\to$ Platform (Web, Mobile) -agnostic, OS-agnostic (MS, Mac), Application-Agnostic (MS Office)한 general하게 web browsing하기 위한 접근법을 제안하자!
2. Contribution
- DOM tree로부터 추출한 interactable region detection dataset를 curate
- 순수한 vision-based UI screen parsing 기법인 OmniParser를 제안함.
- 여러개의 finetuned Model을 모듈화하여 GPT-4V의 screen understanding 능력 & grounded action generation 능력을 향상
- Action Grounding (ScreenSpot) 및 Web Task Automation (Mind2Web, AITW) benchmark에서 SOTA
3. Related Works
3.1 UI Screen Understanding
- User의 screen을 multimodal model를 활용하여 잘 이해하는 연구가 진행됨.
- view hierarchy 혹은 VQA tasks, 혹은 screen summary tasks를 수행
- UI screen understanding 전용 benchmark도 있음
- Mobile domain
- RICO: 66K의 unique한 UI screens + view hierarchies
- Later dataset: RICO(66K) + 500K human annotation을 추가
- Web & general OS domain
- Mind2Web
- MiniWob++
- Visual-WebArena
- OSWorld
- Mobile domain
3.2 Autonomous GUI Agent
-
Task Automation task
-
Training
- Web: Pixel2Act, WebGUM
- Mobile: Ferret, CogAgent, Fuyu
-
Training-free (GPT-4V)
-
Web: MindAct, SeeAct
$\to$ web browser의 DOM 정보를 활용하거나 mobile의 view hierarchies를 참고하여 gt position으로부터 element position을 추출하거나 Set-of-Marks를 통해 element position을 추출함.
$\to$ general platforms에 항상 해당 정보가 존재하지 않으므로, 다른 구조적 접근방식을 채택해야함
-
-
4. OmniParser
-
4가지 모듈로 구성
- finetuned interactable icon detection model
- finetuned ico description model
- OCR module
- GPT-4V
4.1 Interactable Region Detection
-
기존 연구에서는 DOM tree로부터 interactable element의 position 정보를 추출함.
-
본 연구에서는 Icon Detection Model + OCR module을 활용함

- Icon Detection Model을 학습하기 위해, 67K의 unique screenshot 이미지와 bbox를 유명한 website로부터 추출하여 학습함 (Yolo-v8)
- OCR + Icon Detection 중첩되는 경우는 제거하고, merge함
- merged된 bbox들에 unique ID를 부여하여, 해당 ID를 GPT-4V에게 executable item 예측에 활용함
4.2 Incorporating Local Semantics of Functionality
-
위에 제시한 SoM기반의 ID만 가지고는 GPT-4V가 next action을 예측하는데 한계가 있음을 발견함
-
이는, 해당 SoM box들의 의미를 파악하고, 동시에 next action까지 예측을 수행하는 composite task에 취약한 GPT-4V의 한계로부터 시작됨 $\to$ 다른 논문에서도 관측됨
-
이를 완화해주고자, icon의 functionality를 Description해주는 모델을 finetuning함 (Blip-v2)
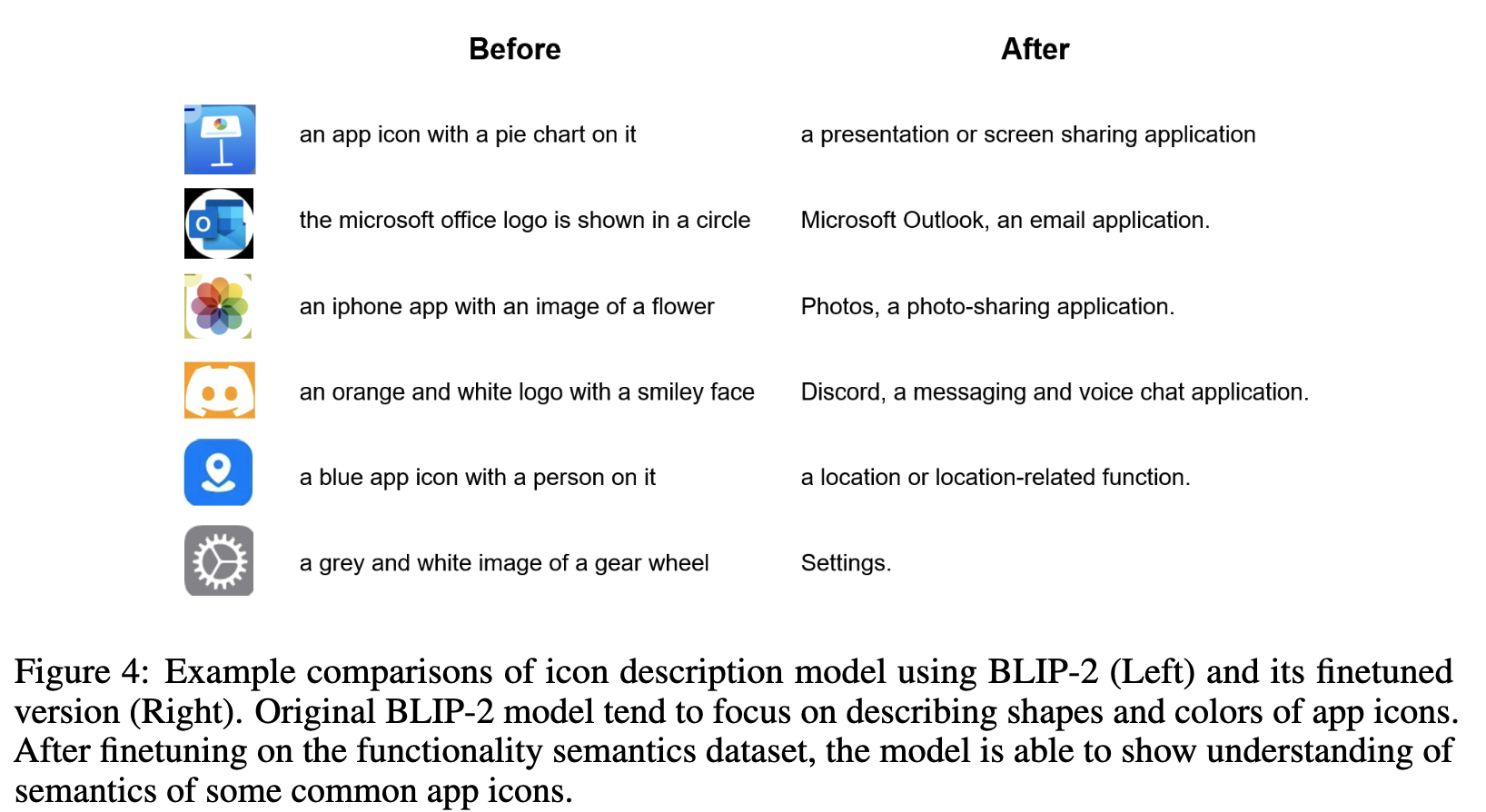
-
text일 경우, ocr의 출력값을 활용
-
GPT-4o를 통해 7k의 icon-description pair를 생성하여 Blip-v2를 학습함
$\to$ 성능이 향상됨
-
5. Experiments
5.1 SeeAsign Evaluation
-
Action Grounding Task
-
3개의 platform (Mobile, Desktop, Web Browser)에 맞는 112 tasks를 handcrated하게 만들고, task description을 생성하여 평가함.
e.g. “click on settings”, “click on the minimize button”
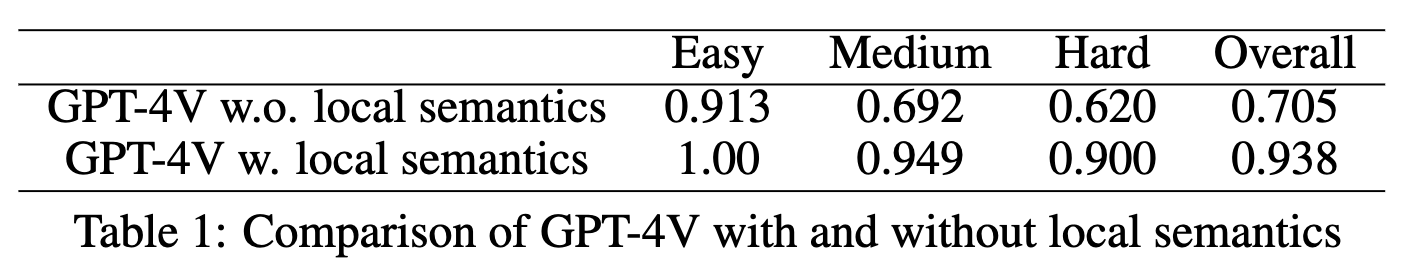

- GPT-4V w.o. local semantics: SoM만 있고, functional description이 없는 경우
- GPT-4V w. Loca semantics.: SoM & functional description 모두 있는 경우
-
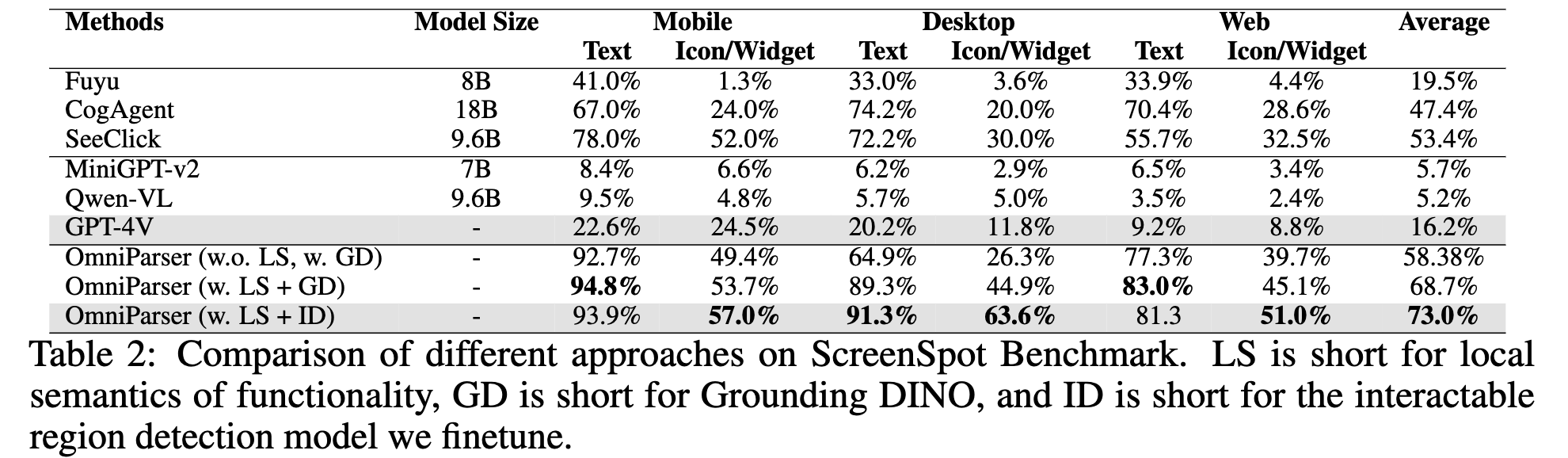
5.2 ScreenSpot Evaluation
-
moble (iOS, Android), desktop (macOS, Windows), web platform에서 추출한 600여개의 screenshot dataset
-
instruction은 manually created
-
결과
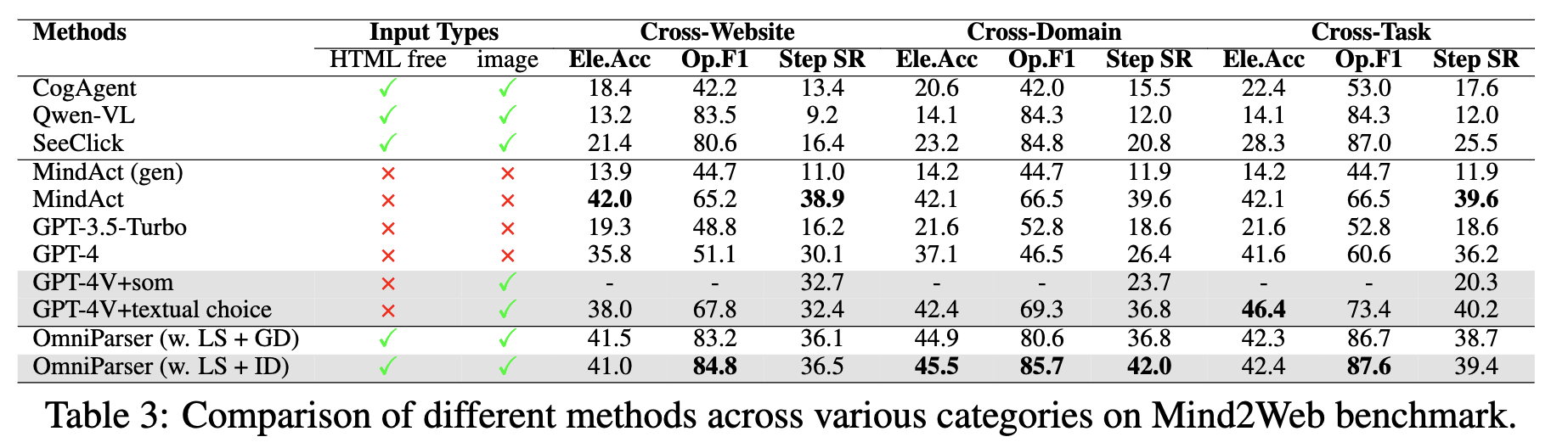
5.3 Mind2Web Evaluation
-
3개의 카테고리 존재: Cross Domain, Cross Website, Cross Tasks
5.4 AITW Evaluation
-
30K instructions + 715k trajectories로 구성된 mobile navigating benchmark

5.5 Discussion
-
Faliure cases
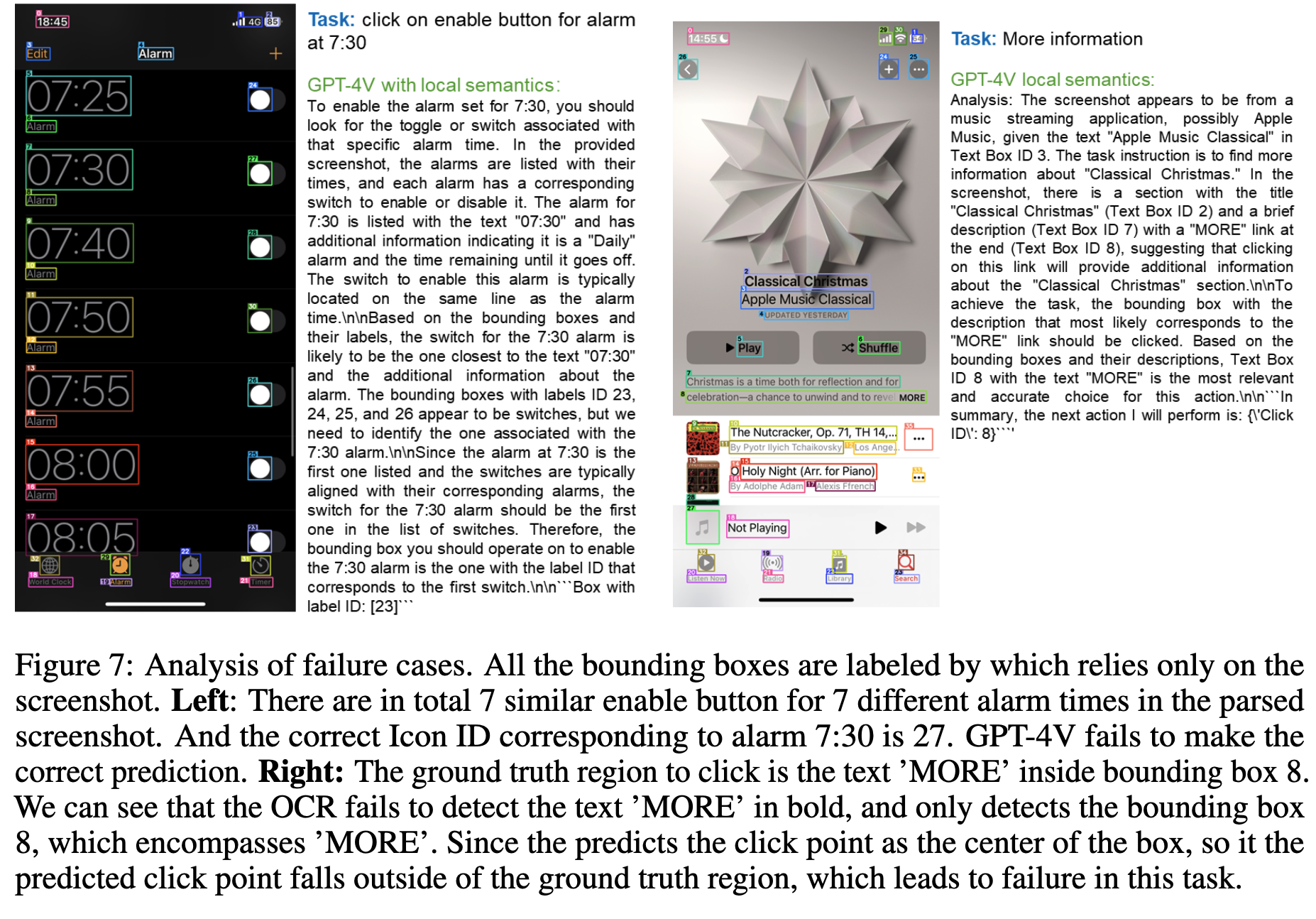
- (좌) 반복된 icon + description 등장할 경우
- (우) OCR text box를 잘못 예측한 경우
-
학습의 의미와 실제 의미가 다른경우
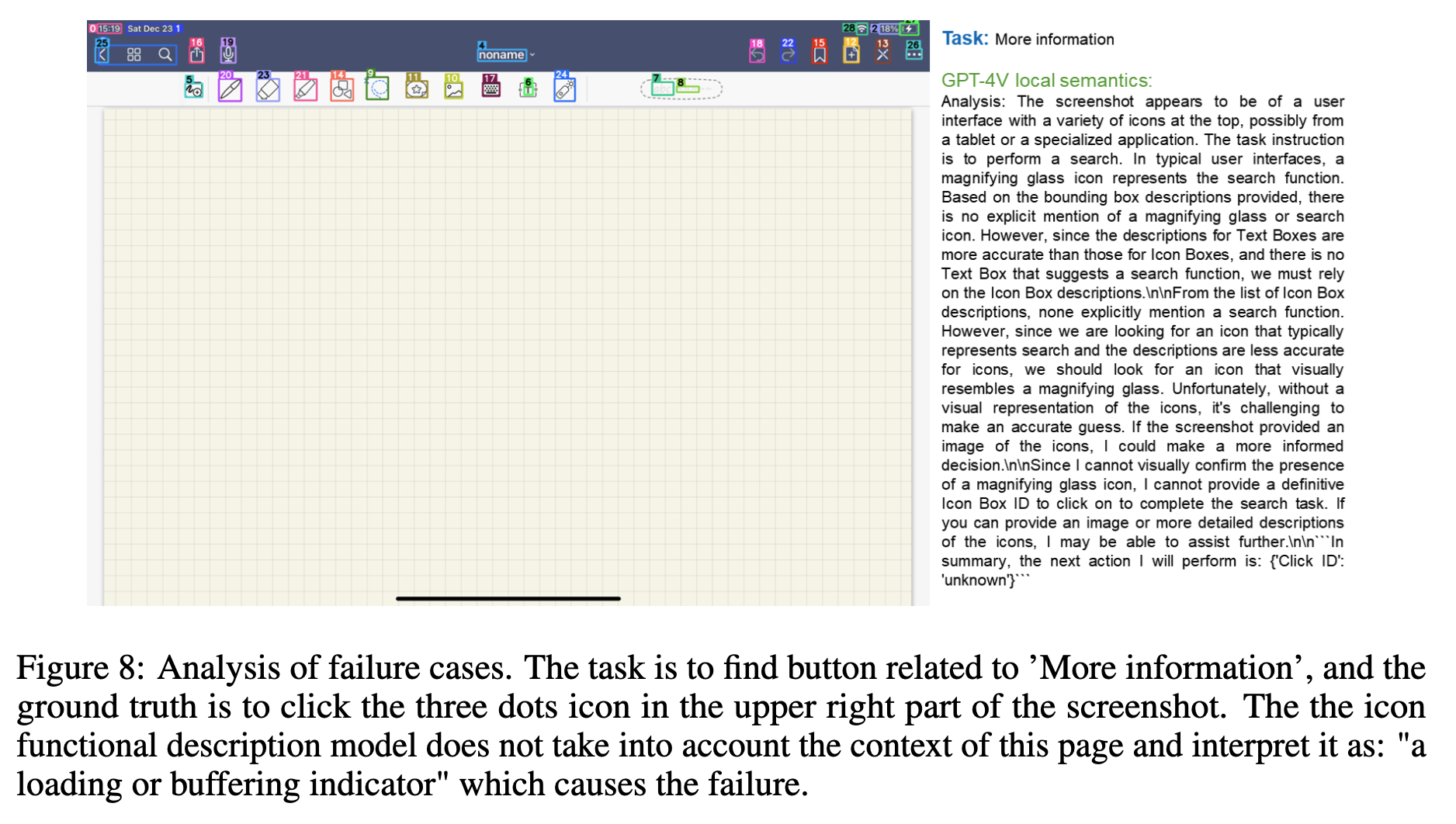
- …이 여기서는 “More Info”지만, functional description model은 “a loading or buffering indicator”로 설명한 경우