OS-ATLAS: A Foundation Action Model for Generalist GUI Agents
[WebAgent] OS-ATLAS: A Foundation Action Model for Generalist GUI Agents
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.23218
- github: https://osatlas.github.io/ (inference code만 제공)
- ICLR 2025 accepted (spotlight, 인용수: 48회, ‘25-05-30 기준)
- downstream task: GUI Ground Task (ScreenSpot, ScreenSpot-V2), GUI Task Automation
1. Motivation
-
기존의 GUI Task를 수행하는 agent에 대한 연구는 commerical 모델 (GeminiPro-Vision, GPT-4o)에 비해 opensource 모델이 GUI grounding, OOD (Out-Of-Distribution) 시나리오에서 성능하락이 발생하고 있다.
- 이는 초대용량의 다양한 applications, resolution sizes로 구성된 GUI dataset기반 pretraining한 모델이 없기 때문이다.
- 일반화하기 힘든 action space (ex. Click vs. Tap), formats
$\to$ Opensource 생태계의 발전을 위해 GUI foundation model을 만들어보자!
2. Contribution
-
Multi-platform GUI grounding data를 생성하는 toolkit를 처음으로 제안한다.
- 자동으로 GUI grounding data를 다양한 platform (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, Web)에서 취득할 수 있다.
-
해당 toolkit을 사용하여 현존하는 가장 대용량의 GUI grounding corpus(data)를 제안한다.
-
2.3M distinct screenshot
-
13M GUi element
$\to$ 기존에 없던 desktop data도 포함한다.
-
추가로, ScreenSpot에 잘못 annotation된 11.32%를 수정한 ScreenSpotV2를 제안한다.
-
-
GUI action foundation model인 OS-ATLAS를 제안한다.
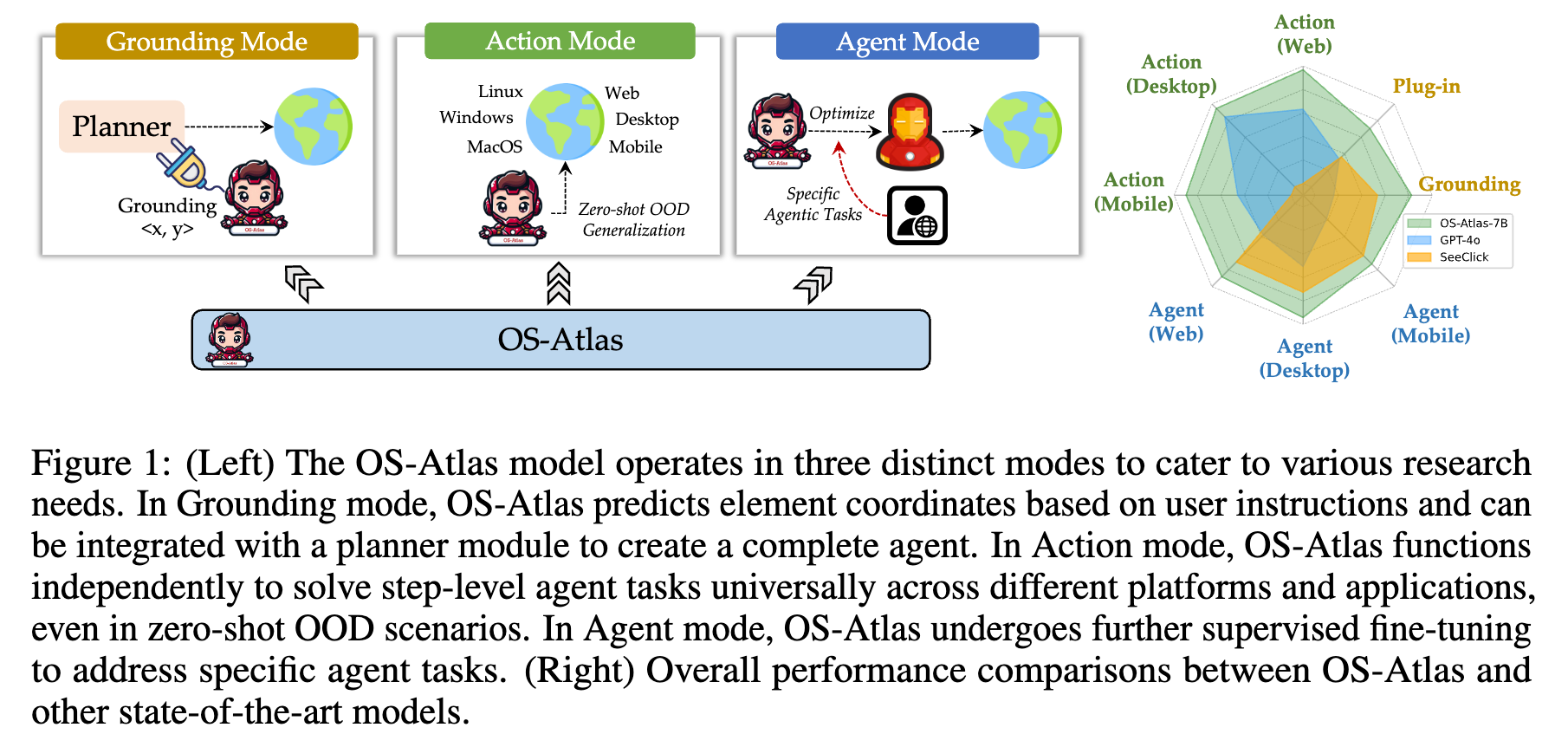
-
GUI agent task에서 SOTA
3. Related Works
3.1 GUI Agents & Large Action Models
- LLM agent가 OS와 program 혹은 API call을 기반으로 interaction을 수행한다.
- 대부분의 commercial software는 내부 API / code에 접근하지 못해 제한이 있다. $\to$ 미리캔버스는 내부 API (비슷찾, 딱맞디, 등) / code (rendering function (table, graph, etc))가 가능하므로 이 방향으로 가도 되겠다.
- 따라서, GUI-based agent는 사람과 같은 mouse / keyboard action을 수행하는 방향으로 발전해왔다.
- 제한된 quantity & diversity로 인해 Large Action Models (LAMs)에 대한 연구에 제한이 있어왔다.
3.2 GUI Executable Language Grounding
-
LAM의 핵심
- input: Natural Language Instructions
- output: GUI Executable actions with its parameters (ex. element coordinates)
-
GUI Grounding data의 유형
-
Referring Expression Grounding (REG)
-
explicit natural reference 기반으로 특정 요소의 위치를 예측하는 것
ex. “click the
openbutton.” -
Webpage데이터를 수집하기 위해서는 crawling & parsing하는 작업이 필요
-
Desktop, Mobile의 경우, 데이터를 수집하기 위해서는 많은 인력 공수가 필요
-
-
Insturction Grounding (IG)
-
REG의 superset으로 볼수 있음
ex. “Delete the last file”
-
특성상 데이터 수집을 위해서는 humman annotation이 필요함
-
-
4. OS-ATLAS
4.1 Task Formulation & Training
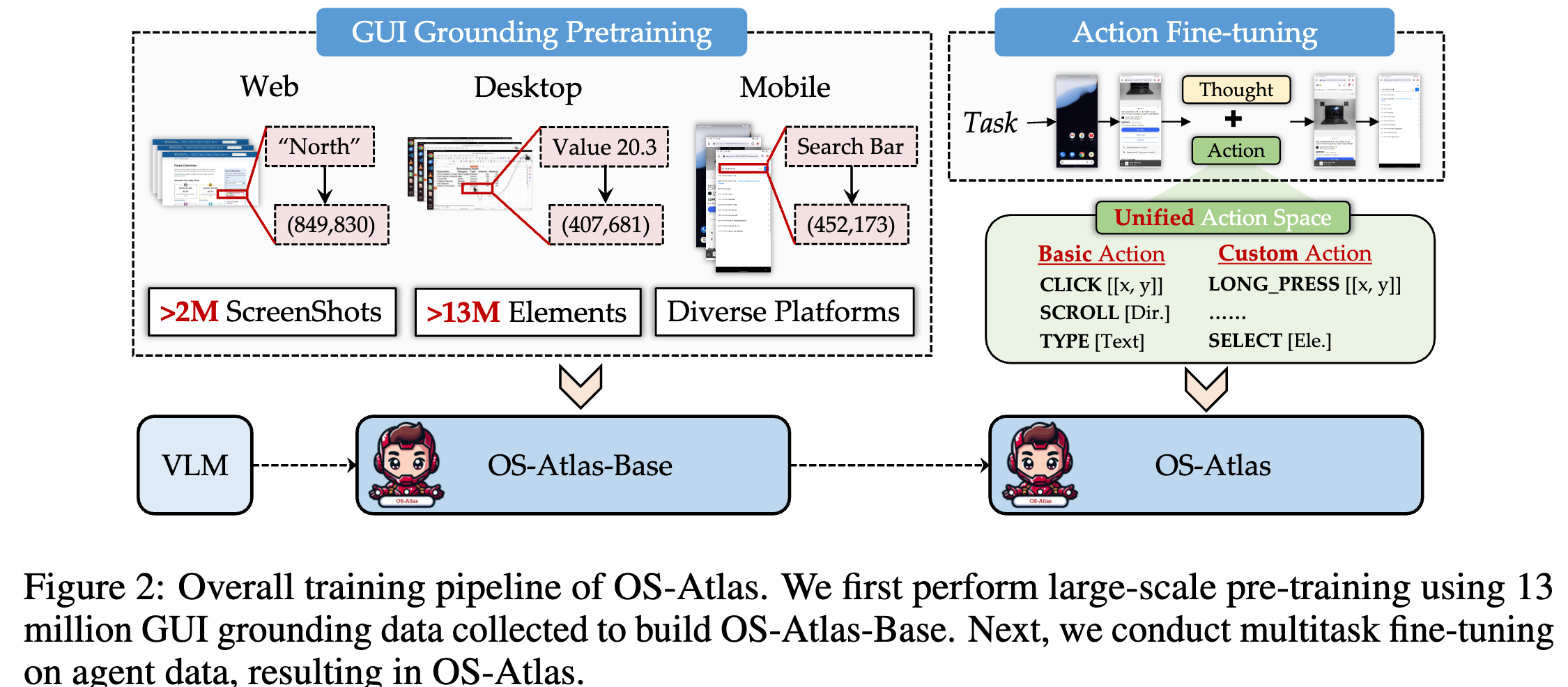
-
GUI Grounding Pretraining
-
VLM에게 GUI screenshot에 대한 지식, screen내 elements를 인식하도록 학습
-
<screenshot, element referring expression / instruction, element coordinatepair로 학습을 수행- input: screenshot, element referring expression / instruction
- output: element coordinate
-
자세한 생성 과정 $\to$ 4.2에서 설명
-
생성된 데이터셋
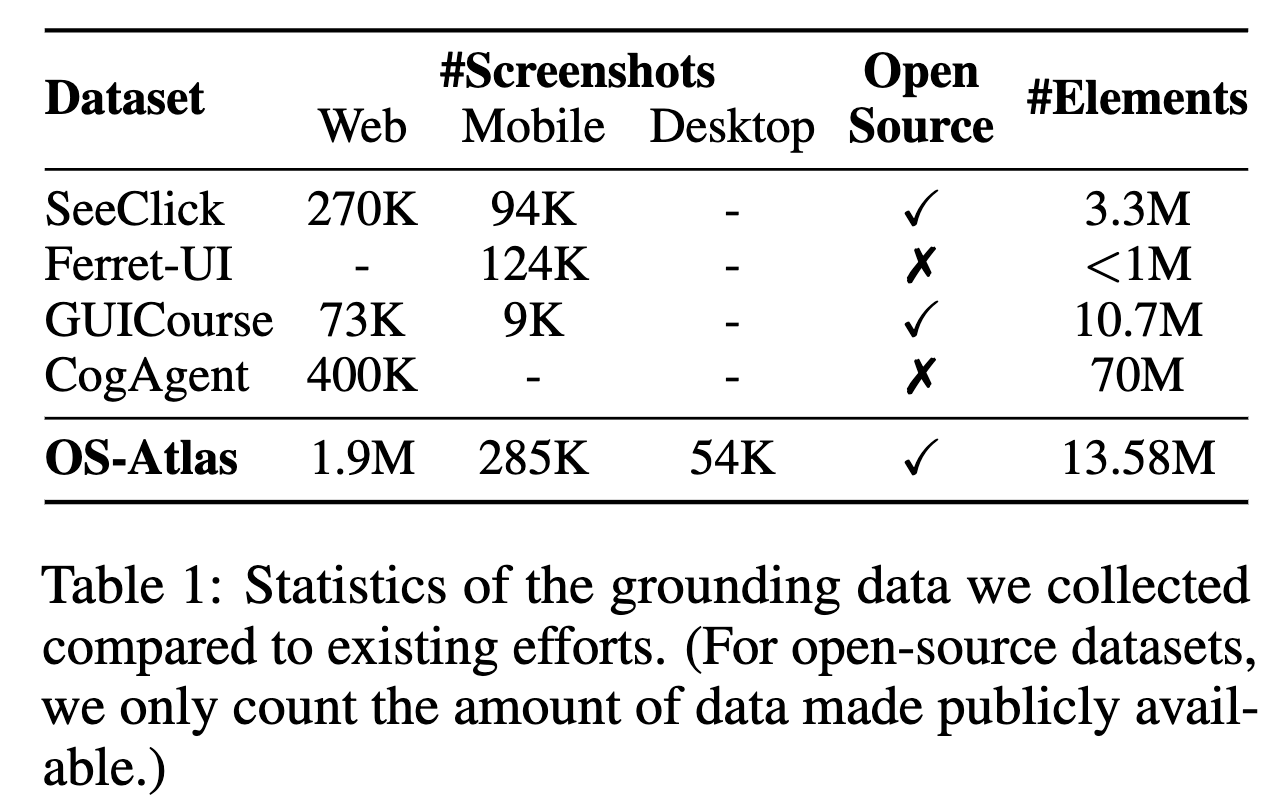
-
-
Action Finetuning
-
Instruction을 Executable GUI actions으로 변환하도록 학습
-
input:
<screenshot, task instruction, action history> -
output:
<thoughts, action type, action parameters (coordinates, etc)>
-
4.2 Grounding Data Collection
-
Web
-
FineWeb논문에서 취득한 최신 URLs (cleaned & deduplicated English dataset from CommonCrawl)로부터 취득
-
HTML code내에서 visible & clickable한 elements (buttons, scroll bars, search bars, hyperlinks, SVG images with titles)를 추출함
-
각 요소별 referring expressions & coodinates를 HTML attribute로부터 추가로 추출함
-
이전 논문들처럼 website의 upper portion만 사용하는게 아니라, 전체 website를 rendering하고, 1920x1080 해상도로 screenshot을 resize함
-
404 error 나는 web제외하여 총 3.7M webpage screenshot / 37M elements를 취득함
- 해당 website중 육안검사 시, low-quality webpage (incompletely rendered / poorly distributed element, etc)를 rule-based filtering을 수행하여 제거함
- diversity를 촉진(?)하기 위해 webpage당 최대 10개 이하의 element에 대해서만 작업을 수행함
$\to$ 최종적으로 1.6M webpage screenshot / 7.7M elements를 취득함
-
-
Desktop & Mobile
- large-scale automated collection을 수행하기 위해서는 두가지 산을 넘어야 함.
- 실제 OS환경에서 simulation 환경을 셋업하여 engineering 노력을 수행해야 함
- 사람의 interaction을 모방하는 program을 design해서, system state를 변경해야 함
- Simulation 환경 셋업
- Android $\to$ AndroidEnv
- Linux $\to$ OSWorld
- Windows & MacOS $\to$ A11y tree (Accessability tree) 접근하여 grounding data를 취득
- Windows: (pywinauto, A11y tree API)
- MacOS: (ApplicationServies, A11y tree API)
- Ubuntu: (pyatspi, A11y tree API)
- 사람의 interaction 모방하는 방법
- Depth Firsth Search
- Random Walk
- large-scale automated collection을 수행하기 위해서는 두가지 산을 넘어야 함.
-
Instruction Grounding Data Collection
- GPT-4o를 사용해서 before-after screenshot에 SoM (Set-of-Mark)를 부여해, 기존에 있는 action history를 통해 target HTML element에 대한 instruction을 생성함
- Mind2Web, AMEX, AITZ, AndroidControl, Wave-UI 데이터를 활용함
4.3 Unified Action Space
-
Multi-source data를 융합해 학습하는데, 동일 기능 & 다른 이름의 함수로 학습 시, 성능이 떨어지는 이슈가 존재함. $\to$ unified action space를 제안함
-
Action은 BASIC, CUSTOM으로 구성됨

5. Experiments
5.1 Evaluation Details
-
Training data
- AMEX (mobile)
- AITZ (mobile)
- Mind2Web (web)
-
Evaluation data
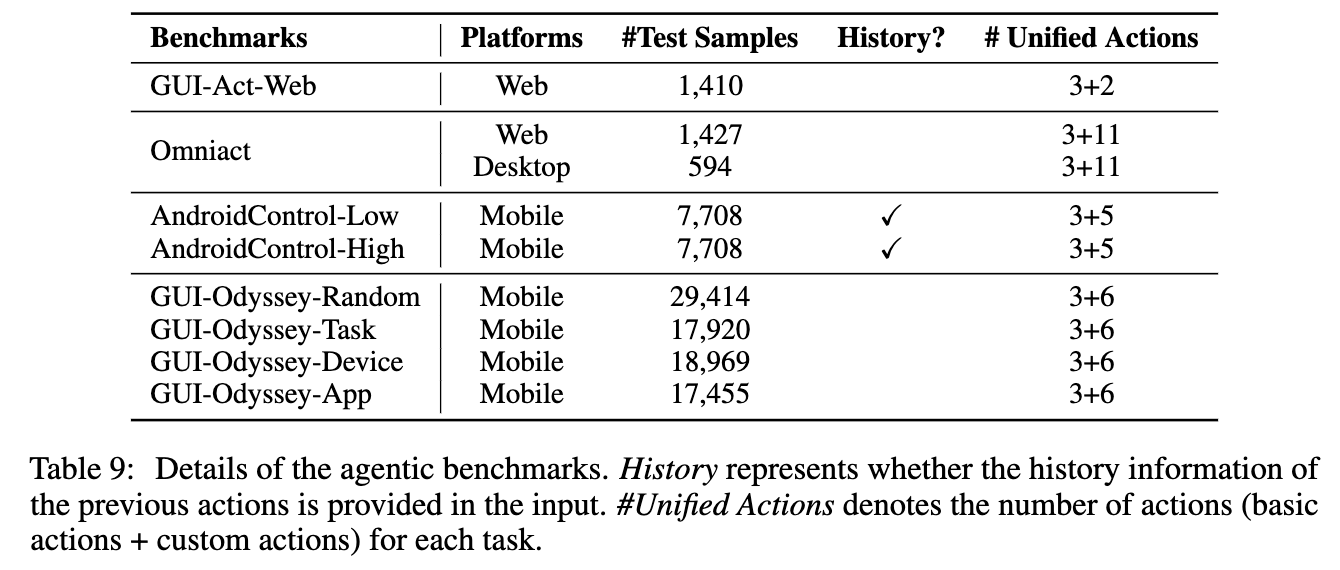
- AndoridControl, GUI-Odyssey (mobile agents)
- GUI-Act-Web, OmniAct-Web (web agents)
- OmniAct-Desktop (Windows environment)
-
Model
- InternVL-2-4B
- Qwen2-VL-7B
-
Settings & Baseline
- zero-shot OOD setting (Action mode in Fig. 1): unseen tasks, domains, applicatiaons을 zero-shot manner로 수행
- baseline: GPT-4o
- SFT setting (Agent mode in Fig. 1): 특정 specific domain에 특화된 agent setting
- InternVL-2, Qwen2-VL, grounding model (SeeClick)
- zero-shot OOD setting (Action mode in Fig. 1): unseen tasks, domains, applicatiaons을 zero-shot manner로 수행
-
Metrics
- action type accuracy (Type): 예측된 action type에 대한 Exact match score
- coordinate prediction accuracy (Grounding): GUI grounding에 대한 성능
- success rate (SR): step-wise success rate을 의미. (type + argument 모두 만족시)
5.2 Results & Analysis
-
Grounding Accuracy
-
ScreenSpot
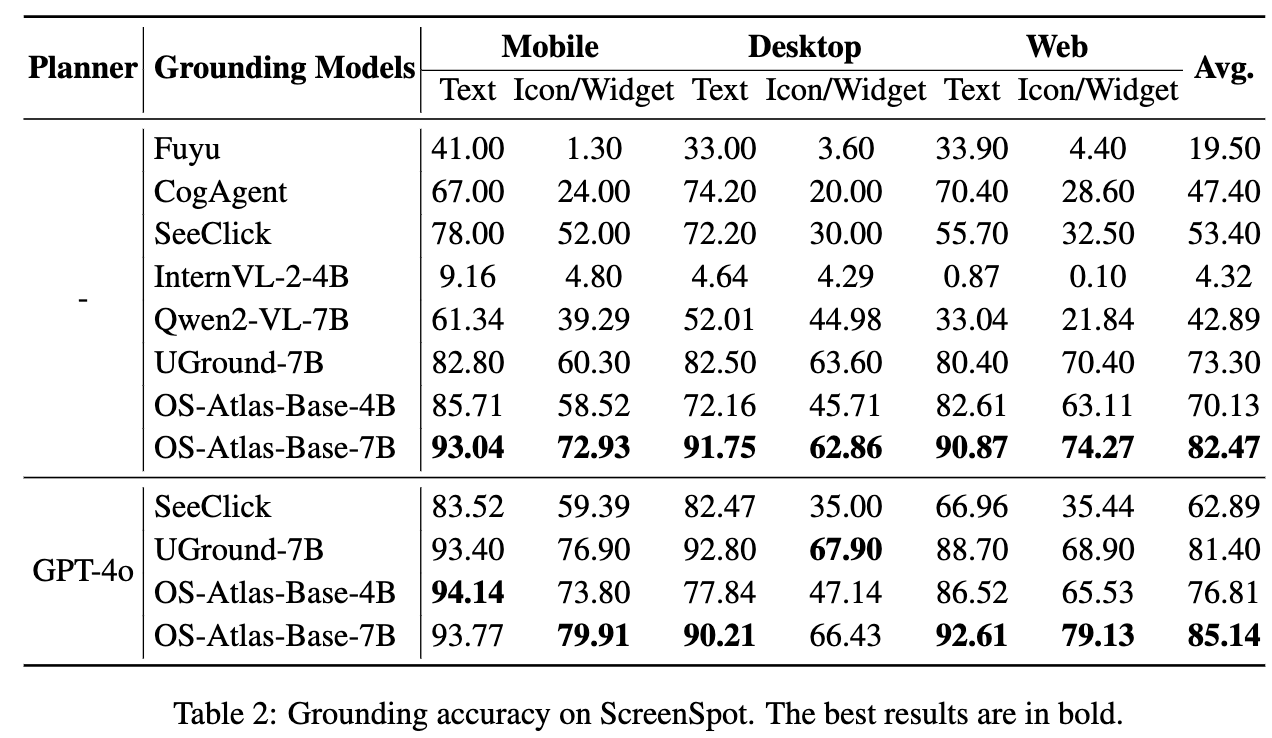
-
ScreenSpot-V2
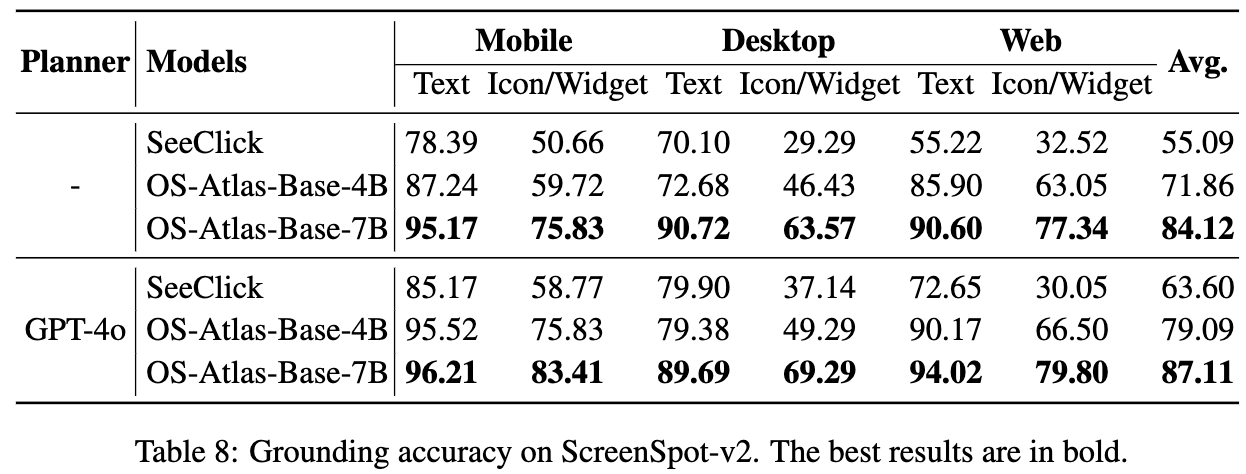
- ScreenSpot의 annotation error를 발견해 (11.32%) 수정한 버전
- Error 유형
- spelling mistakes / reference elements가 존재하지 않는 경우 $\to$ 제거함
- question이 ambiguous하여 multiple valid answer가 존재함 (그런데 gt는 1개) $\to$ 새로운 질문으로 reformatting
- 여러 질문들이 서로 매우 높은 유사도를 보임 $\to$ 새로운 질문으로 대체함
- bbox가 잘못 labeling됨 $\to$ 수정함
-
-
Action Prediction
-
Web & Desktop
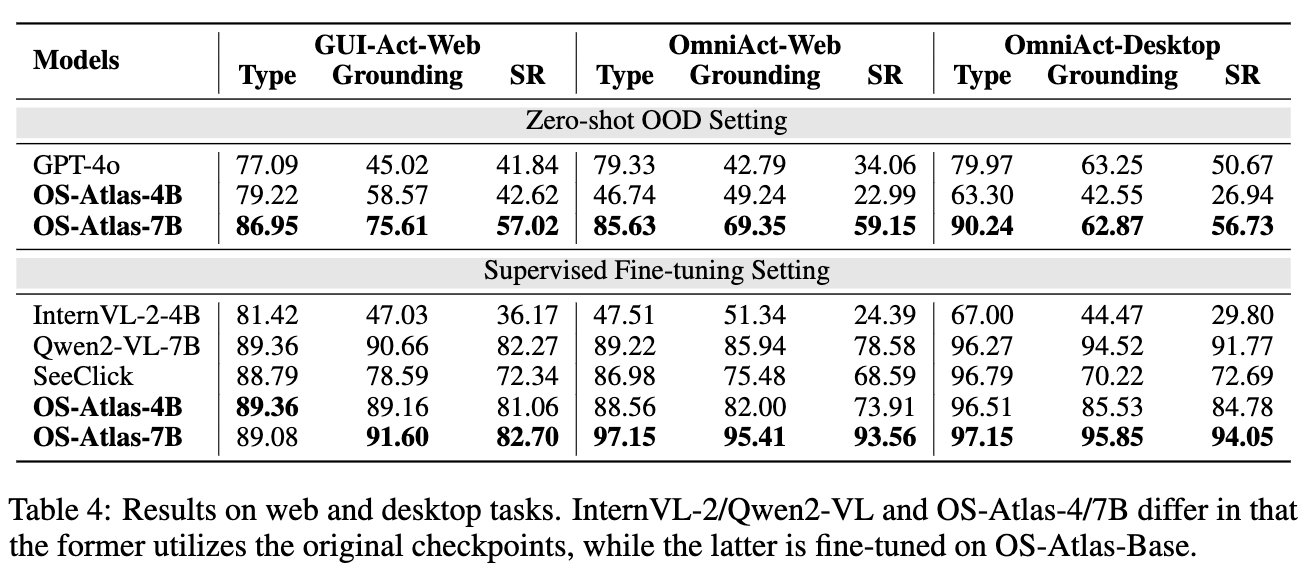
-
Mobile
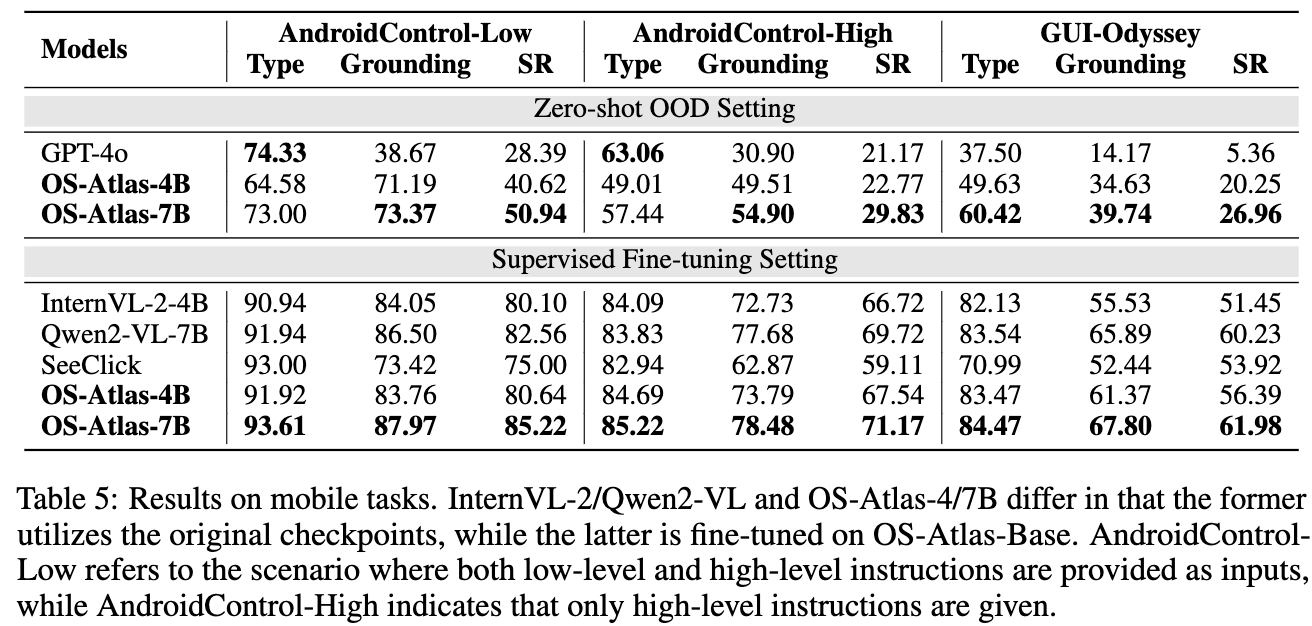
-
-
정성적 결과
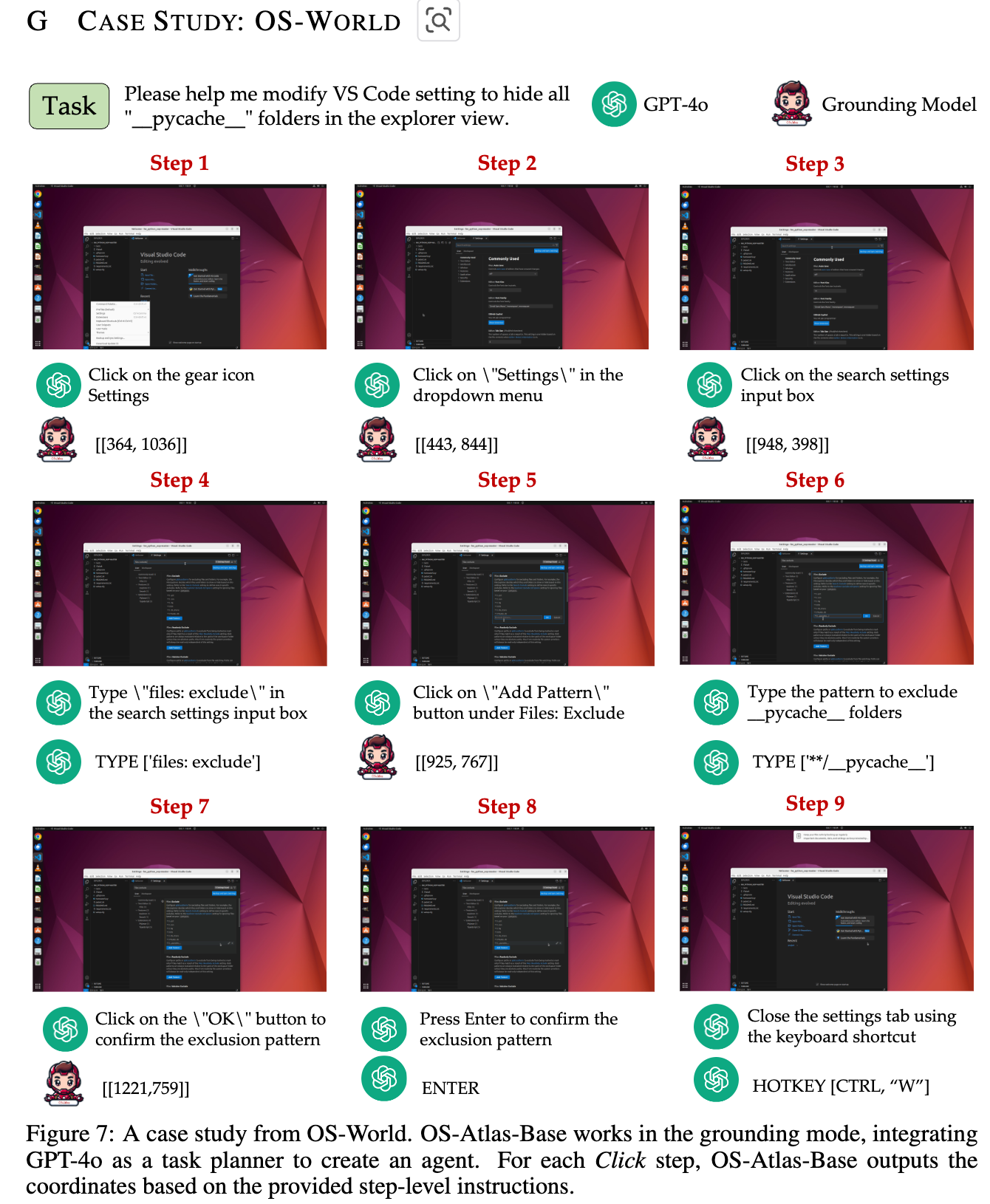
-
Analysis
-
Grounding pretraining / Unified Action space 유무에 따른 성능 분석
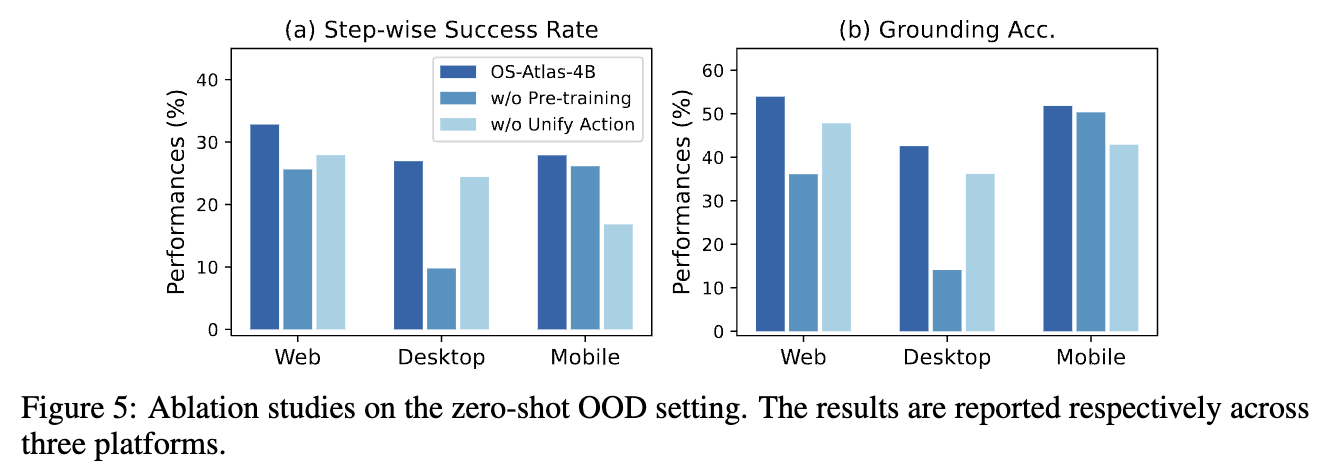
- Unified Action space 전(17 action type) $\to$ 후 (10 action type)
-
위에 report는 OOD 특성을 분석하기 위해 3개의 dataset으로만 학습함. 이를 7개로 확장해봄 (OS-Atlas-Pro)
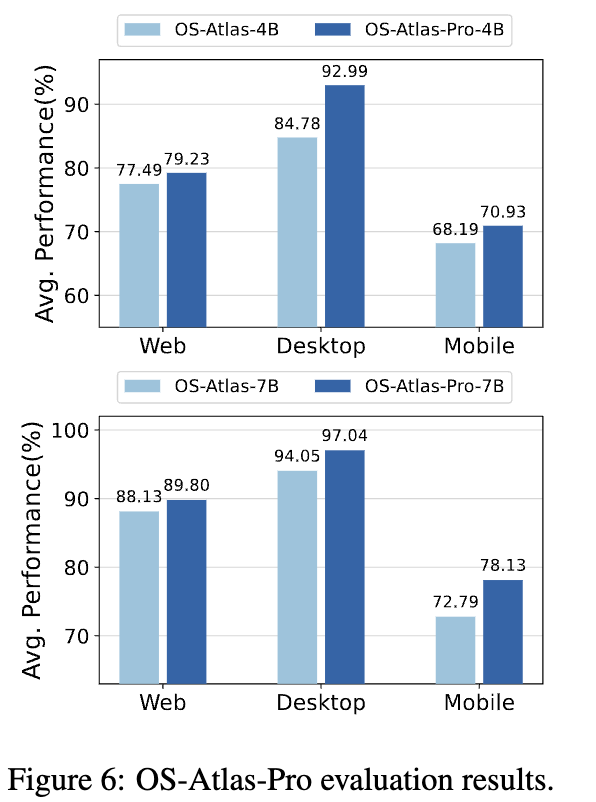
-