From Perception to Reasoning: Enhancing Vision-Language Models for Mobile UI Understanding
[MobileUI] From Perception to Reasoning: Enhancing Vision-Language Models for Mobile UI Understanding
- paper: https://aclanthology.org/2025.findings-acl.1295.pdf
- github: https://github.com/iitbsrib/MoUI (깡통)
- ACL 2025 accepted (인용수: 0회, ‘25-07-29 기준)
- downstream task: Mobile UI grounding & QA
1. Motivation
-
VLM에게 정밀하게 text & visual element를 grounding하는 것은 해당 요소를 인식하고, text query의 context를 고려하여 이해해야하는 어려움이 있다.
-
이는 Mobilie UI domain에서 domain specific한 structured UI dataset이 pretraining 시에 부족함 때문이다.
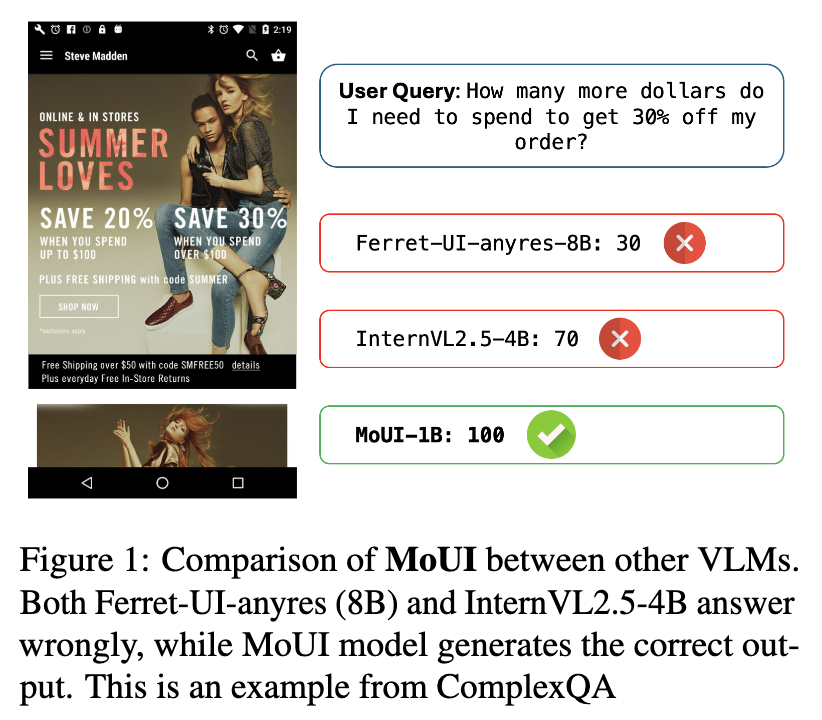
$\to$ User의 의도와 Mobile UI의 시각적 의미간의 gap을 bridge하는 학습 방법을 제안해보자!
2. Contribution
- MoUI (Mobile UI) lightweight models을 제안함 (1B, 2B, 4B)
- UI screens기반 복잡한 reasoning tasks에 사용됨
- 2 stage training
- perception: MoUI기반 학습
- reasoning: Rico data기반 다양한 task
- SoTA 성능을 달성함
- UI Instruct dataset(MoIT)을 제안함
- Mobile UI grounding 기반 150K instruction-tuned dataset
- user의 queries와 UI element간의 alignment
- MoIQ: 3K의 사람이 수동으로 라벨링한 reasoning evaluation benchmark
3. MoUI
3.1 Dataset Contstruction & Tasks
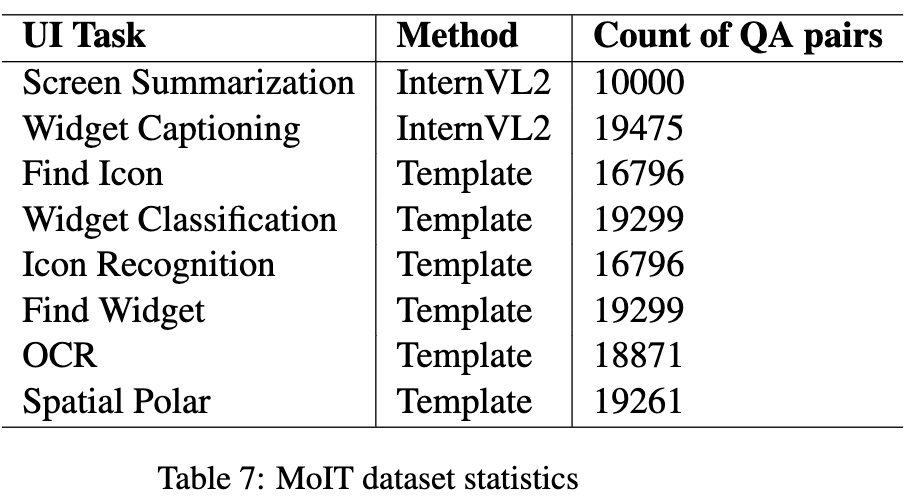
3.1.1 Perception Tasks
-
Elementary Tasks: model에게 다양한 UI element들, 함수들, 스크린 상의 위치에 대한 깊은 이해력을 키우게 함
- Reco를 기반으로 10개의 variant로 데이터셋을 구현.
- Referring task: user query에서 타켓으로 하는 요소를 분류하는 task. Grounding task와 Q/A를 바꾸면 됨.
- OCR: 요소 내 text를 묻는 task
- Icon Recognition: 특정 bbox에 놓인 icon 요소의 type을 예측하는 task
- Widget Rcongition: 특정 bbox에 놓인 widget 요소의 type을 예측하는 task
- Grounding task: referring task와 정반대. 즉, 묘사된 element의 bbox를 예측하는 task (Find Icon, Find Text, Find Widge)
- Spatial Polar task: 요소간의 상대적 위치관계를 묻고 답하는 task (2D screen을 가정하여, left, right, above, below)을 묻는다. 해당 task은 screent annotation dataset을 사용함.
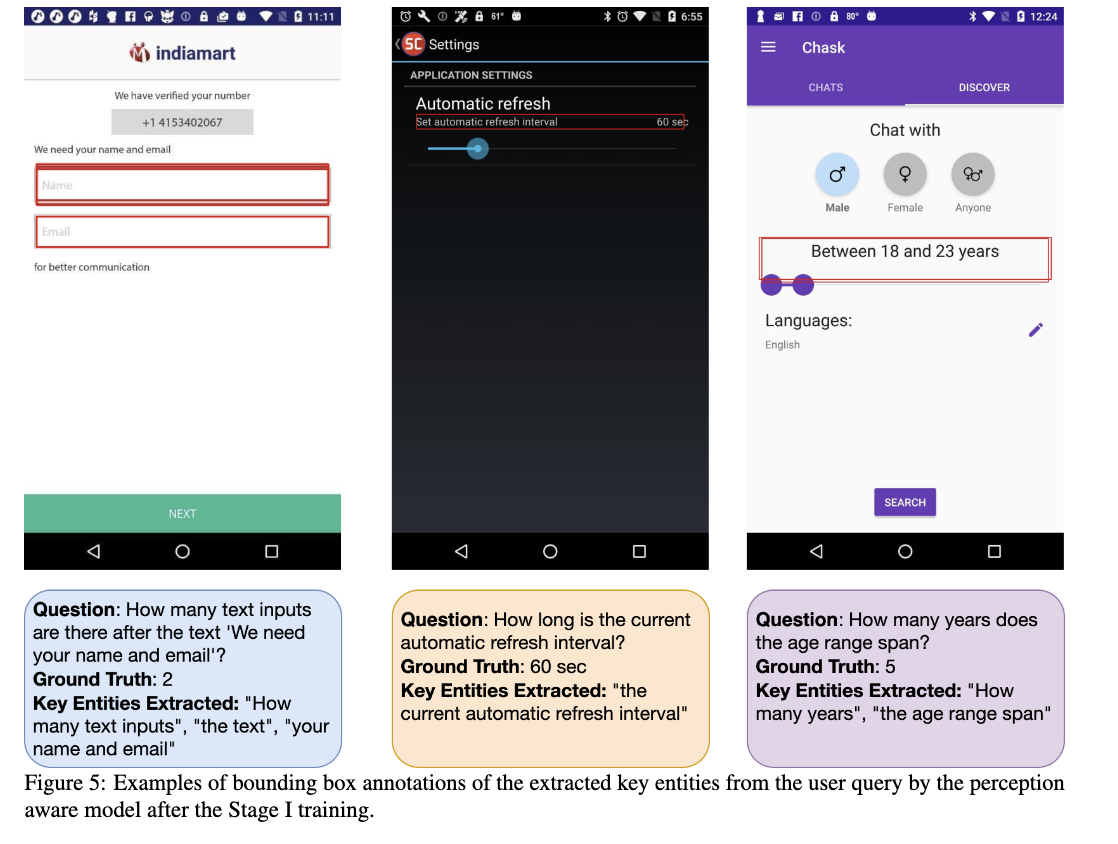
- text, icon, widget type의 element bbox를 추출하고, template 기반 QA를 생성 (아래 그림 참고)
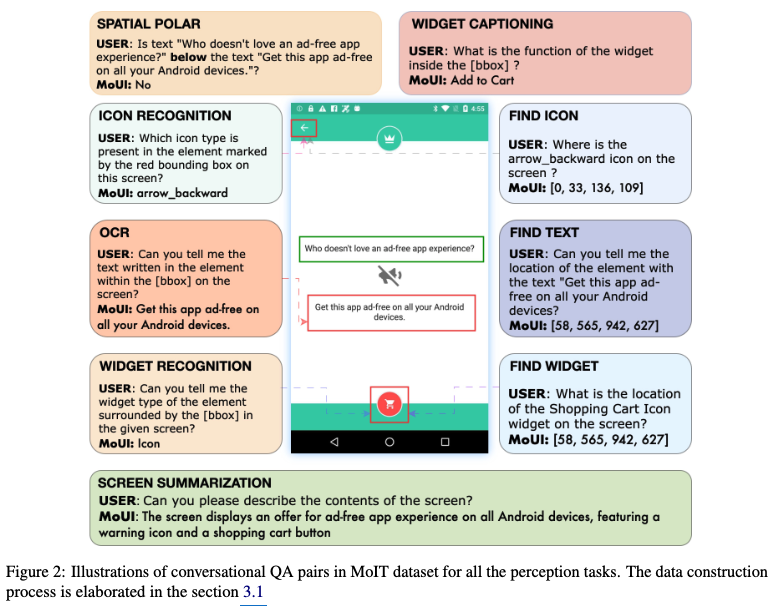
- Reco를 기반으로 10개의 variant로 데이터셋을 구현.
-
Spotlight Tasks:UI element의 contextual 이해력을 키우기 위함
- Screen Summarization task: Screen의 contents를 상세하게 설명하는 task $\to$ Reco기반 Screen2Word dataset
- Widget Captioning task: (widge) element의 functionality에 대한 상세한 설명을 묻는 task $\to$ Reco기반 Widget Captioning dataset
-
데이터 구축 과정
-
InternVL2-40B 모델을 활용하여, 기존재하는 annotation을 guidance로 하여 structured QA conversations를 생성
-
Human이 verfify를 수행하여 최종 완성
-
3.1.2 Advanced Reasoning Tasks
- Dataset
- Opensource dataset인 ScreenQA / ScreenQA Short를 사용
- 새로운 3K human annotated dataset MoIQ를 제안
- Rico dataset의 885개의 screentshot 이미지 기반
- 다양한 element의 개입해야만 답할수 있는 sample들로 구성
- functionality, positions, color, spatial relationship을 묻는 질문
- 대부분 2~3 단어의 answer로 구성
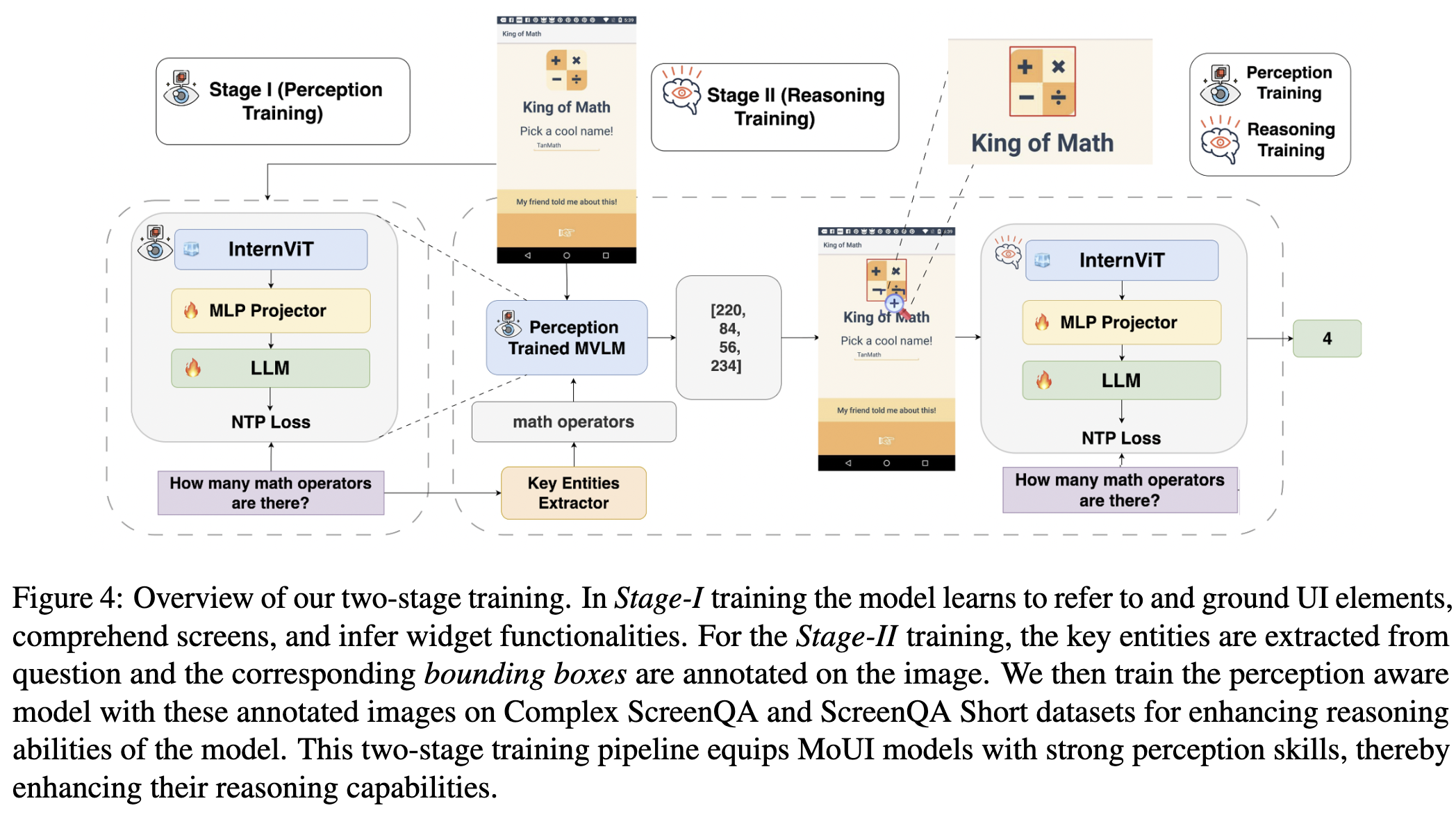
3.2 Training Strategy
-
Stage 1: Grounding, Referring, and Spatial Understanding
-
mobile UI screen의 인지 능력을 향상하도록 학습하여, 자연어 기반 instruction과 이와 연관된 visual component간의 정렬되도록 함
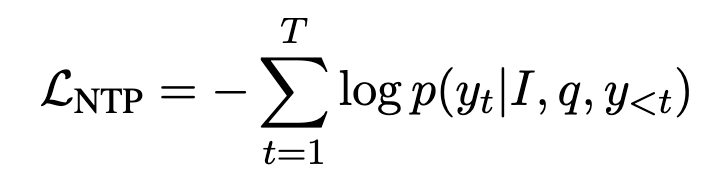
-
-
Stage 2: Perceptual guidance를 토대로 Reasoning
-
user queries로부터 key entities를 entitiy recognition function기반 추출 $\Epsilon=g(p)={e_1,e_2,..,e_n}$
-
Stage 1에서 학습된 모델이 key entity를 기반으로 bbox를 생성 (grounding) $b_j=f_{perception}(I,e_i)$
-
SuperImposed된 이미지를 생성 $I’=Superimpose(I, {b_i}_{i=1}^n)$
-
NTP기반 학습
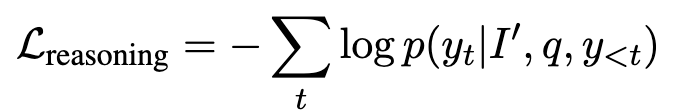
-
4. Experiments
-
Model: InternVL 2.5 / Qwen 2.5 VL
- vision encoder: InternViT-300M-448px
- LLM: InternVL 2.5, Qwen 2.5 VL
- MLP: 2-layer-MLP
-
Training
- MLP + LLM만 학습
-
결과
-
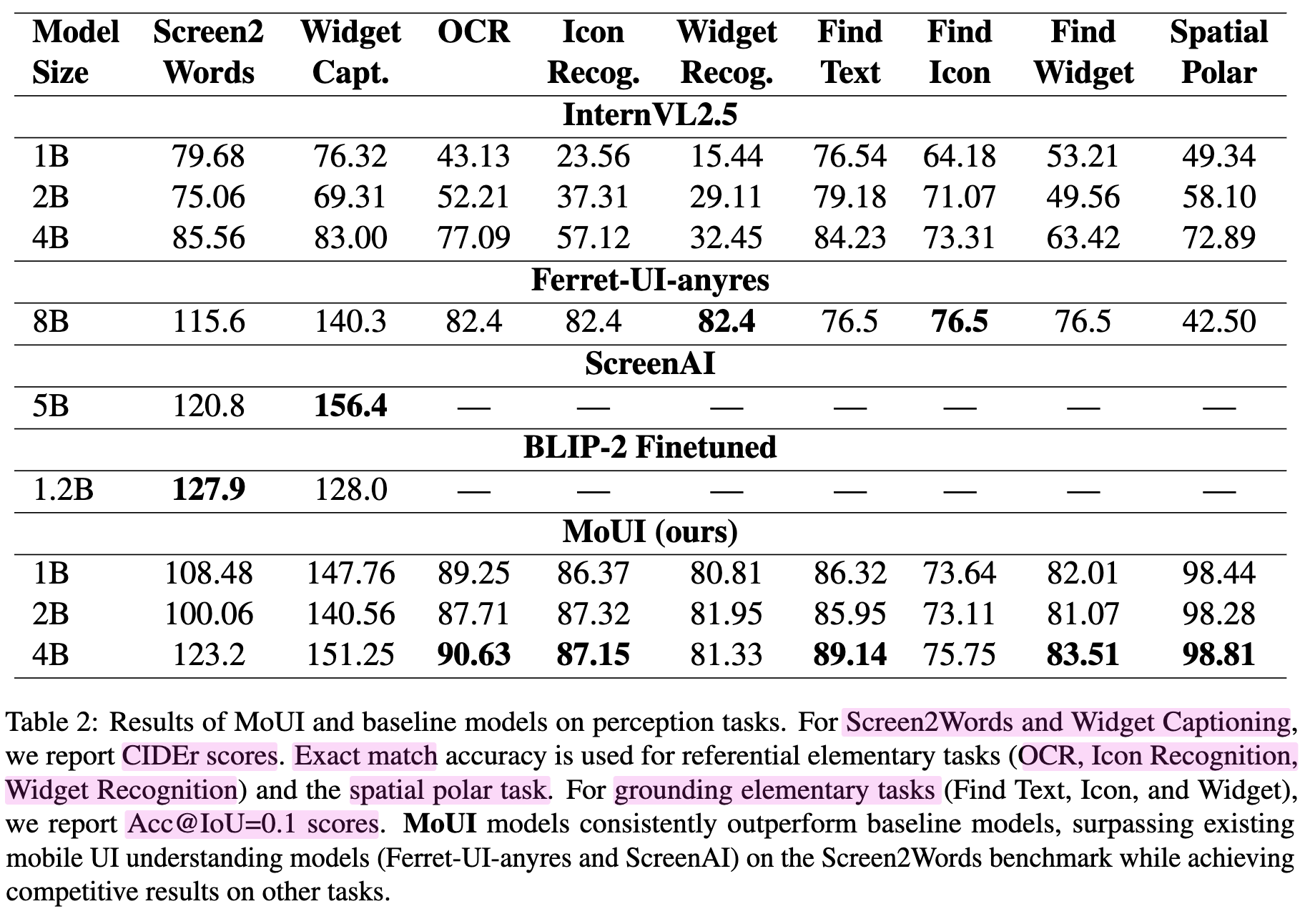
정량적 결과
-
Perception
-
Reasoning
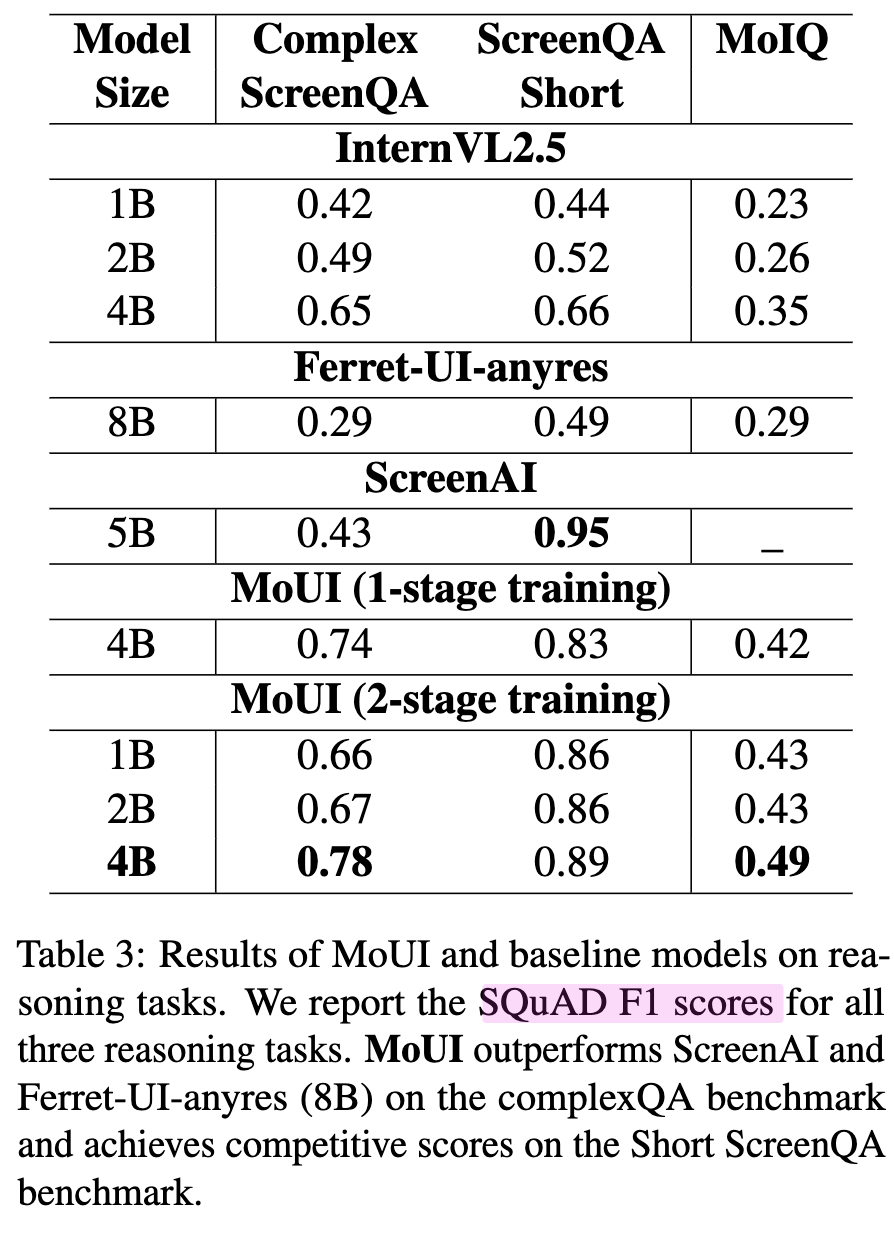
-
-
정성적 결과 (Error-case)
-
OCR task에서 옆에 있는 text로 오답하는 경우
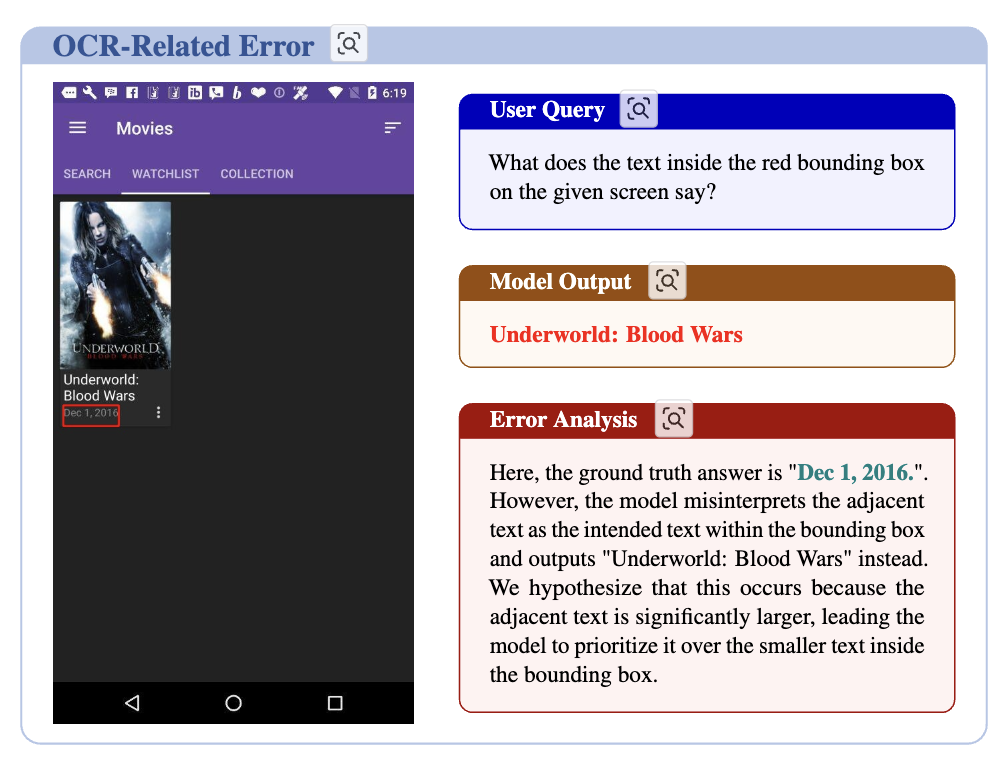
-
visually siilary한 element로 오인식하는 경우
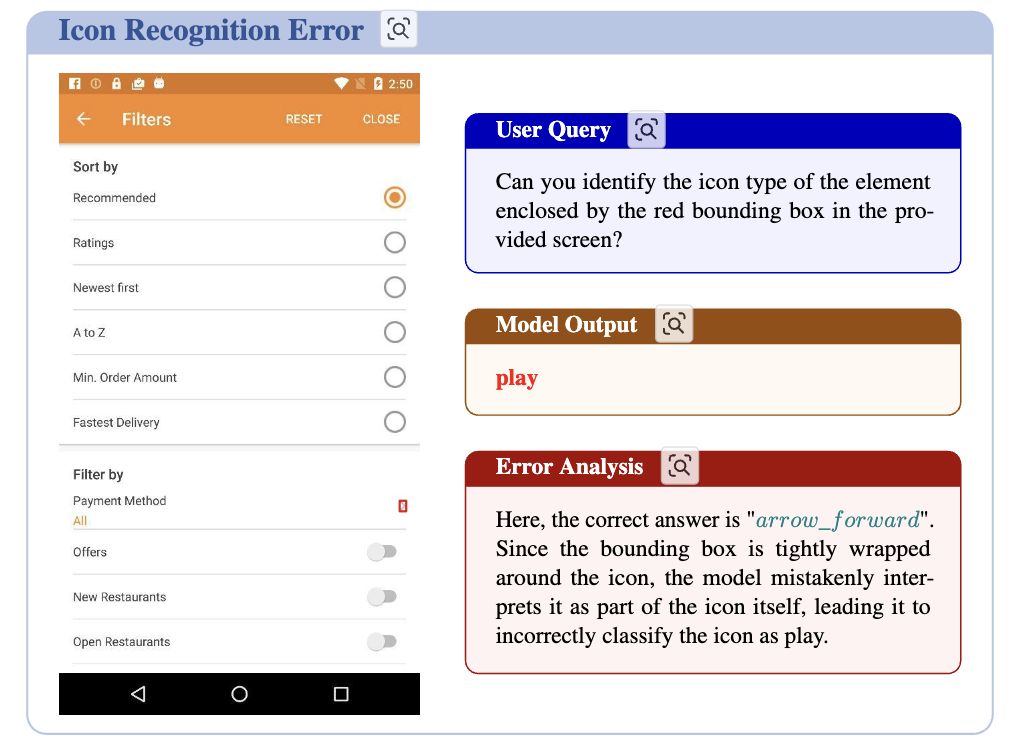
-
Multiple element가 연관된 경우, 오답
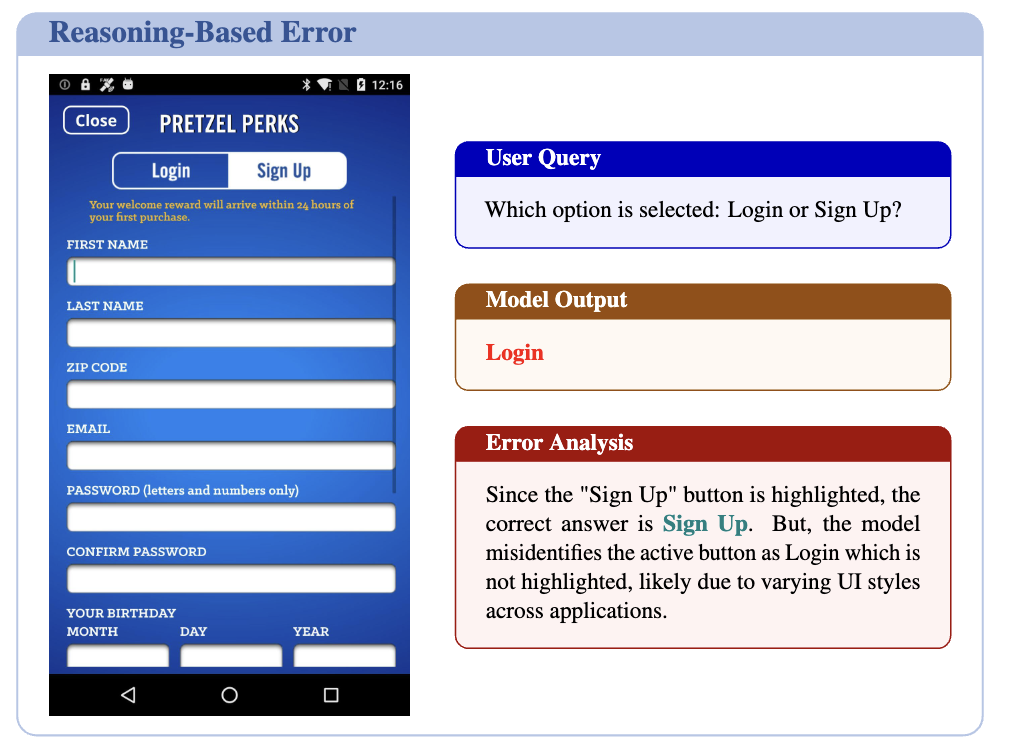
-
-
Ablation Studies
-
Perceptual Guidance 유무에 따른 성능

- reasoning : 74% $\to$ 78%
-
Reasoning 학습 후 Perceptual task 성능 분석 (Catastrophic Forgetting)
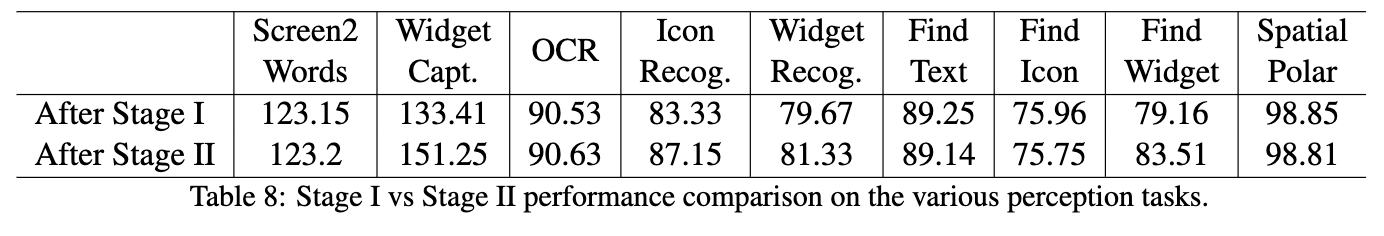
-
-