[DLA] RoDLA: Benchmarking the Robustness of Document Layout Analysis Models
[DLA] RoDLA: Benchmarking the Robustness of Document Layout Analysis Models
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.14442
- github: https://yufanchen96.github.io/projects/RoDLA/
- CVPR 2024 accepted (인용수: 0회, ‘24-06-16 기준)
- downstream task: Robust Document Layout Understanding
1. Motivation
-
기존 Document Layout Analysis (DLA) 모델들의 robustness에 대한 연구는 미진행
-
기존 모델들은 document perturbation에 매우 취약한 특징이 있음
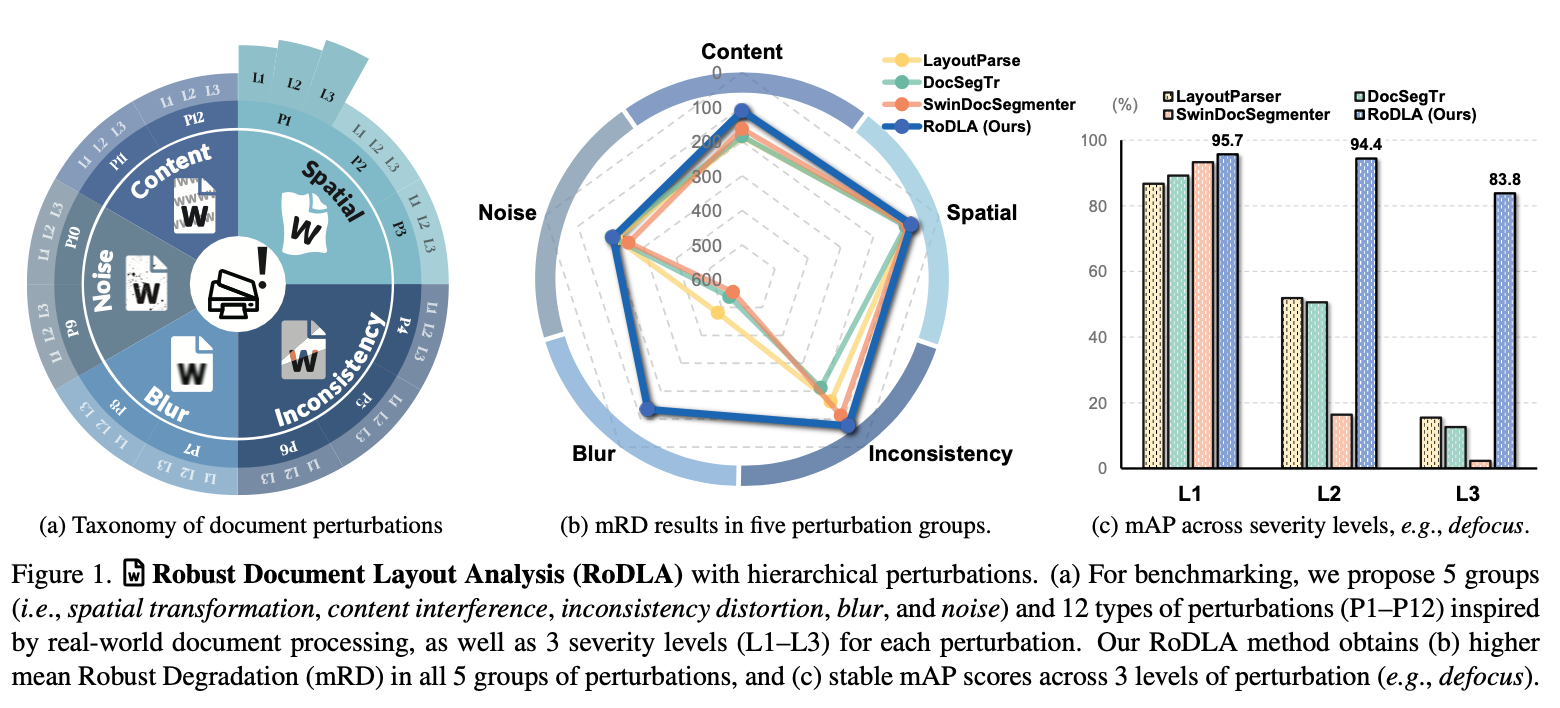
$\to$ document robustness 측정할 dataset & metric이 필요!
2. Contribution
-
DLA model들의 robustness를 분석하고, benchmark를 제안한 최초의 논문
- 450K document image를 제안
-
Document image perturbation에 대한 상세한 분류체계를 제안함
-
5개의 group (content, spatial, inconsistency, blur, noise)
-
3개의 severity level
$\to$ 12개의 typ
-
-
DLA Robustness를 측정할 새로운 metric을 제안함
- mPE (Mean Perturbation Effect)
- mRD (Mean Robustness Degradation)
-
새로운 baseline model RoDLA (Robust Document Layout Analysis)를 제안 $\to$ SOTA
3. RoDLA
-
Hierarchical Perturbation
- Real-world document dataset에 존재하는 perturbation을 12가지 perturbation으로 규정하고, 각각을 severity별로 level 1~3으로 분류함
- 5가지 type으로 대분류 - 12가지 perturbationㅇ로 소분류
- 대분류: content, spatial, inconsistency, blur, noise
- 소분류: 아래 그림 참고
- 전체 dataset의 평균값을 통해 model의 performance를 측정함

-
Perturbation 소개
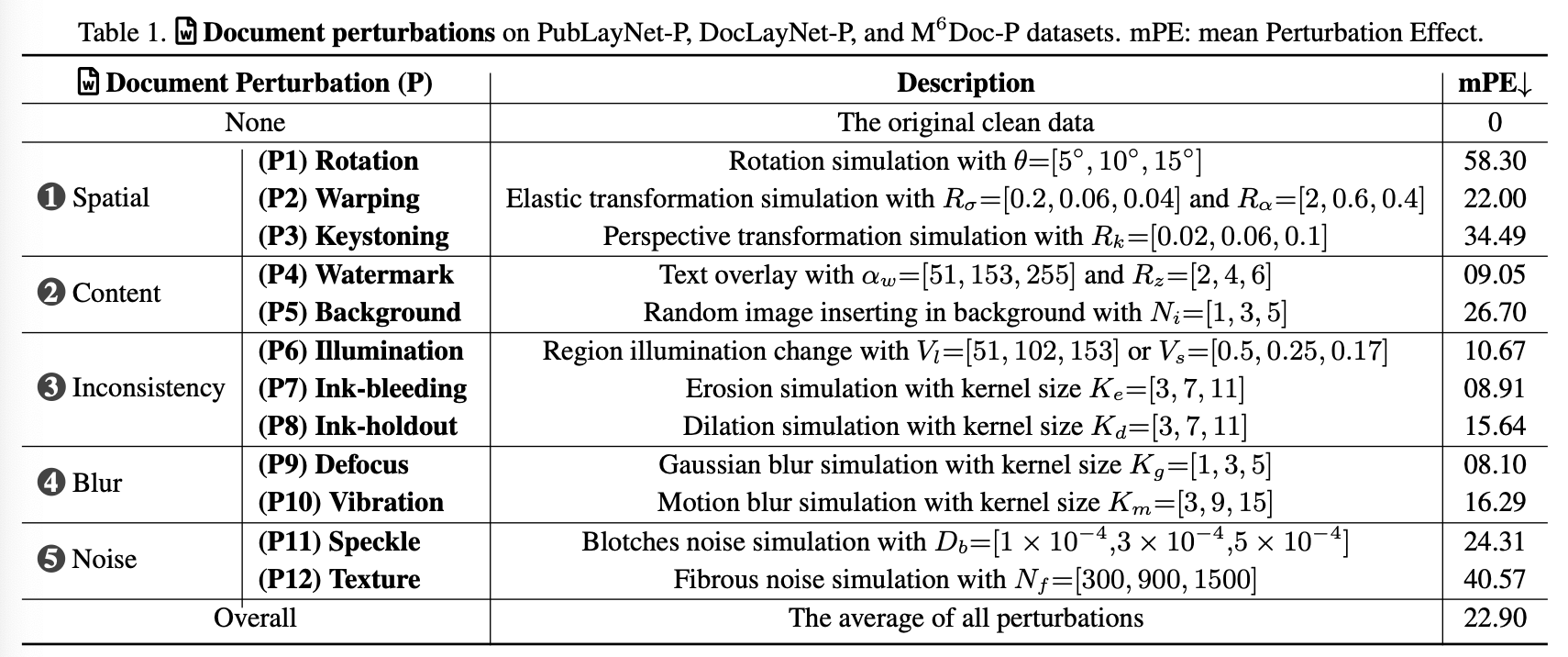
- Spatial-Warping: gaussian filter $g$, smoothness를 조율하는 $R_{\sigma}$, magnitude를 조율하는 $R_{\alpha}$로 구성
- Spatial-Keystoning: perspective transformation을 관여함 Homograph matrix $H$로 original $\to$ new coordinate mapping을 모델링. Standard deviation $R_k$로 제어.
- Content-backbround: Background image로 random하게 ILSVRC dataset을 추가함으로써 severity level을 제어
- Inconsistency: ink, illuminator, 등 distortion을 제어
- Blur: Blurring effect를 point spread fuction (PSF)로 제어
- Noise: speckle, texture등 noise level로 제어
-
Perturbation Evaluation Metrics
-
MS-SSIM (Multi-Scale Structural Similarity Index)
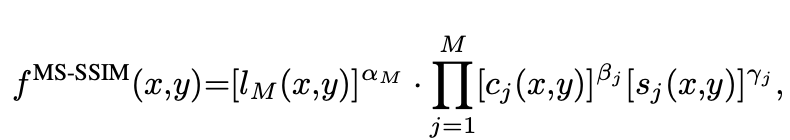
-
$l_M$: M개의 scale luminace(휘도) 차이
-
$c_j(x,y), s_j(x,y)$: x,y 위치에서 j번째 scale의 contrast. & structure 차이
$\to$ watermark & warping에 대해 둔ㄷ감한 반면, rotation & keystoning에 예민함
-
-
CW-SSIM (Complex Wavelet Structural Similarity Index)
- Wavelet domain으로 pixel intensity를 변환하여 측정한 SSIM
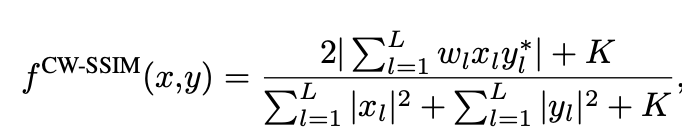
-
$x_l, y_l$: wavelet coefficients
-
$w_l$: l번째 coefficient weight
-
K: tiny value
-
*: complex conjugation
$\to$ defocus에 둔감함
-
Degradation: 얼마나 모델의 performance가 해당 perturbation으로 성능이 하락했는가를 평가하는 지표
\[D=1-mAP\]$\to$ background & texture에 overly 민감함
-
Mean Perturbation Effect (mPE)
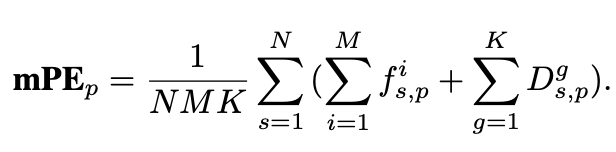
- $D_{s,p}^g$: severity level s, specific perturbation p에 따라 model g의 mPE
- $f_{s,p}^i$: SSIM별 IQA metrics (MS-SSIM, CW-SSIM)
-
-
RoDLA overall diagram
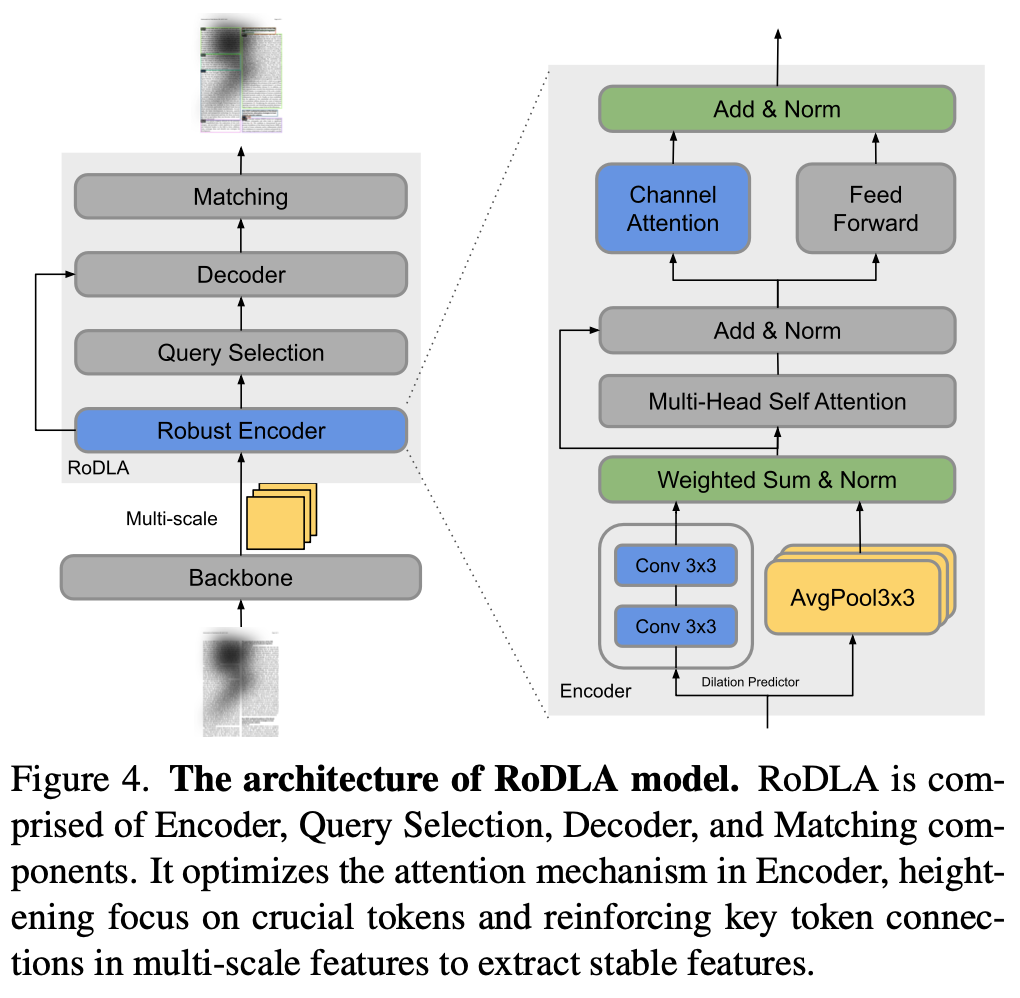
-
baseline: DINO (object detector)
- backbone: InternImage (ImageNet22K pretrained)
-
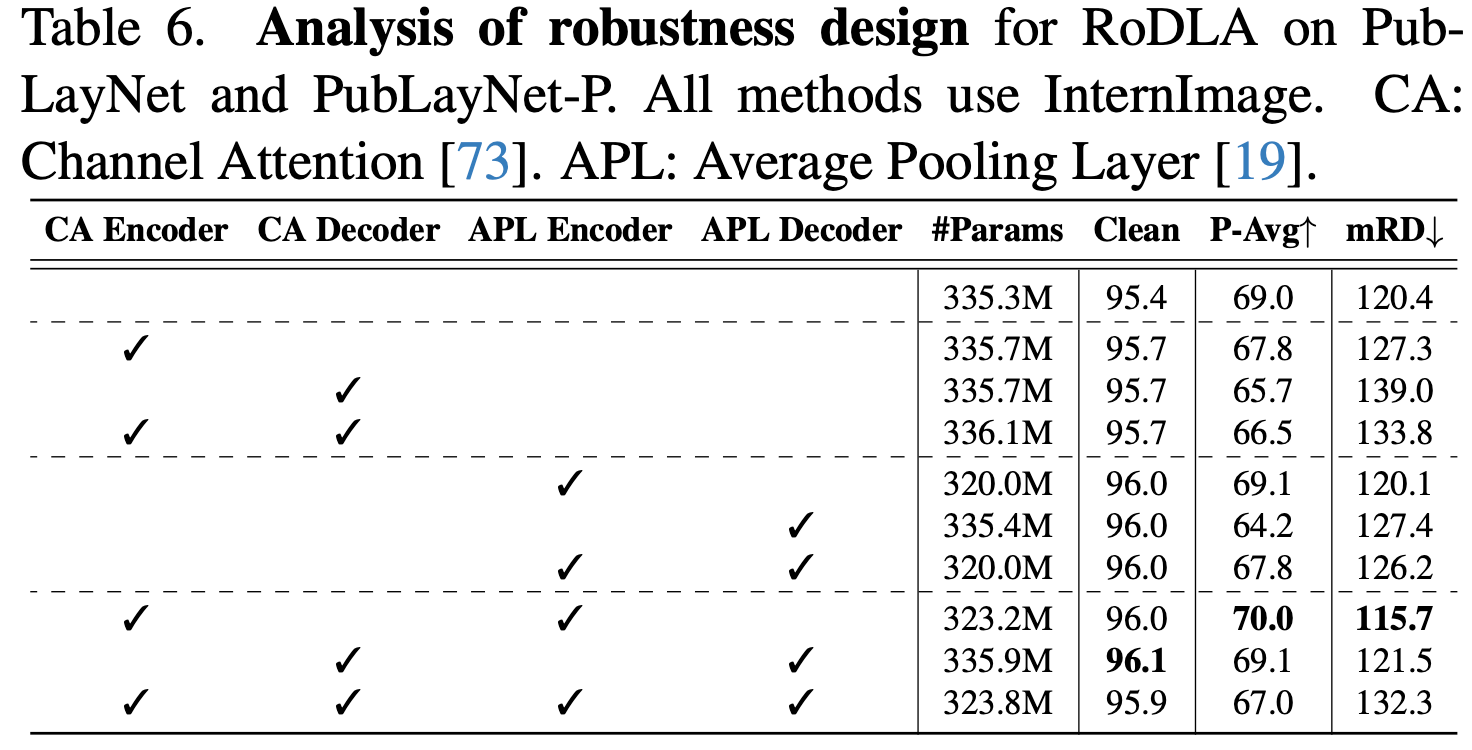
Robust Encoder
- 기존 self-attention layer는 irrelevant token들을 overemphasize하는 경향이 있음
- 3x3 conv + avg pooling layer를 통해 이를 완화할 수 있음 (?)
-
Channel-wise Attention layer
-
channel dimension d로 attention을 수행함으로써 local feature를 channel-wise하게 획득할 수 있음
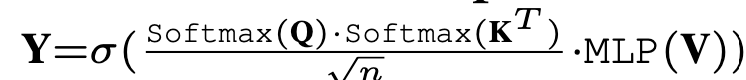
- Q, K, V: $\in \mathbb{R}^{d \times n}$
-
-
4. Experiments
-
Datasets
- PubLayNet-P: 360K document & class 5개
- DocLaynet-P: 80.8K document & class 11개
- $M^6$Doc-P: 9K document & class 74개
-
Evaluation metric: mRD (Mean Robustness Degradation)
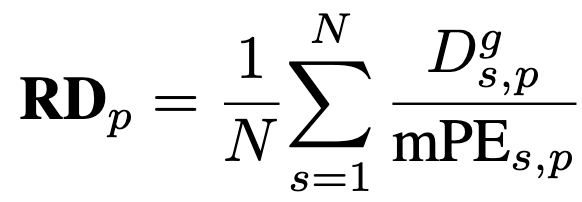
-
p: perturbation index [1,12]
$mRD>100 \to$ perturbation으로 인해 예상보다 model performance가 더 줄어듦을 의미하므로 robustness는 낮을수록 좋음
-
-
정량적 결과
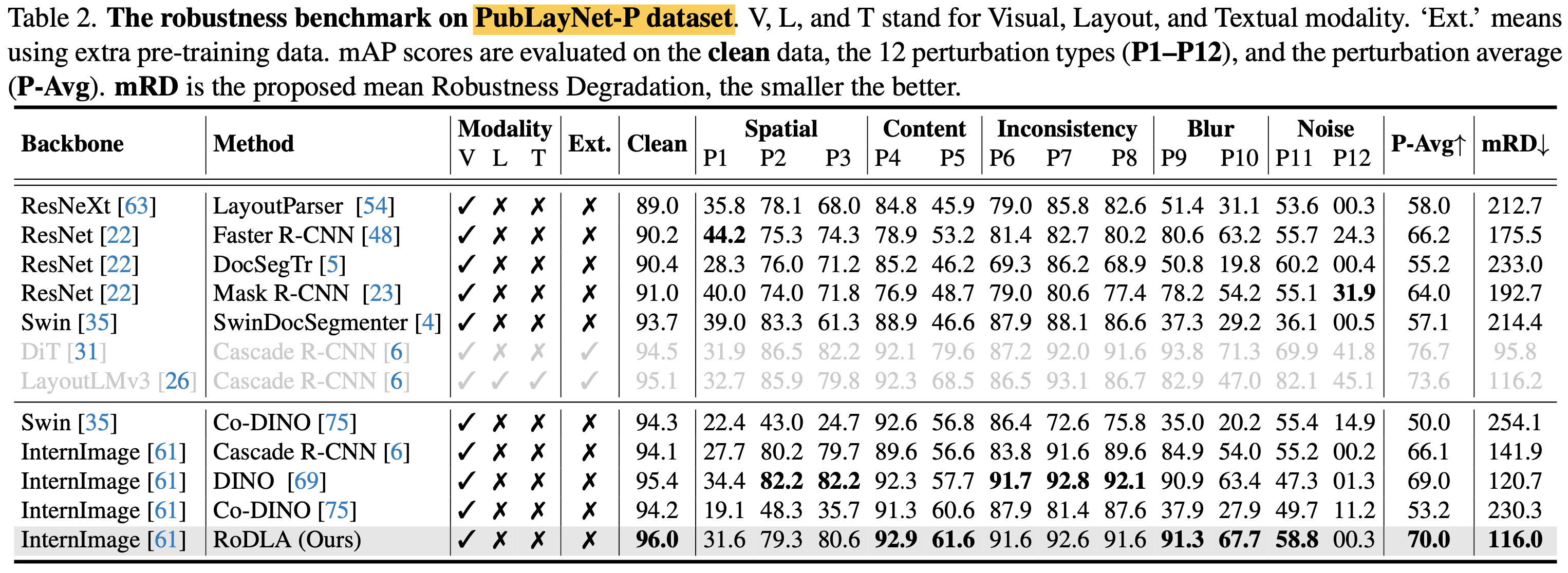
- 대량의 class가 5개인 PubLayNet으로 pretrain한 결과.
- DiT > LayoutLMv3 > RoDLA순 $\to$ pretrained data 영향이 큰 것으로 보임
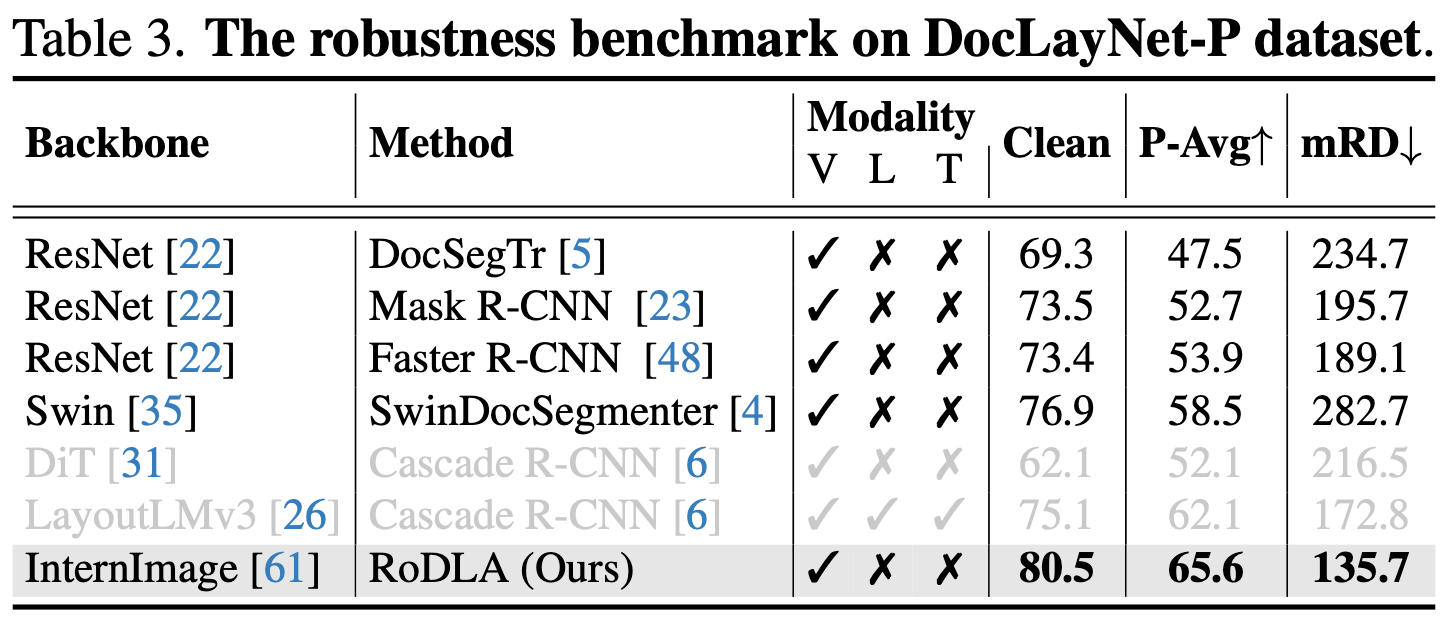
- RoDLA > DiT > LayoutLMv3
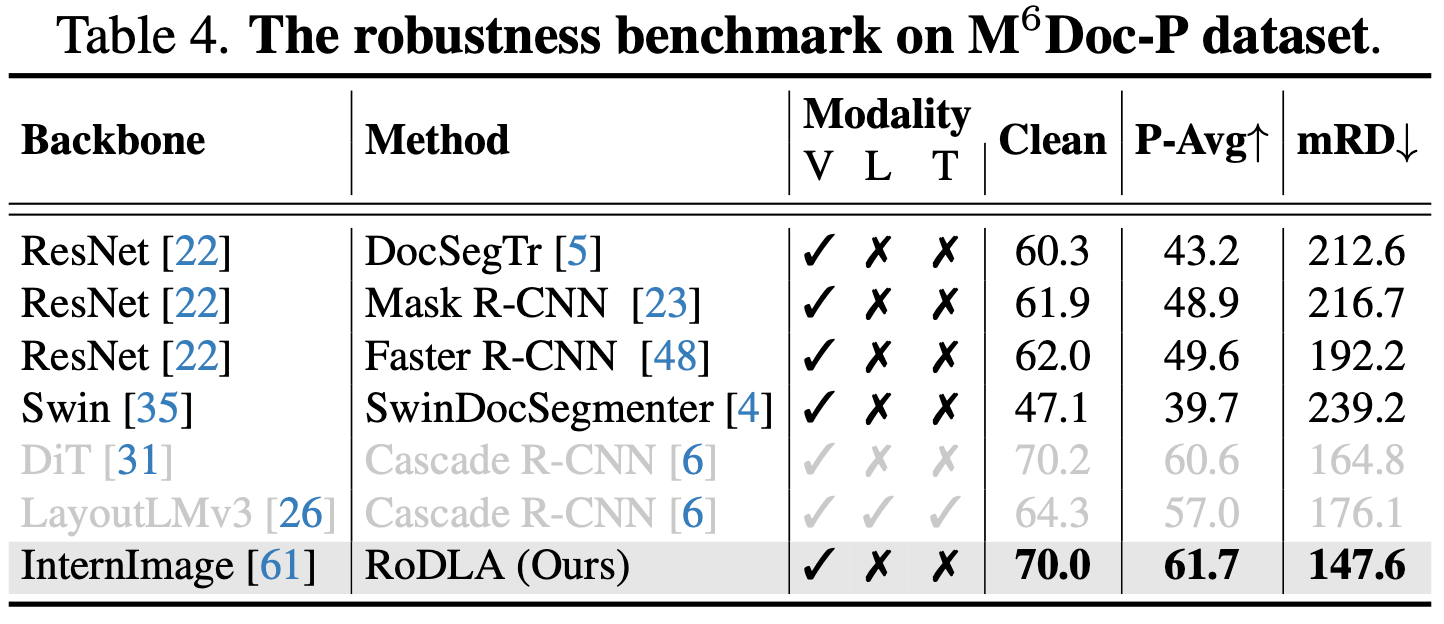
- RoDLA > DiT > LayoutLMv3
-
Ablation studies
-
backbone
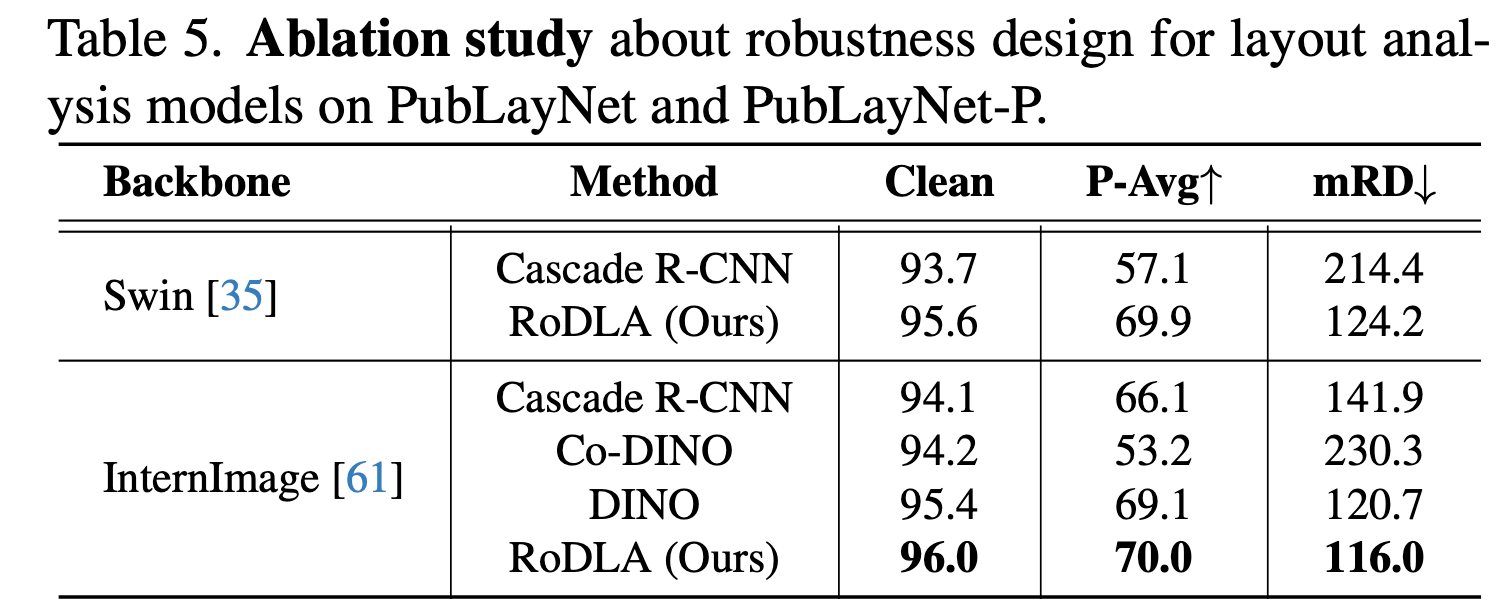
-
Model Architecture
-
Perturbation
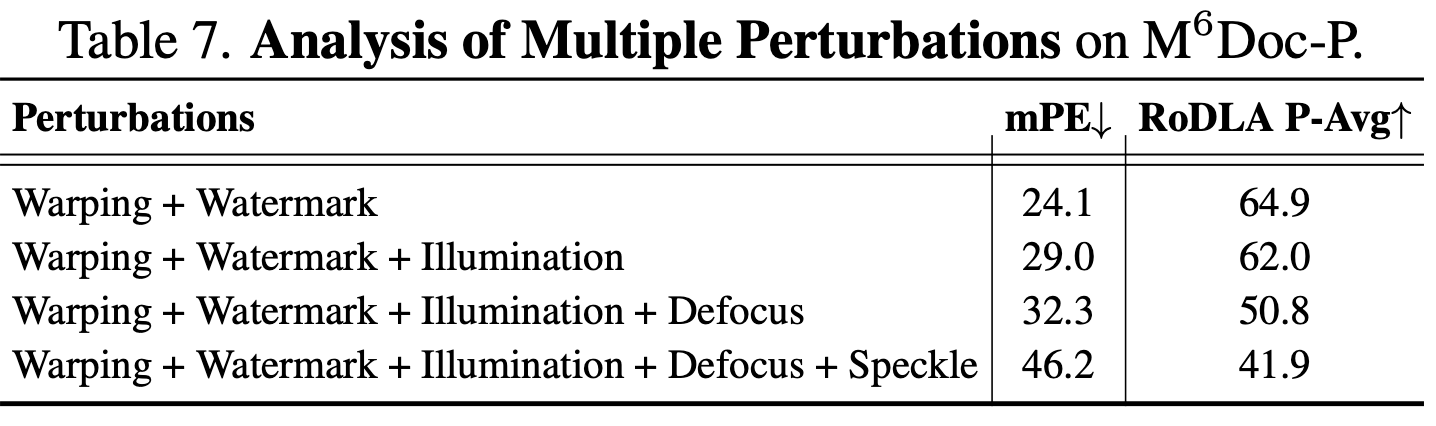
-