[Agent] PPTAgent: Generating and Evaluating Presentations Beyond Text-to-Slides
[Agent] PPTAgent: Generating and Evaluating Presentations Beyond Text-to-Slides
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2501.03936
- github: https://github.com/icip-cas/PPTAgent
- archived (인용수: 10회, 25-08-03 기준)
- downstream task: Agentic PPT Generation
1. Motivation
-
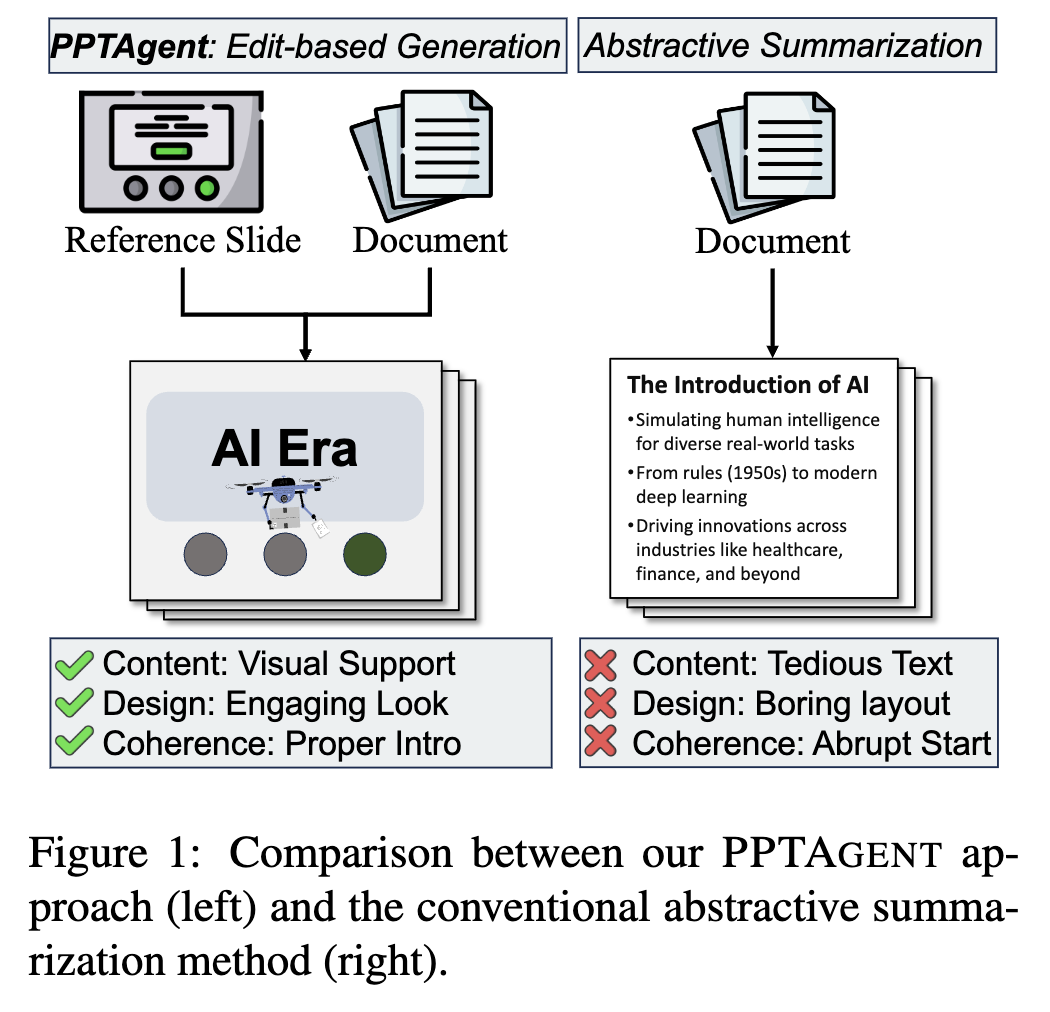
Presentation은 그들의 visual communication하는데 있어 시각적으로 효과적인 매체이다.
-
고품질의 presentation을 만들기 위해서는 매혹적인 stroyline, 잘 디자인된 layout, 그리고 설득력있는 content가 필수적이다.
-
이에 따라 presentation creation을 자동화하는 연구가 진행되고 있다.
-
하지만 기존 연구는 MLLM/LLM기반 text-to-slides 패러다임에 빠져, content에만 집중하고, visual-centric한 presentation의 본질을 잊는다.
$\to$ 단조로운 text-centric한 결과물이 나오므로, 청중의 관심을 효과적으로 유인하지 못한다.
-
반면, 사람이 ppt를 만들때는 reference presentation (템플릿)을 선택하고, 해당 page를 편집하는 과정을 거친다.
$\to$ 사람의 과정을 모방한 PPTAgent를 만들어보자!
2. Contribution
-
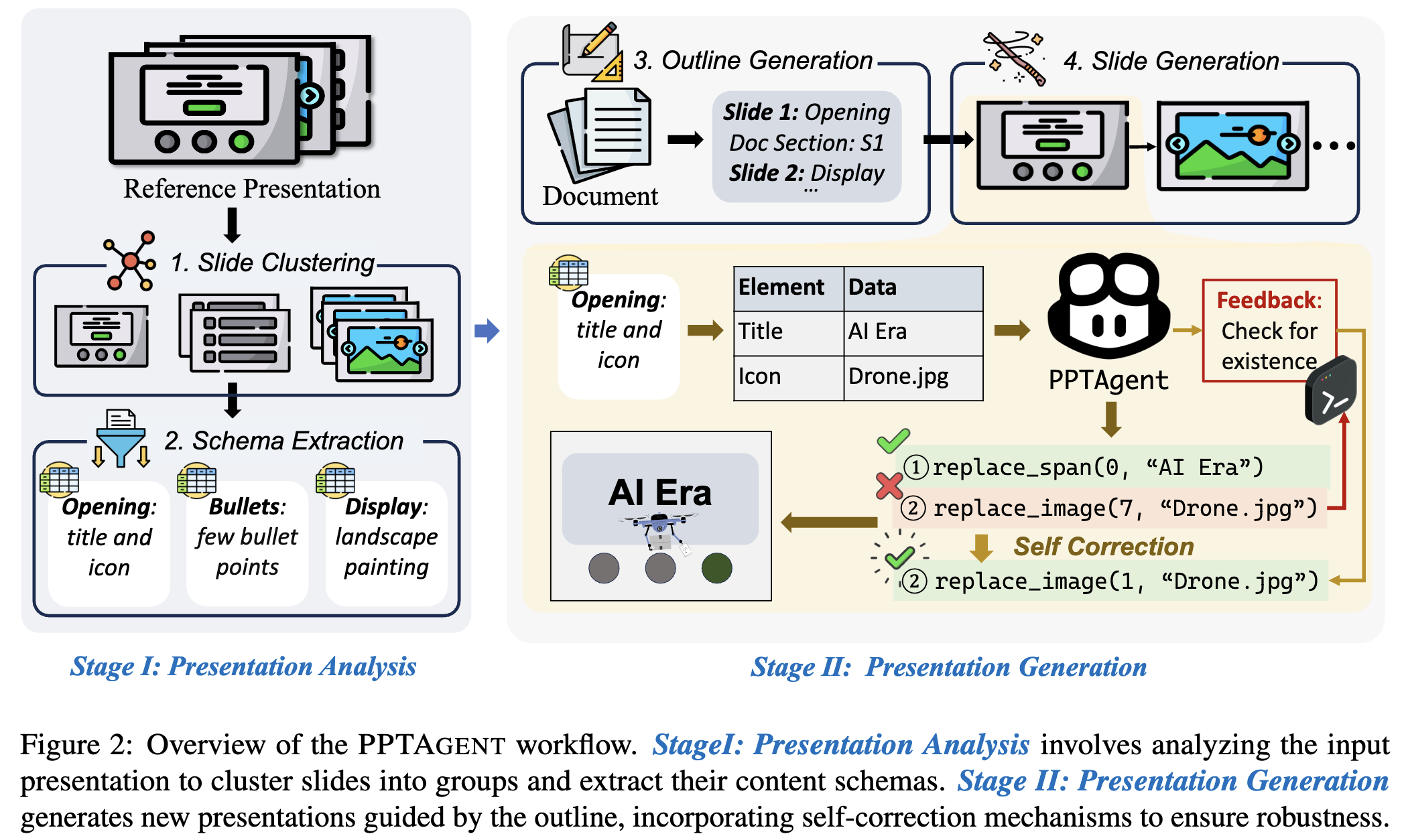
주어진 Reference Presentation을 먼저 이해하여 slide(page)별로 clustering하고, 각 slide별 편집을 여러 API를 사용하는 2-stage pipeline PPTAgent를 제안
-
Stage 1: XML format으로 저장된 reference ppt를 이해하고, slide별로 clustering (opening/ending/table of contents/section header) & schema를 추출하는 단계

-
Stage 2: edit & rendering 가능한 HTML로 만들어 slide generation하는 단계.
- Reference slide (주로 Opening slide)를 기반으로 edit을 수행 (e.g.
replace_span) - 여기서 self-correction 매커니즘을 적용하여 반복적으로 수정 작업을 수행할 수 있음.
- Reference slide (주로 Opening slide)를 기반으로 edit을 수행 (e.g.
-
-
MLLM-as-a-judge 기반
PPTEval시스템을 제안하여, 3가지 축을 기준으로 평가- Content
- Design
- Coherence
-
PPTEval과PPTAGENT뿐만 아니라 presentation dataset인Zenodo10Kdataset을 공개함
3. PPTAgent
PPTAgent? Edit-based 매력적인 ppt를 생성하는 agent
3.1 Problem Formulation
-
Conventional method
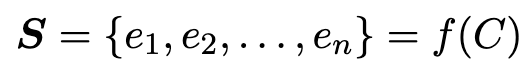
C: content- $\bold{S}$: n개의 slide로 구성된 presentation
- f: 사람이 수동으로 style, layout 적용하는 과정을 함수화한 모습
-
PPTAgent
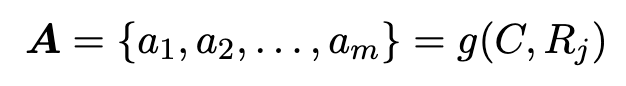
- C: input content
- $R_j$: Reference ppt의 j번째 slide
- g: executable edit action (code로 생성)
3.2 Stage 1: Presentation Analysis
-
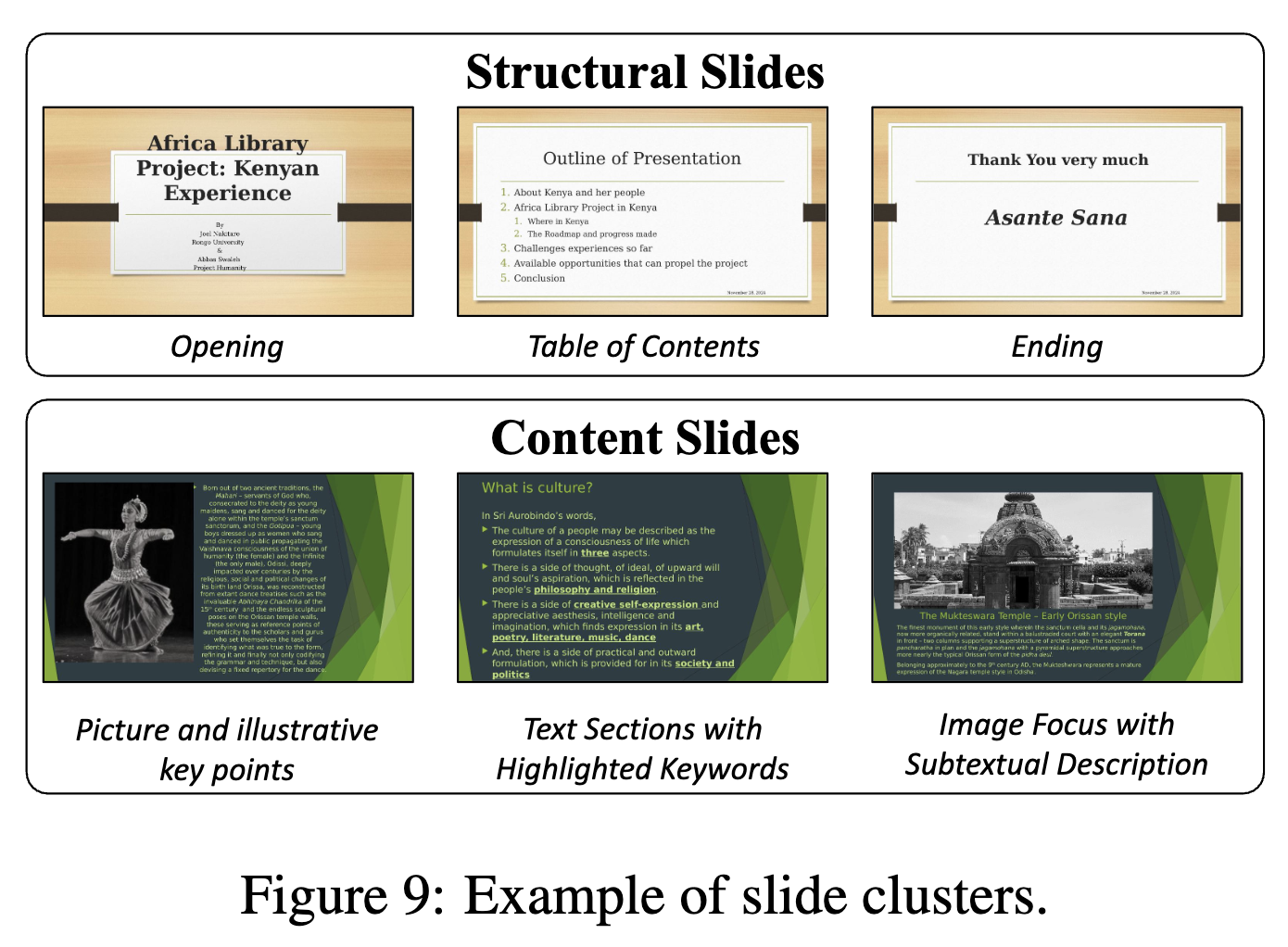
Slide Clustering: Reference ppt내의 slide(page)를 LLM을 활용하여 Content slide / structural slide중에 하나로 분류
-
Structural Slide: LLM기반으로 opening / table of contents / section header / ending 여부를 분류
-
Content Slide Clustering

-
Content에 agnostic하게 하기 위해, 모든 text를 ‘a’로 표현
-
모든 slide를 이미지화 한 후, ViT embedding의 유사도 0.65를 기준으로 같은 cluster로 묶음
-
Clustering 결과 예시
-
Clustering에 활용된 prompt

-
-
-
Schema Extraction: 각 slide별로 명확하고 구조화된 schema를 추출하여, 향후 slide generation에 활용
- schema: Slide내 key content element에 대한 Category / Description / Data
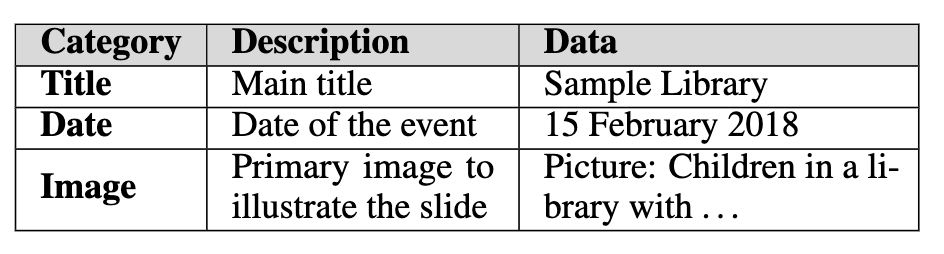
-
schema 추출에 활용된 prompt

3.3 Stage 2: Presentation Generation
-
Outline Generation
- LLM을 사용하여 multiple entries outline(개요)를 생성.
- 각 entry는 잠재 slide이며, entry별로 reference slide & entry에 연관된 document content를 포함함.
- reference slide: Stage 1에서 제공한 slide description 기반으로 reference schema를 선택.
- relevanct document: input document 기반으로 identified.
-
Slide Generation
-
Entry별로 반복적으로 slide가 생성됨
-
Reference slide의 layout과 input으로 주어진 image의 caption을 활용하여 LLM이 content의 일관성, layout의 명료성을 부여하며 편집
-
LLM이 Edit API를 활용하여 편집을 수행할 수 있도록 HTML representation을 채택함

-
Self-correction을 통해 LLM에게 해당 action에 대한 feedback 을 REPL기반으로 제공
- (Read-Eval-Print Loop)이란?
REPL은 “읽기-평가-출력 반복”의 약자로, 컴퓨터 프로그램 환경에서 사용자가 입력한 단일 표현식(코드)을 읽고(Read), 이를 평가한(Eval) 다음, 그 결과를 사용자에게 출력하고(Print) 이 과정을 반복(Loop)하는 대화형 프로그래밍 환경을 의미합니다.
- 읽기(Read): 사용자가 입력한 코드를 읽어들입니다.
- 평가(Eval): 읽어들인 코드를 실행하고 계산합니다.
- 출력(Print): 코드 실행 결과 또는 오류 메시지를 사용자에게 보여줍니다.
- 반복(Loop): 위 과정을 사용자가 프로그램을 종료할 때까지 계속 반복합니다.
- (Read-Eval-Print Loop)이란?
REPL은 “읽기-평가-출력 반복”의 약자로, 컴퓨터 프로그램 환경에서 사용자가 입력한 단일 표현식(코드)을 읽고(Read), 이를 평가한(Eval) 다음, 그 결과를 사용자에게 출력하고(Print) 이 과정을 반복(Loop)하는 대화형 프로그래밍 환경을 의미합니다.
-
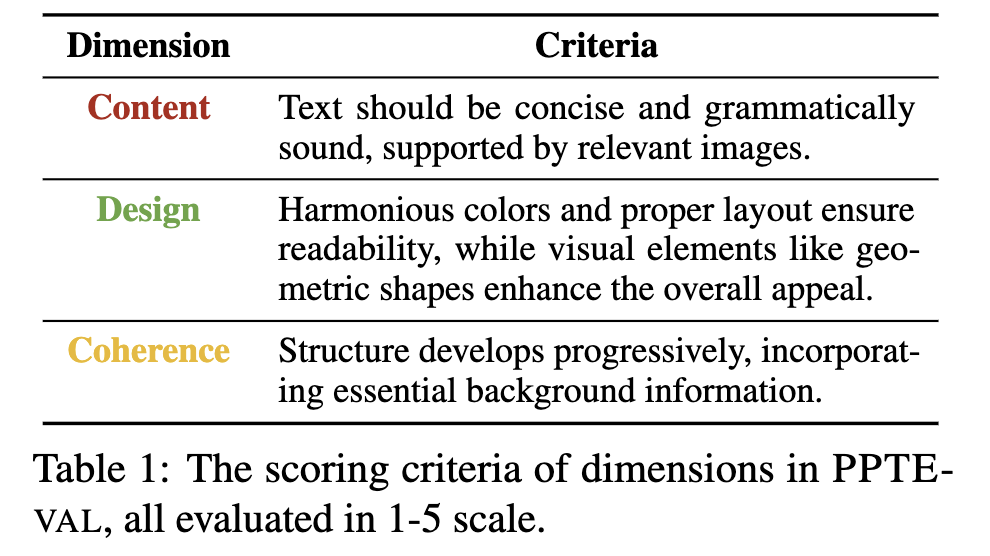
4. PPTEval
-
생성된 presentation의 quality를 측정하기 위해 도입된 MLLM-as-a-judge framework
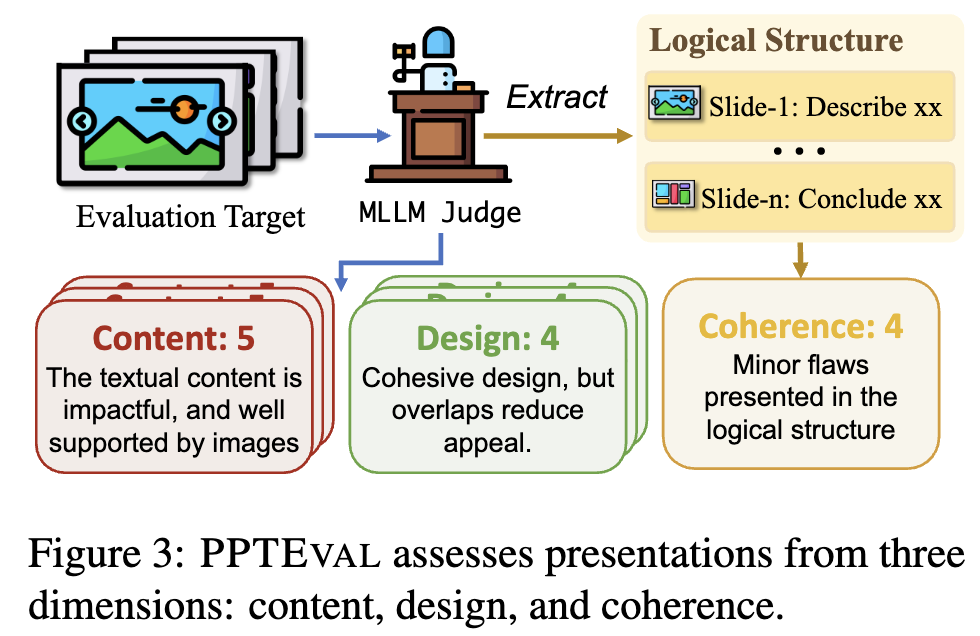
-
Durate2008/2010에 근거하여 3개의 축으로 1~5점 사이로 평가
-
content

- content 내 내용이 적절한가?
- content가 명료하고, 품질이 우수한가?
- image가 text를 보완하는가?
-
design

- color scheme이 잘 선택되었는가? (content와의 대조가 잘 이루어졌는가? 색의 조화롭게 쓰였는가?)
- visual element가 적절한가? (기하적 모양, ppt의 표현력을 좋게 하는가?)
- 전반적 design이 우수한가? (요소간의 overlap이 없는가? 전달할 content를 방해하지는 않는가?)
-
coherence

- storyline이 논리적인가?
- contextual 정보가 풍부한가?
-
5. Experiments
-
Dataset
-
Zenodo10K: 다양한 domain & clear license의 10,448 presentations dataset
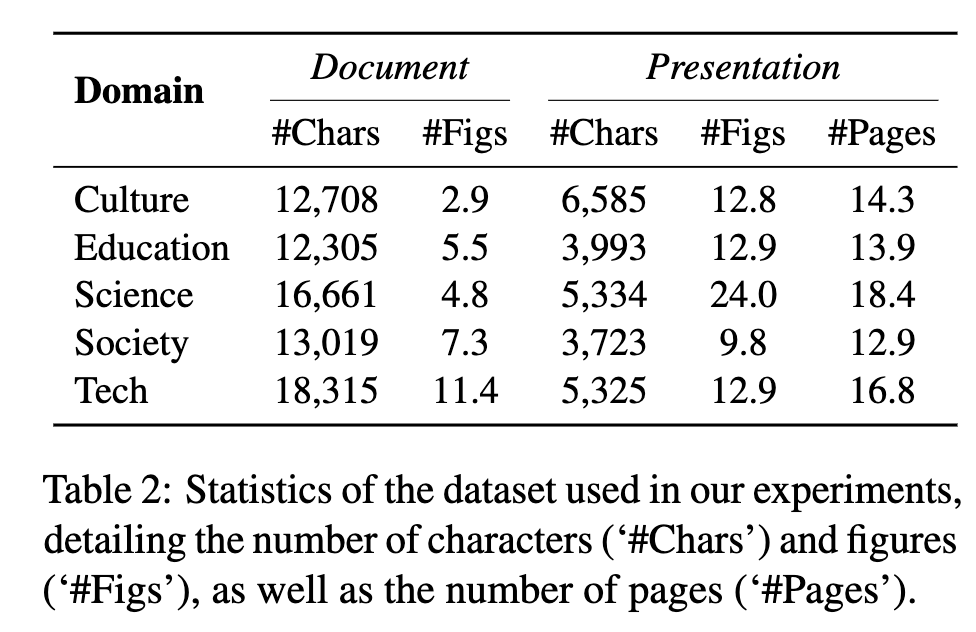
- 5 domain에 대해 50 sample를 reference presentation로 선택하여 입력으로 활용
- 선택 기준
- 비용효율을 감안하여 12-64 page로 한정
- text length는 2,048 ~ 20,480로 한정
- image의 duplication을 배제 (이미지 cosine sim. 0.85이상 / text consine sim. 0.8 이상은 제외)
- 선택 기준
- 5 domain에 대해 50 sample를 reference presentation로 선택하여 입력으로 활용
-
-
Implementation Details
- model
- GPT-4o(2024-08-06)
- Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct
- Qwen2-72B-Instruct
- data
- 5 domains x 10 input documents x 10 reference pages)
- embedding
- text: BGE-M3
- image: ViT
- model
-
Baselines
- DocPres: rule-based narrative-rich approach + similarity based 매커니즘
- KCTV: pre-defined template기반 중간 representation 생성 (vision x)
-
Evaluation Metrics
- Sucess Rate(SR): 성공적으로 task를 수행한 비율.
- Perplexity(PPL): Llama-3.1-8B model의 출력 결과 likelyhood. 낮을수록 좋음
- Rouge-L: 생성된 text & reference text 중 가장 긴 text간의 유사도
- FID: 생성된 & reference slide image간의 feature 유사도 (64 dim)
- PPTEval: GPT-4o as a judge
-
Overall Result
-
정량적 결과
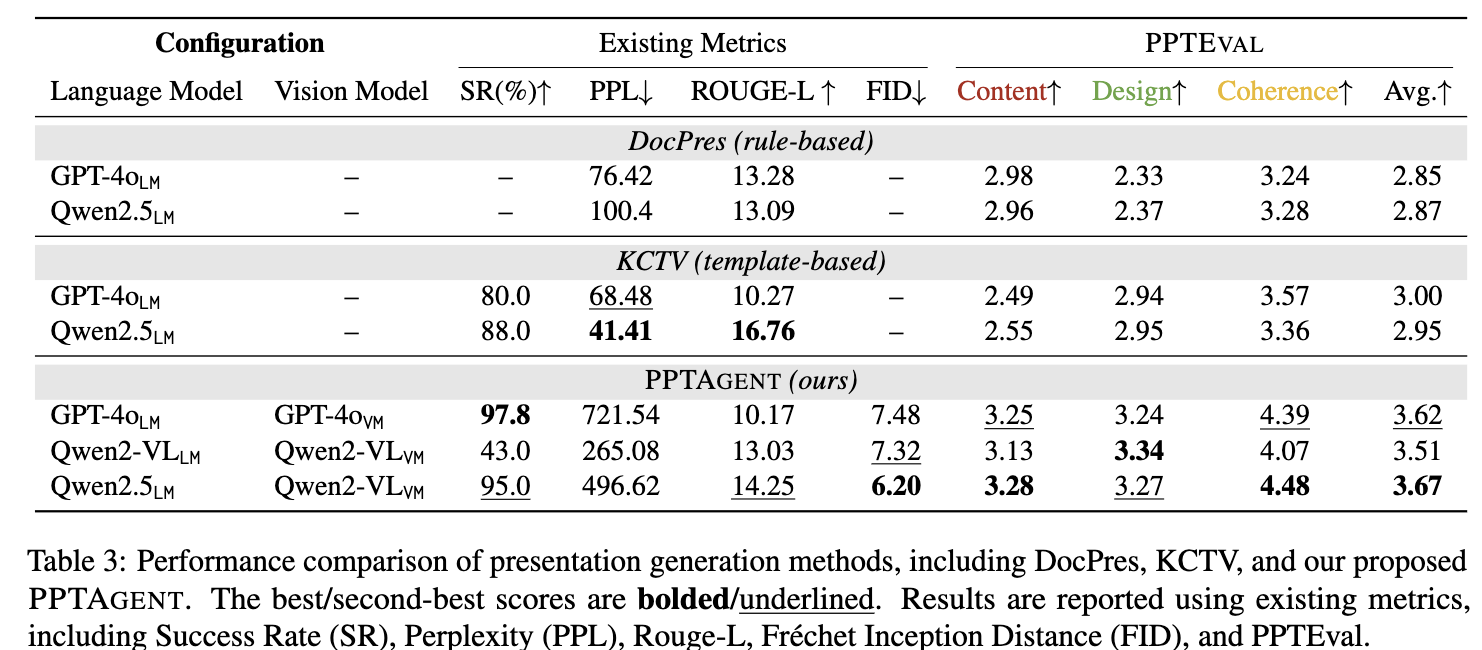
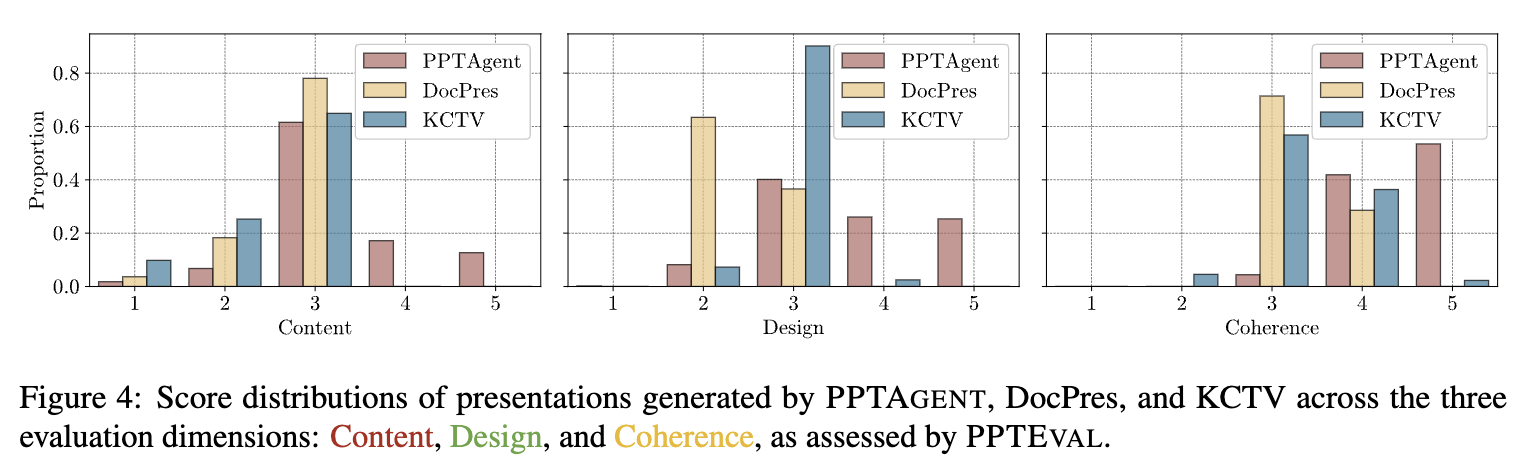
- Conventional metrics (ROUGE-L, PPL)은 정성적 결과와 align이 안되는 경향을 보인다.
-
정량적 결과2
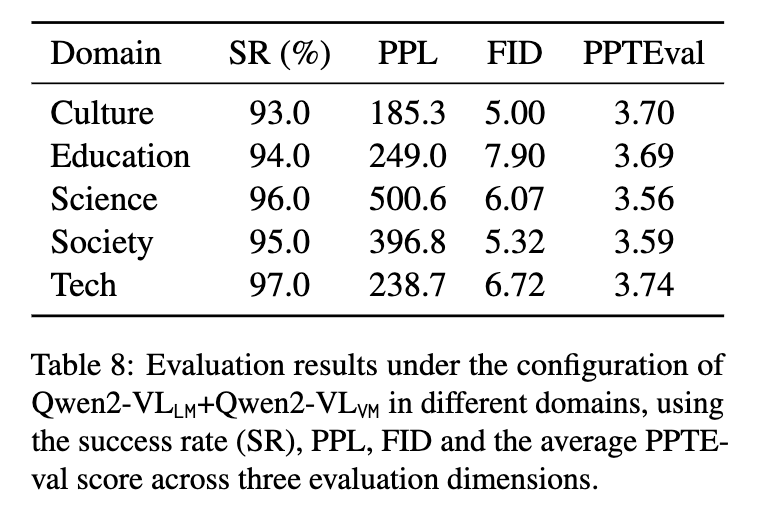
-
정성적 결과
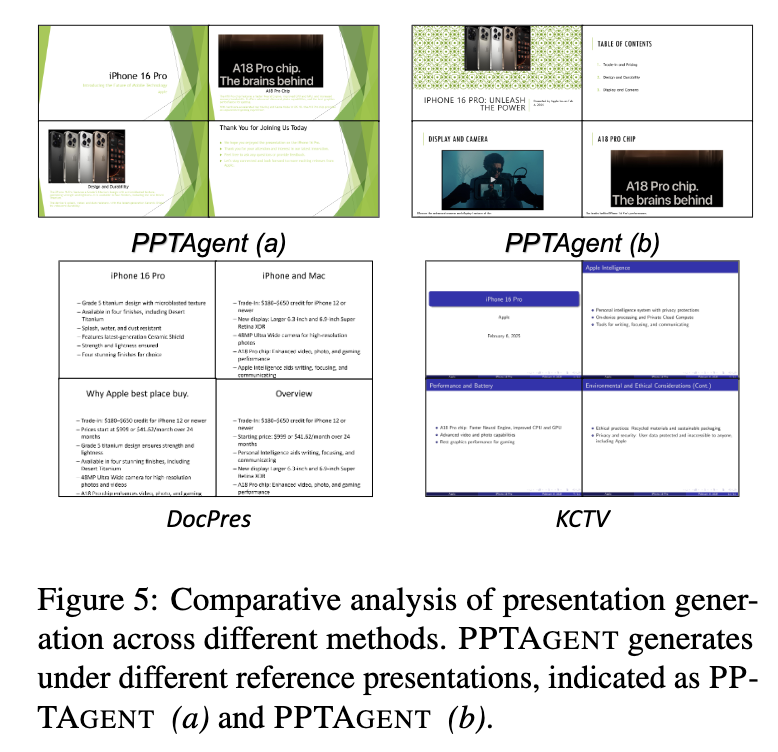
-
-
Ablation Studies
-
outline 유/무 (무: reference slide random selected)
-
structural slide 유/무
-
slide representation 방식(HTML) PPTC로 변경 (w/o codeRender)
-
content schema guidance 유/무
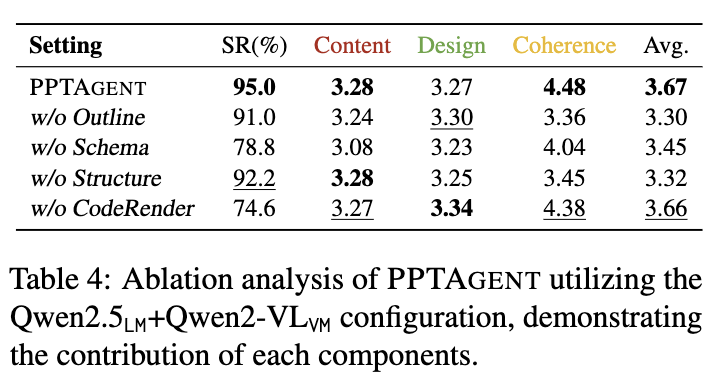
- slide representation (HTML) 방식이 SR에 매우 중요함 (95.0 vs. 74.6)
- presentation analysis 과정이
- outline/structure/schema: slide generation 에 매우 중요함 (Coherence 4.48 vs. 3.36/3.45/4.04)
-
iteration에 따른 Self-correction required 갯수
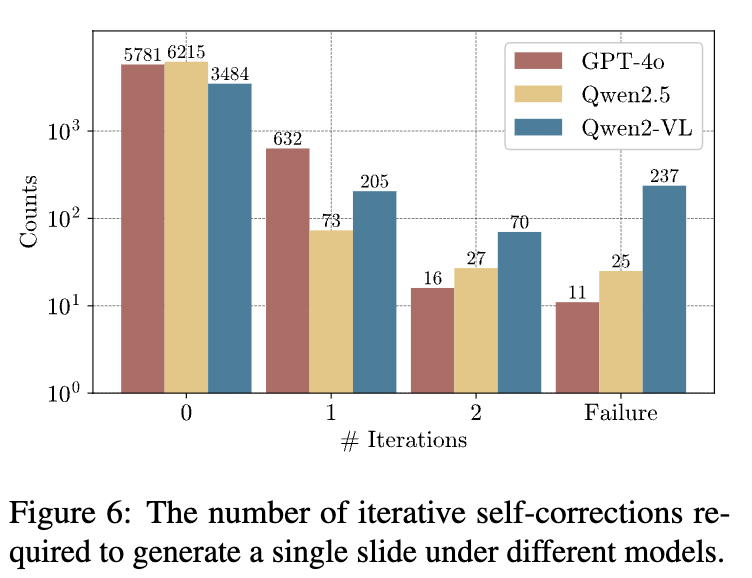
- Self-correction 유효성: GPT > Qwen2.5 > Qwen2
-
Human Preference Alignment
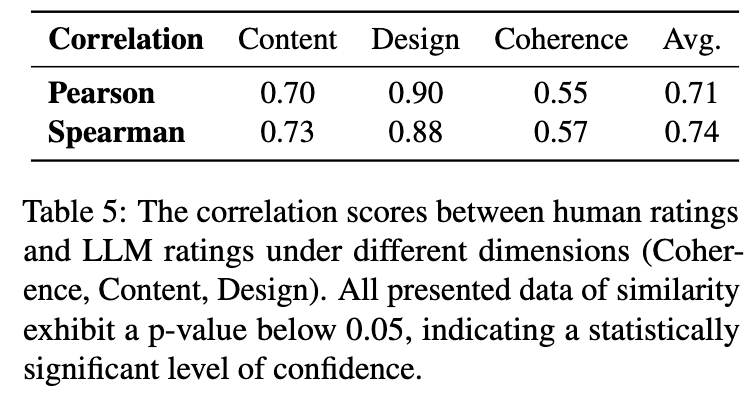
- Pearson Correlation 0.71이면 MLLM-as-a-judge와 Human preference가 양의 상관관계를 보인다고 볼수 있음
-
다른 Metric들과
PPTEVAL간의 연관성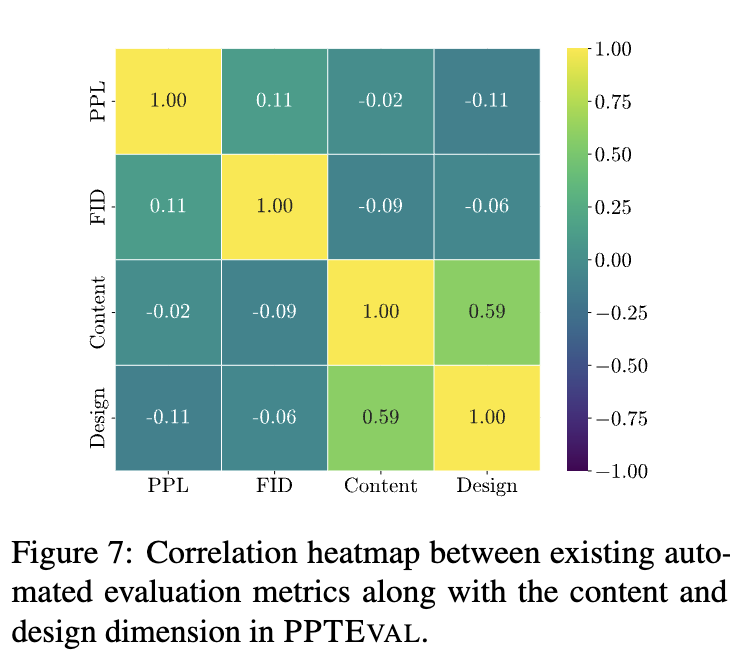
- 매우 낮고, 이는 고전 evaluation이 비효과적임을 입증
-