[DG][OD] Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator: Mine the Non-causal Factors for Object Detection in Unseen Domains
[DG][OD] Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator: Mine the Non-causal Factors for Object Detection in Unseen Domains
Abstract
-
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.02950.pdf
-
github: X
-
CVPR 2023 accepted (인용수: 5회, ‘23.12.15기준)
-
downstream task : DG for OD
1. Introduction
-
Multi-Source Domain Generalization for Object Detection
- Source와 Target domain간의 domain shift가 있는 상황을 가정
- Domain Adaptation과 다른 점
- Target domain에 대한 정보가 전혀 없다. (Unlabeled image마저도)
- Source data가 2개 이상일 수 있다. (Multi-source)
- Target Domain에 대한 정보가 전혀 없을 때, Multi-source domain에서 domain invariant한 특성을 학습하여 unknown target domain에 대해 general하게 성능이 잘 나오는 detection 모델을 구축하는것이 목적
-
문제제기 : 기존에 DAL (Domain Adversarial Learning)은 자연태생적으로 Single-View 이다.
-
Single-View : Multi-View와 대비되는 개념으로, domain의 feature를 single latent space로 mapping하는 것을 의미함
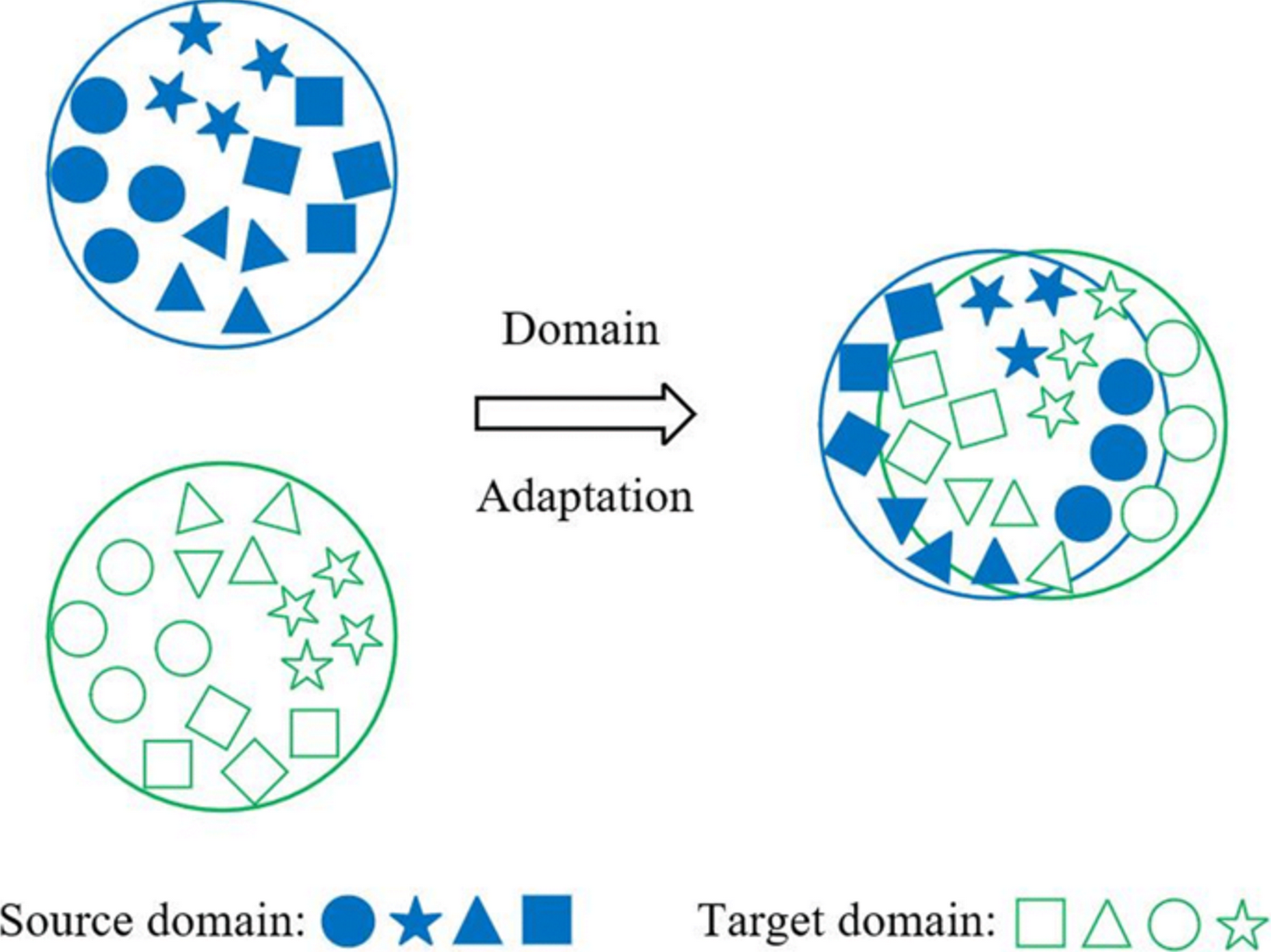
-
-
그런데 Domain Generalization에서는 특정 도메인에서 non-causal insignificant factor였던 게, 다른 도메인에서는 significant factor일 수 있다. 왜?? Data가 Multi-mode structure로 이루어졌기 때문에
-
즉, significant factor가 domain간에 align되지 못했으므로, domain-invariant한 common feature를 온전하게 학습한게 아니다.
-
Proof of Concept
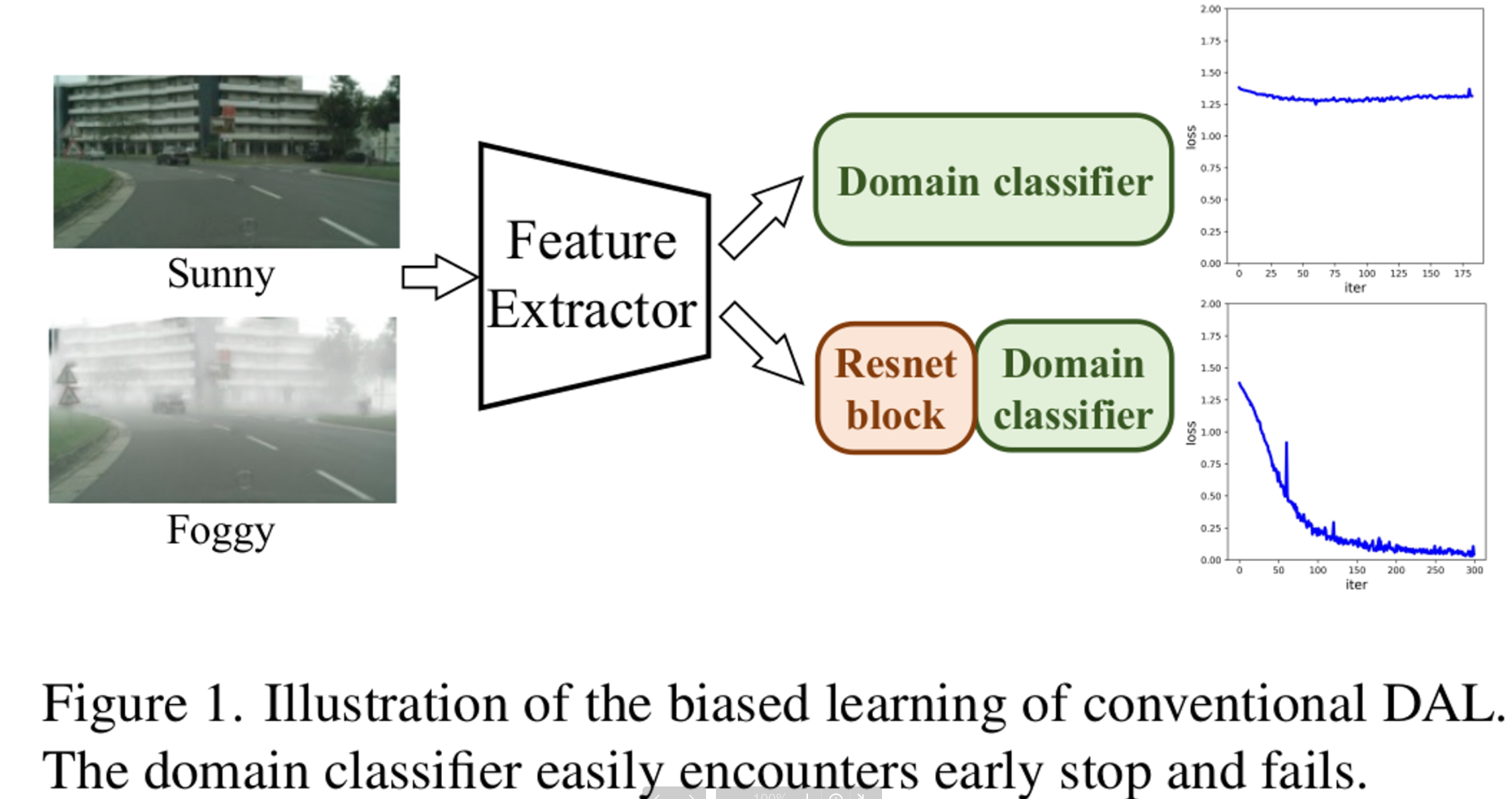
- 기존에 DAL (Domain Adversarial Learning)중 하나인 DANN으로 실험 진행
- DAL로 classifier가 수렴한 뒤, Feature Extractor를 freeze시키고, random init.된 Resnet block를 classifer head 앞단에 붙인 뒤 추가로 DAL로 학습 수행
- 그러자 loss가 감소함. (Loss 감소 == domain alignment할 수 있는 feature가 남아있었다)
- 즉, Resnet Block을 추가한 view (embedding space)에서는 기존에 view 에서 alignment하지 못한 domain specific한 feature를 충분히 정화시키지 못했음. → Multi-View가 필요함!
-
-
해결 방안 :
-
Causality
관점으로 해석해보자!
- Cityscapes vs. Foggy Cityscapes에서 non-causal한 feature는?
- Weather
- Domain Generalization 관점에서 non-causal한 feature는?
- Weather
- Camera angle
- Light color
- Background
- Causal한 feature는?
- objects (ex. car, pedestrian, etc)
- Domain common하지만 non-causal한 feature들을 효율적으로 없애야 Domain Generalized Object Detection이다!
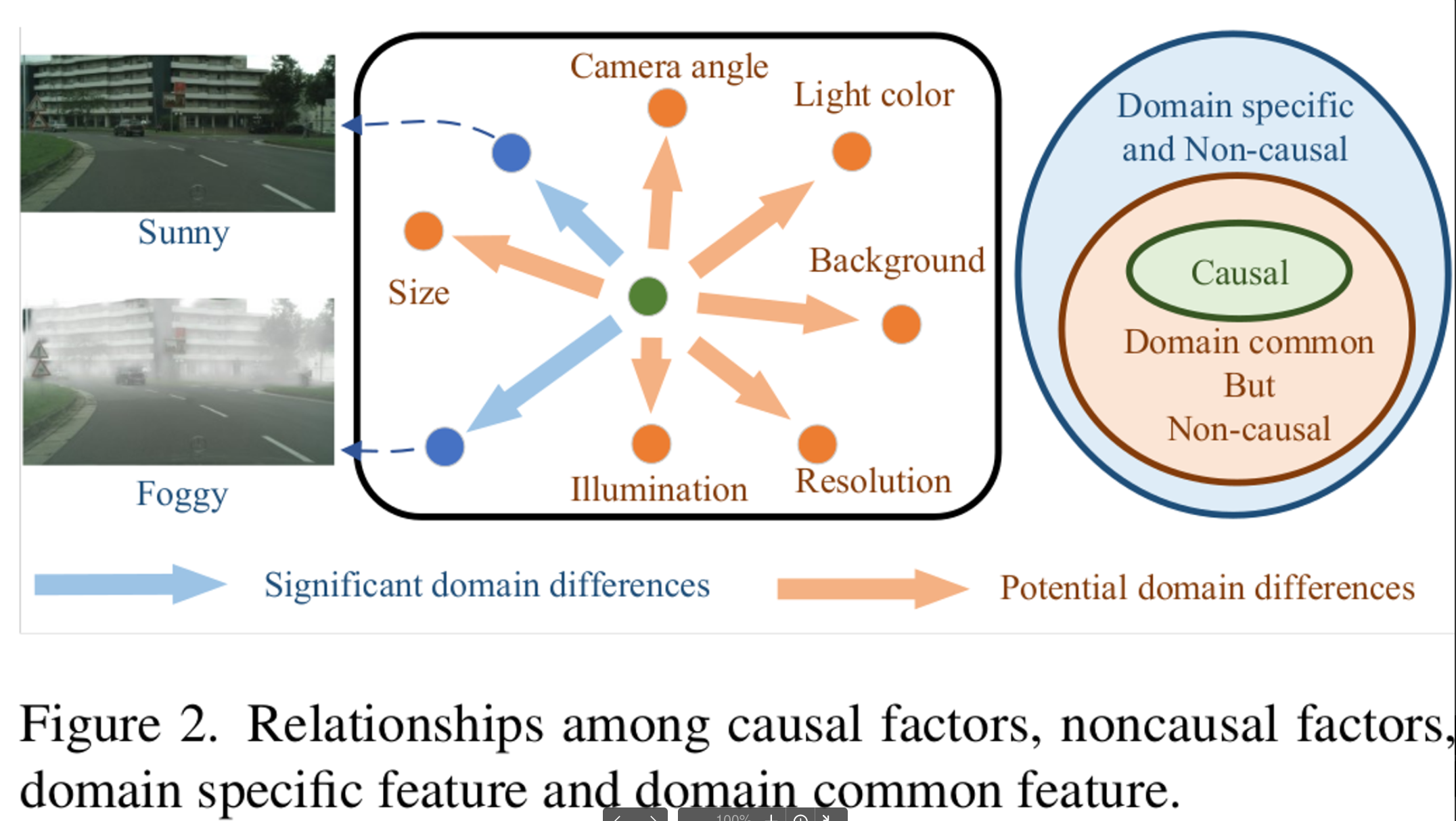
- Cityscapes vs. Foggy Cityscapes에서 non-causal한 feature는?
-
Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator : Multi-view Domain Classifier를 통해 feature들을 multiple latent spaces (views)로 mapping하게 학습함 → Multi-view로 살펴본 후에도 non-causal인 factor들은 제거되고, domain-invariant feature들만 정화됨
-
Toy Example
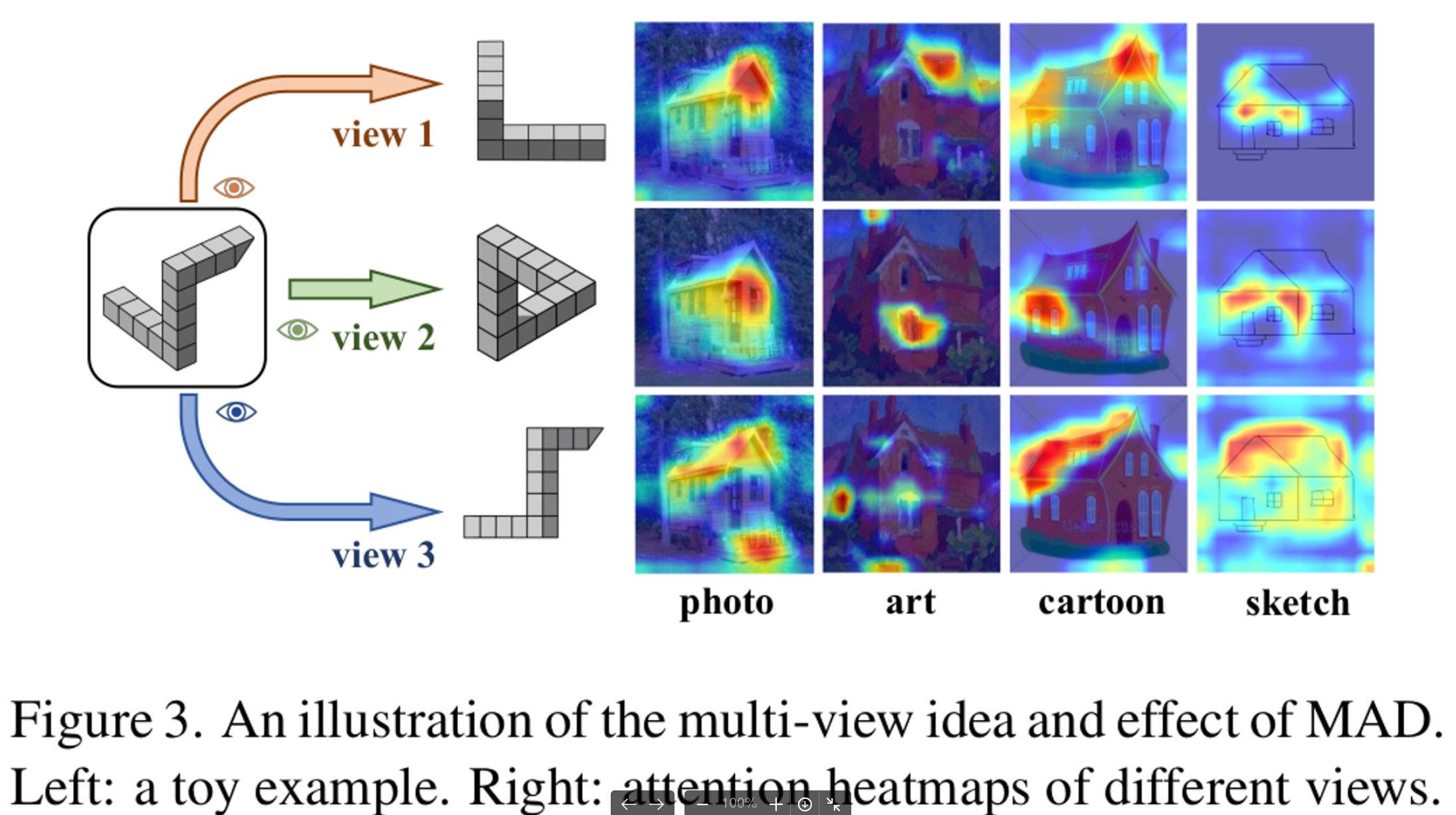
- Auto-encoder 여러개로 feature들을 여러 latent space로 mapping하게 한 후에, MVDC (multi-view-domain-classifer)들로 각각의 feature들이 어느 domain에서 왔는지 맞춰보게 함 (즉, Multi-View Adversarial Learning을 수행해봄
-
-
Spurious Correlations Generator (SCG) : 주파수 domain으로 이미지를 변환하여, domain-variant한 극소, 극대 주파수를 random 하게 augmentation수행하여 domain diversity를 향상
→ reference 논문 : https://alcherainc.atlassian.net/browse/MLR-42 (Frequency Space Domain Randomization)
-
-
Contributions
- 기존 DAL의 한계점을 지적함
- Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator를 제안함 → implicit한 non-causal factor들을 효율적으로 제거하는 기법
- standard dataset에서 효율성을 입증함
2. Related Work
-
Domain Adaptive Object Detection
-
Adversarial based
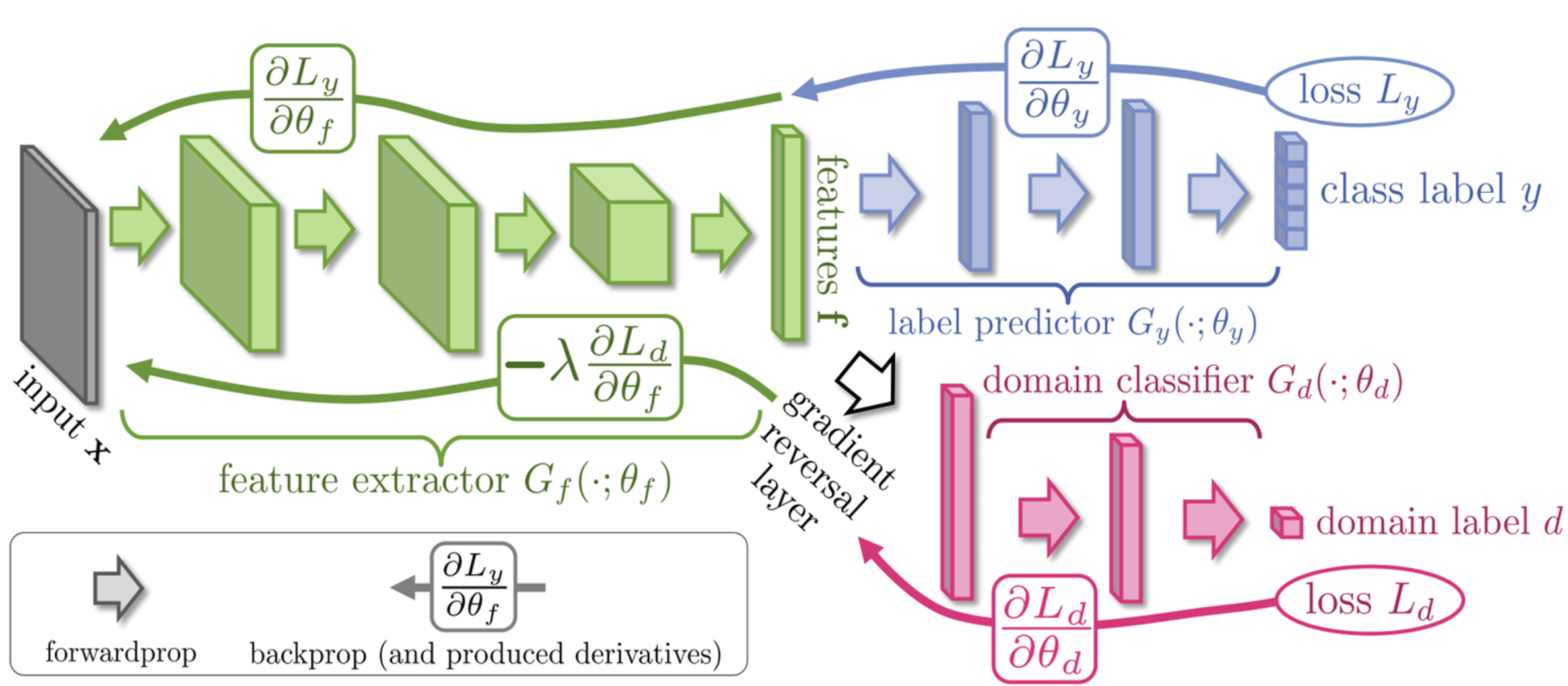
- Adversarial training기법을 적용하여 별도의 binary discriminator (class: target, source)와 generator (backbone)간의 minmax game을 풀며 target과 source feature간의 alignment를 진행하는 기법
-
Reconstruction based
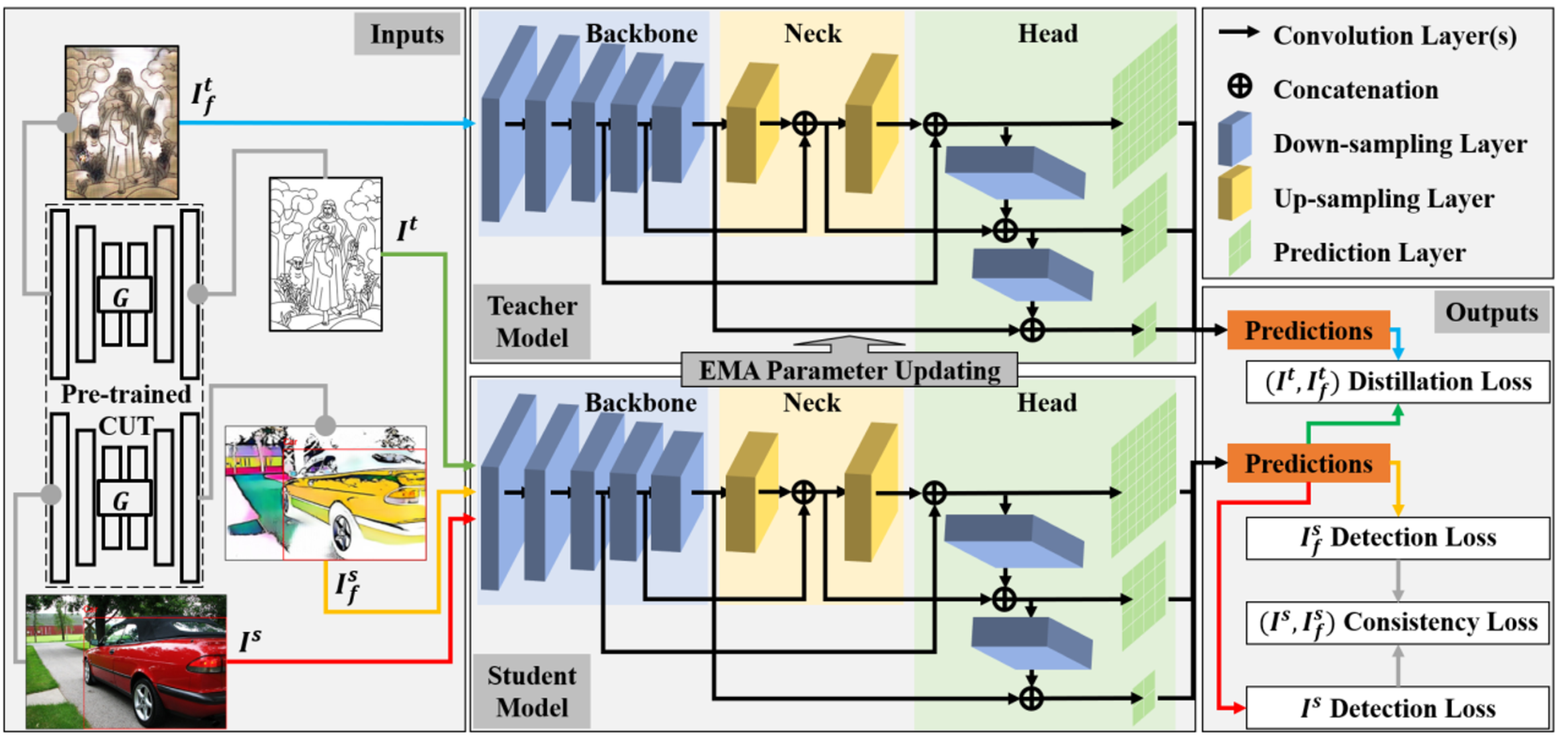
- Image to Image Transfer를 통해 Target-like source image 혹은 Source-like target image를 두고 학습하는 기법
-
(Self-training?)
-
-
Domain Generalization
- Domain Augmentation : Source domain을 augmentation시키는 방법론
- FSDR: https://alcherainc.atlassian.net/browse/MLR-42
- Fourier based: https://alcherainc.atlassian.net/browse/MLR-47
- Representation Learning : DAL을 활용한 방법론
- Meta-Learning : Optimization meta-learning 방법론: https://alcherainc.atlassian.net/jira/software/c/projects/MLR/boards/158?modal=detail&selectedIssue=MLR-43
- Domain Augmentation : Source domain을 augmentation시키는 방법론
-
Causal Mechanism
- Causal Mechanisms : 인과관계를 통계적으로 접근하려는 시도는 신뢰 할 수 없다
- Causal correlation vs. non-causal correlation이 존재하기 때문
- ex. 노란 이, 흡연, 폐암
- 노란 이 vs. 폐암 → non-causal correlation
- 흡연 vs. 폐암 → causal correlation
- ex. 노란 이, 흡연, 폐암
- Causal correlation vs. non-causal correlation이 존재하기 때문
- Causal Mechanisms : 인과관계를 통계적으로 접근하려는 시도는 신뢰 할 수 없다
3. Approach
3.1 MAD Overview
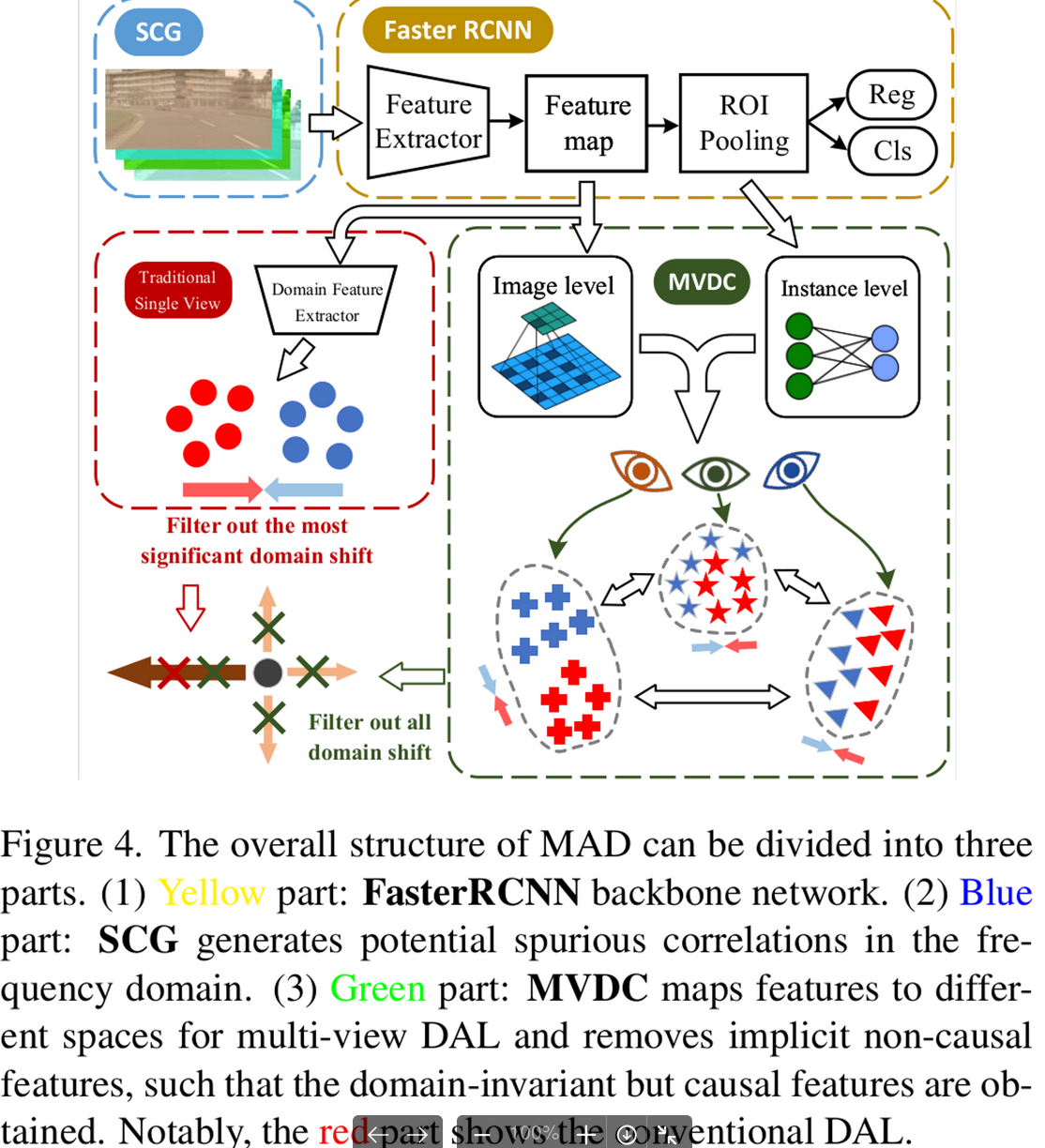
-
SCG (Spurious Correlations Generator) : Source domain Image에서 non-causal한 영역을 gaussian random noise로 대체하여 diversity를 늘리는 module (Non-trainable)
-
MVDC (Multi-View Domain Classifier) : Non-causal factor를 제거하여 pure한 domain-invariant feature들만 학습하기 위해 multi-view (latent vectors) domain discriminator를 도입 (Image-level, Instance-level)
3.2 Spurious Correlation Generator
- Discrete Cosine Transform을 통해 input image $x \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times W}$에 대한 frequency spectrun $\mathbb{F}(x)$ 구함
- Band pass filter를 통해 extremely high & extremely low frequency를 제거함
$ M(r)=e^{-\frac{u^2+v^2}{2R_H^2}}-e^{-\frac{u^2+v^2}{2R_L^2}} $
- $u,v$: position of spectrum
- $r(R_H, R_L)$: cut-off frequency of low and high frequency
- Randomize non-causal frequencies
- Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform을 통해 augmented image $\hat{x}$를 구함
$ \hat{x}=\mathbb{F}’(R_G(M(r) \times \mathbb{F}(x))+(1-M(r))\times \mathbb{F}(x)) $
3.3 Multi-view Domain Classifier
-
DAL vs. Ours
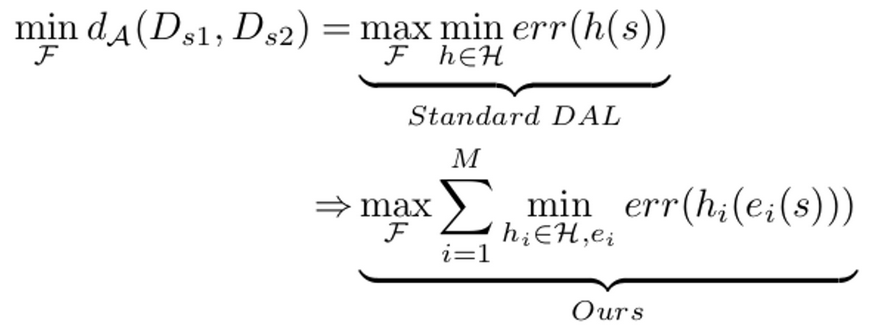
- $h$ : $H$에 속한 1개의 domain classifer
- $e_i$: i번째 encoder로서, feature를 latent space에 mapping하는 함수 역할
- $h$는 각각의 domain 조합간에 significant domain-private feature를 제거하게 되고, 이를 $_MC_2$번 반복하여 제거함으로써, feature extractor $F$가 domain-invariant feature만 학습하도록 함
-
Classifier Sturcture
- auto-encoder(encoder-decoder구조)와 classifer로 구성
- encoder : Feature를 특정 latent space로 mapping하는 역할
- decoder : Feature의 semantic content를 유지하기 위해 복원하는 역할
- Image-level vs. Instance-level
- Image-level classifer는 global context (색깔, 조도(illumination), 배경 texture, etc) 등의 non-causal factor를 제거 하기 때문에 convolution layer를 활용함 → translation invariance 한 특성을 가정하는 듯
- Instance-level은 각 instance마다의 camera angle 과 같이 instance의 섬세한 non-causal factor를 제거 하기 위해 Fully-Connetect Layer를 활용 → inductive bias를 가정하지 않음
- auto-encoder(encoder-decoder구조)와 classifer로 구성
-
Loss Function
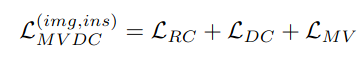
-
Reconstruction Loss : mapping된 latent vector가 input feature의 semantic 정보를 유지고 있도록 강제시키기 위해 reconsturction loss를 줌
$ L_{RC}=\frac{1}{M}\sum_{m=1}^MMSE(s,g_m(e_m(s))) $
- $M$: multi-view domain classifier의 갯수
- $g_m$: m번째 decoder
- $e_m$: m번째 encoder
- $s$: input feature
-
Adversarial Loss : domain specific factor를 align시켜 제거하도록 encoder와 classifer가 adversarial하게 학습
$ L_{DC}=-\frac{1}{M}\sum_{m=1}^M\sum_{k=1}^Ky_k \times log(p(D_m(e_m(s_k)))) $
- $s_k$: k번째 domain의 feature (K-domain, M-branches)
-
view-differenct loss : auto-encoder들이 mapping하는 latent vector들이 충분히 거리가 떨어져 있도록 밀어내도록 제약을 주는 역할 → insignificant non-causal factor들을 significant하도록 disentanlge(제가 사용한 용어) 시키는 역할
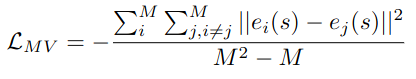
-
cross-level consistency loss : instance level prediction($p_{j,n}$)과 image-level prediction ($p_i^{(u,v)}$)간의 consistent해지도록 average값의 차이를 loss로 둠
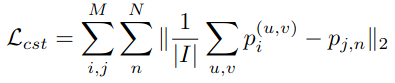
- N: 전체 instance의 갯수
- I: pixel의 갯수
-
4. Experiments
-
Datasets
- Cityscapes, Foggy Cityscapes, Rainy Cityscapes
- SIM10k : Synthetic rendered image
- KITTI
- BDD 100K
- Pascal VOC
→ {S, C, F, R, B, K, V}
-
Multi-Source DGOD Results
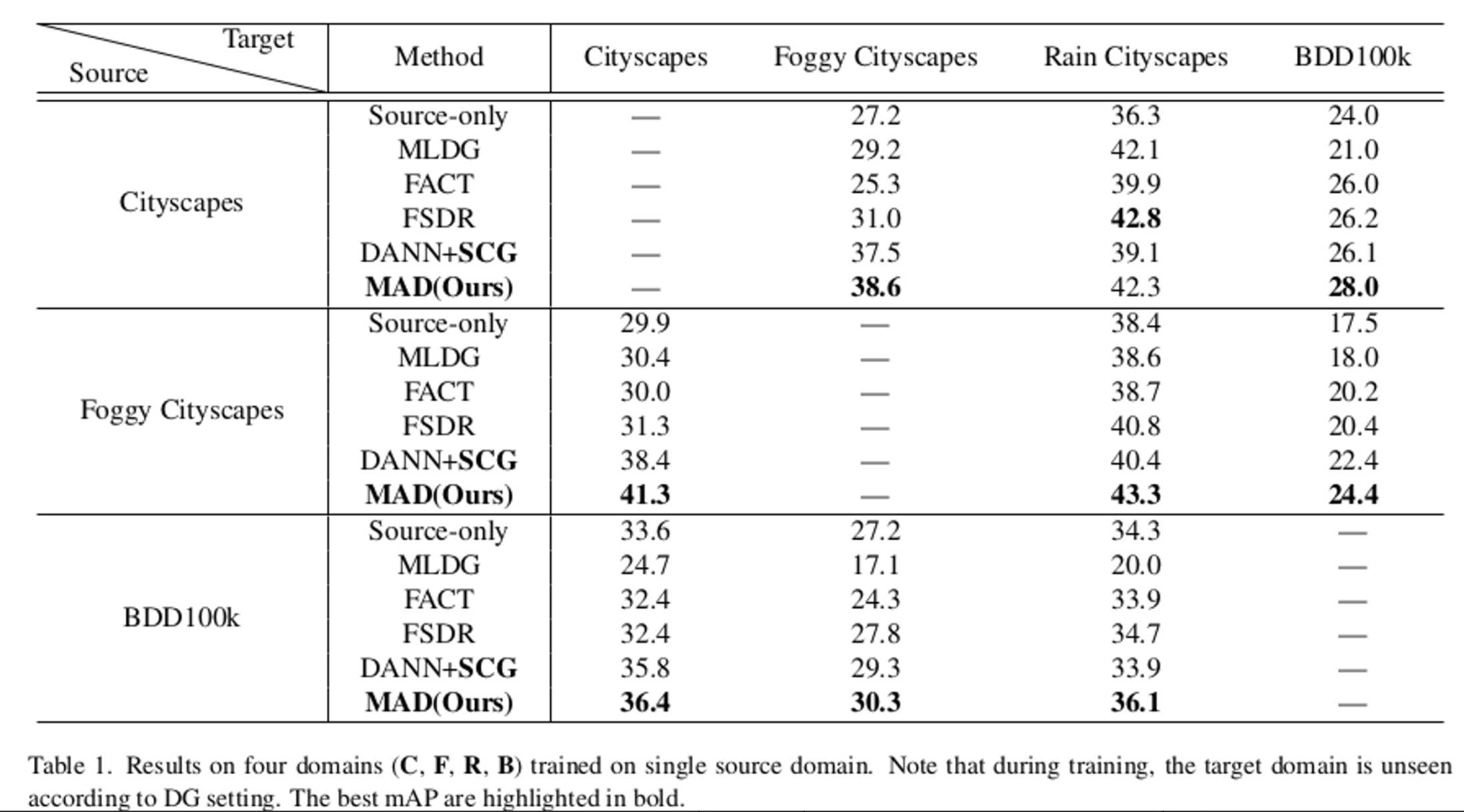
- Implementation Details
- Multi Source {C,F,R,B} 일 경우
- Training set : 4개 중 3개 선택
- Validation set : 나머지 1개 선택
- Baseline : Faster-RCNN (VGG16) with SGD
- Multi Source {C,F,R,B} 일 경우
- Implementation Details
-
vs. Multi/Single Source DGOD, DAOD (Domain Adaptive OD)
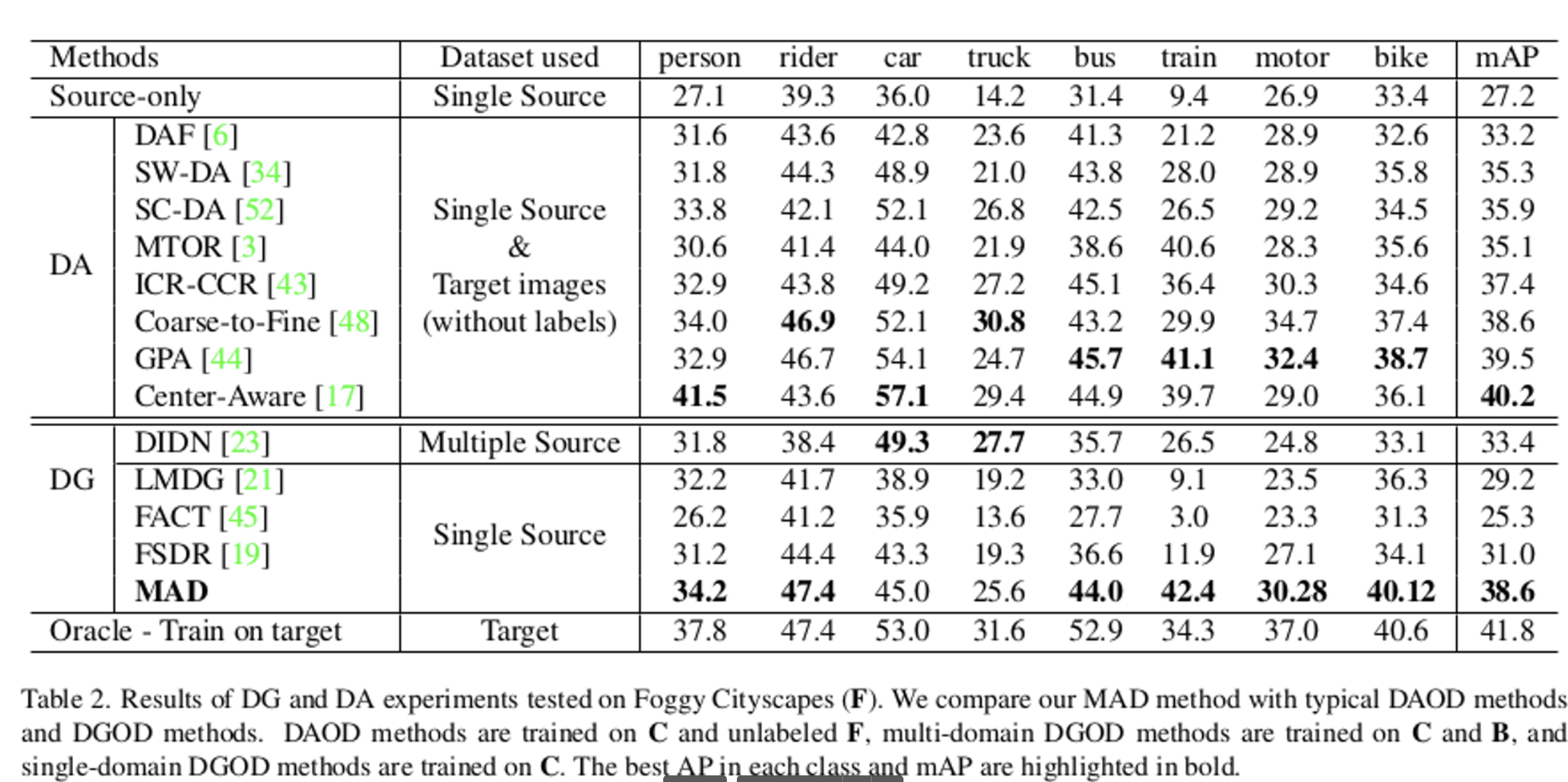
-
Multi-view DGOD with 7 Datasets
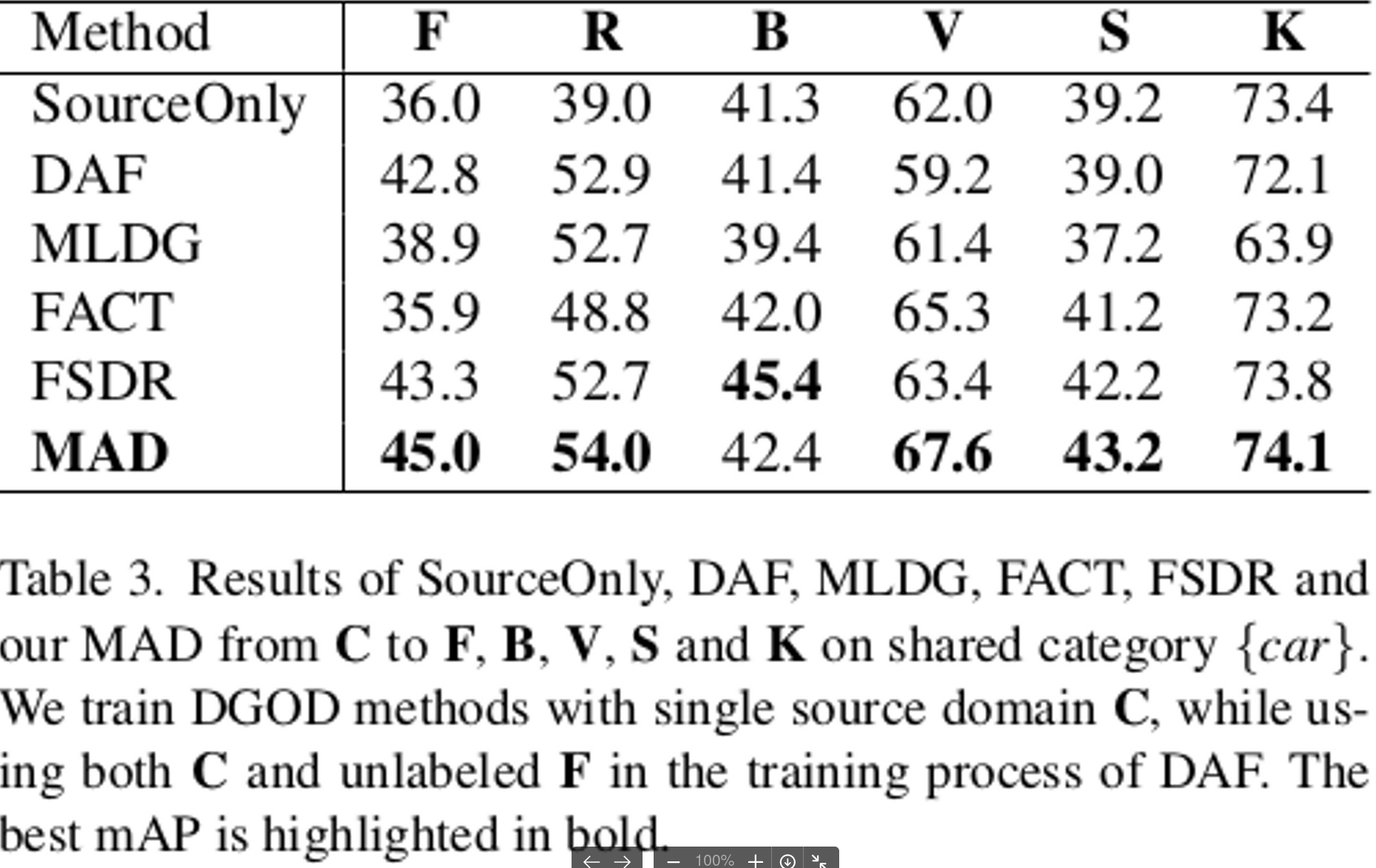
- 공통 되는 class인 ‘car’에서만 실험을 진행
-
T-SNE
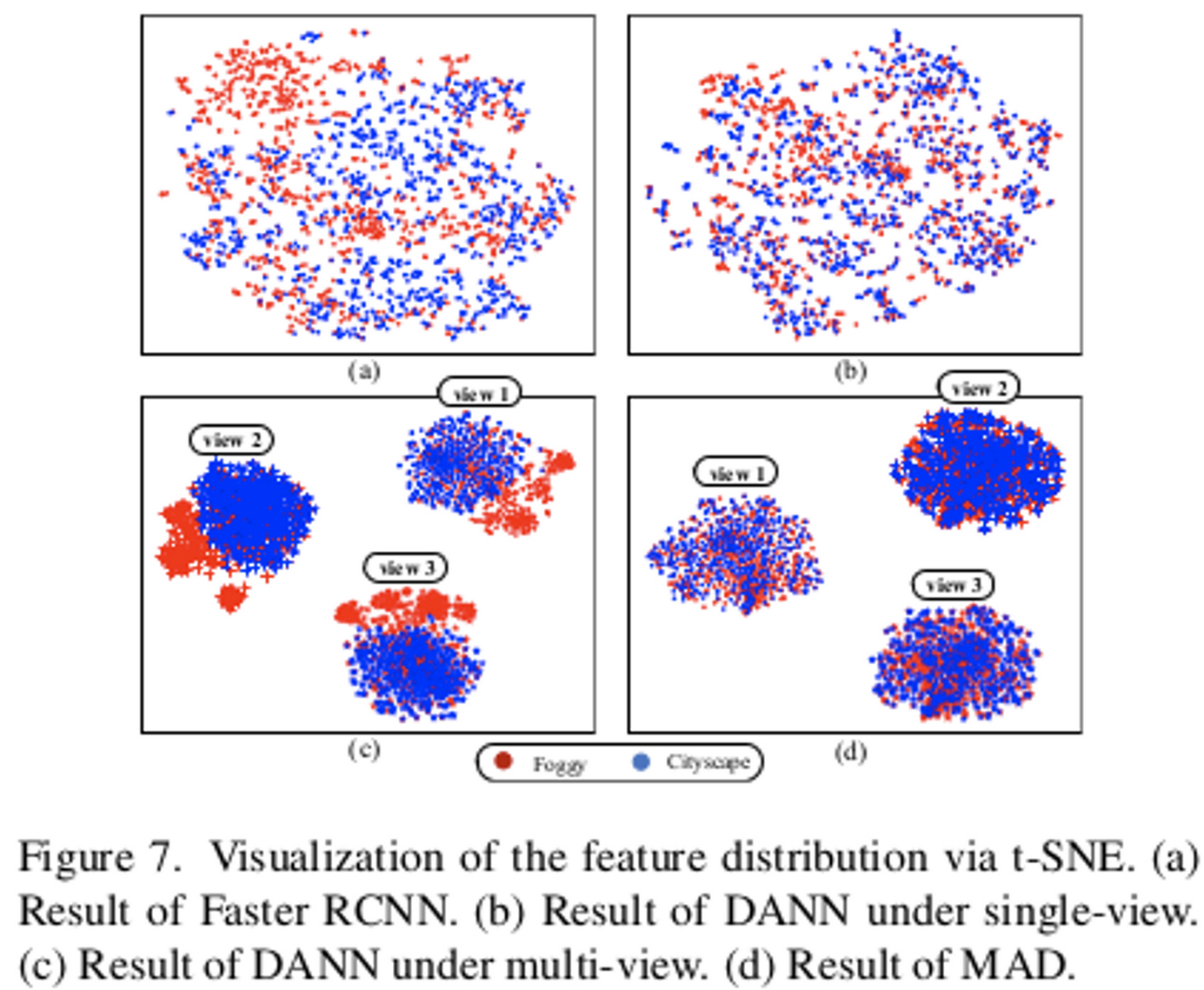
- C2F (Cityscapes to Foggy-Cityscapes)의 car class 분포
- (a) DAL적용 전 Faster-RCNN의 분포. C,F가 align되어 있지 않음 (안좋음)
- (b) DAL적영 후 (DANN) Faster-RCNN의 분포. C,F가 align되어 있음 (좋음)
- (c) Multi-view Discriminator를 적용한 DANN의 분포. C,F가 align되어 있지 않음 (안좋음) (d) Multi-view Discriminator를 적용한 DANN의 분포. C,F가 align되어 있음 (좋음)
-
MAD를 DGC (Domain Generlization for Classification)에 적용한 결과
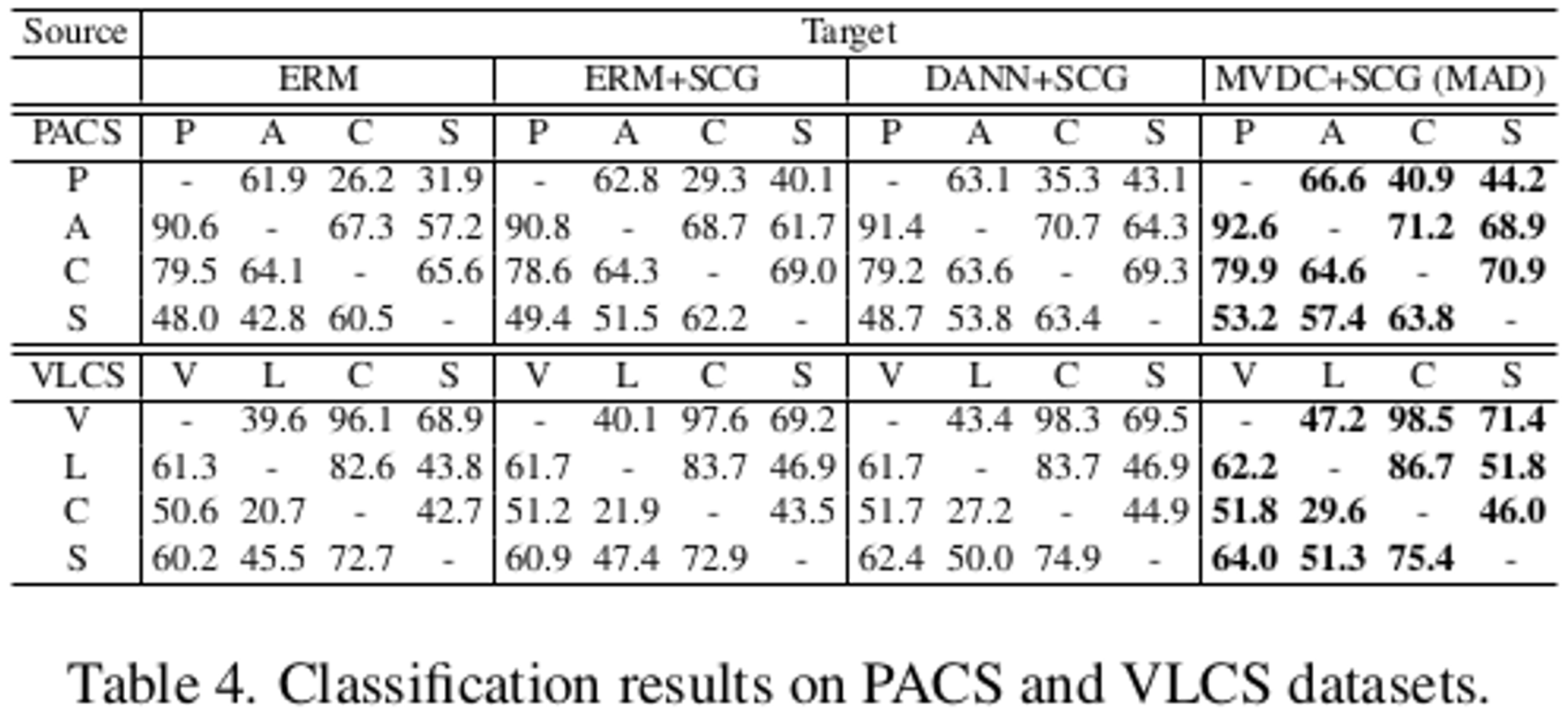
- Dataset : PACS, VLCS
- MAD기법은 기존 DG기법과 Orthogonal하므로, Classification DG Task에도 적용 가능해 해보니, 좋았다.
-
Ablation Study
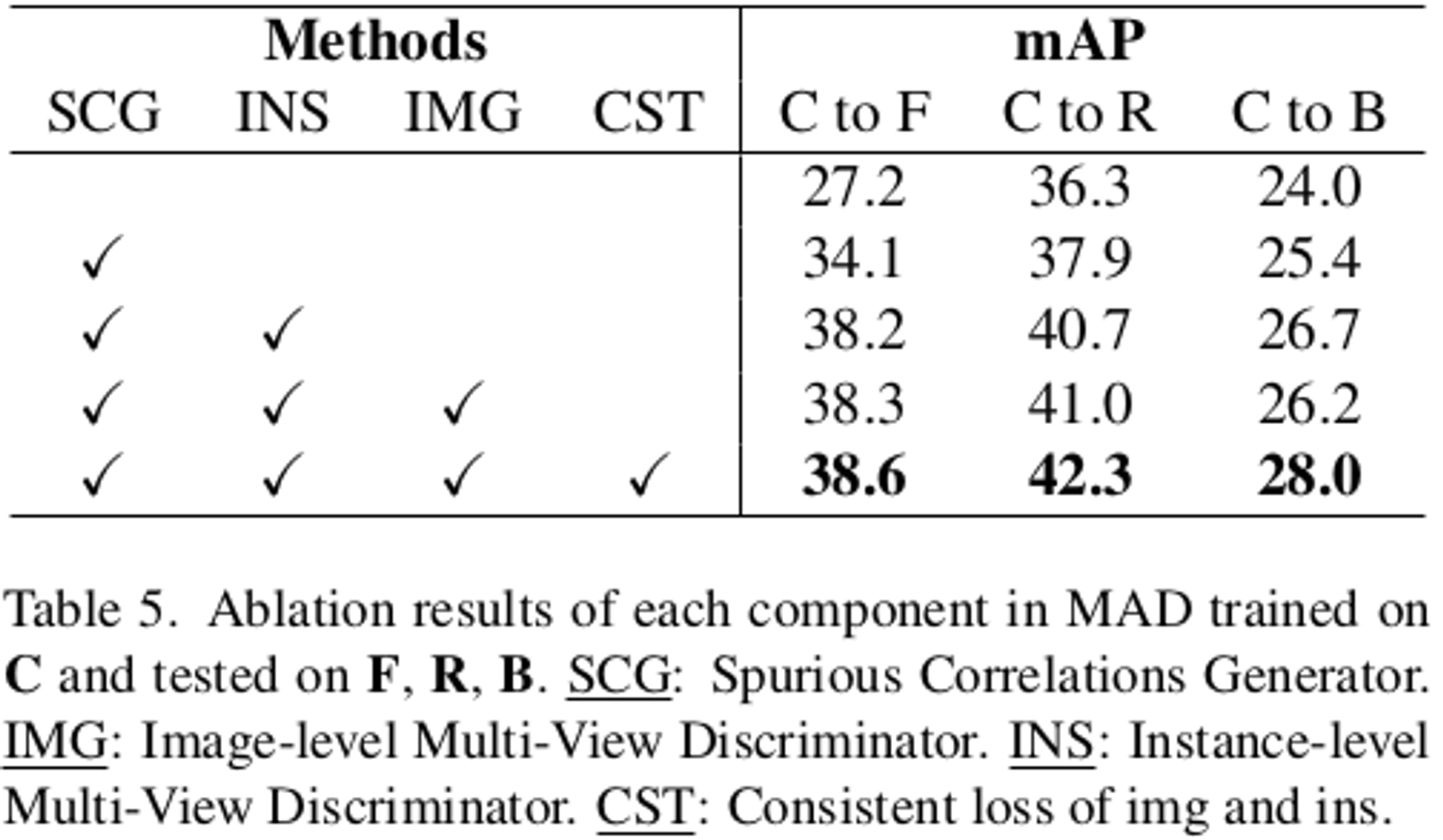
-
Hyperparameter 분석
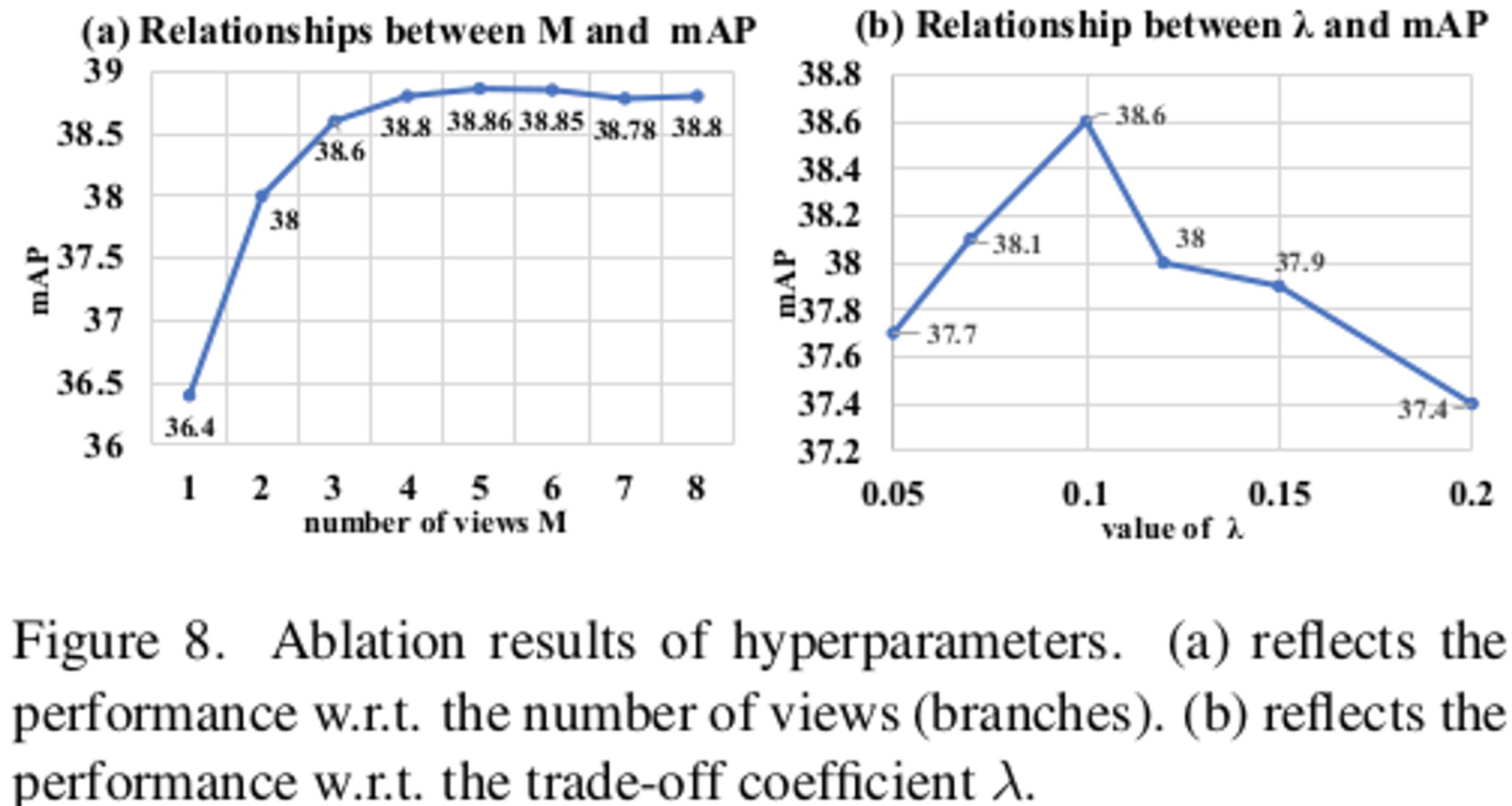
- M, $\lambda$
5. Conclusion
- DAL의 분제를 point했다
- Multi-view Adversarial Discriminator를 제안했다. → non-causal factors in latent space를 효율적으로 제거하고, domain-invariant causal factor만 학습하도록 유도했다.
- SCG와 함께 source domain을 diversify했다.
- OD benchmark에서 좋은 성능을 거두었다.