[L][LG] LayoutNUWA: Revealing The Hidden Layout Expertise of Large Language Models
[L][LG] LayoutNUWA: Revealing The Hidden Layout Expertise of Large Language Models
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.09506
- github: https://github.com/ProjectNUWA/LayoutNUWA
- ICLR 2024 accepted (인용수: 5회, ‘24-05-13 기준)
- downstream task: Layout Generation by LLM
1. Motivation
- 기존 연구들은 Graphic Layout Generation task를 numerical optimization task로만 바라봄으로써, layout의 relationship등 semantic information을 간과하고 있음
- 숨겨진 전문가 (LLM)를 이용하여 layout을 생성함으로써 이를 극복해보면 어떨까?
2. Contribution
- LLM을 활용하여 Layout generation task를 code generation task로 바라보는 첫 모델 LayoutNUWA를 제안함
- Code Instruction Tuning을 제안함으로써, 모델이 layout의 semantic information 이해도를 향상시키고, 정교한 code 생성이 가능해짐
- Multiple bencmark에서 SOTA를 찍음
3. LayoutNUWA
-
Problem Formulation
-
Definition: $S=\s_{i=1}^N$의 well-organized Layout을 생성하는 임무
-
N: layout에 있는 element의 갯수
-
$s_i=(c_i, x_i, y_i, w_i, h_i)$
- class index, center points, scales
-
-
Training & Inference: Conditional Generation task
-
M element가 masking된 상황에서 전체 layout $s_i$를 prediction
\[S=f_{\theta}(S_{\\M})\] -
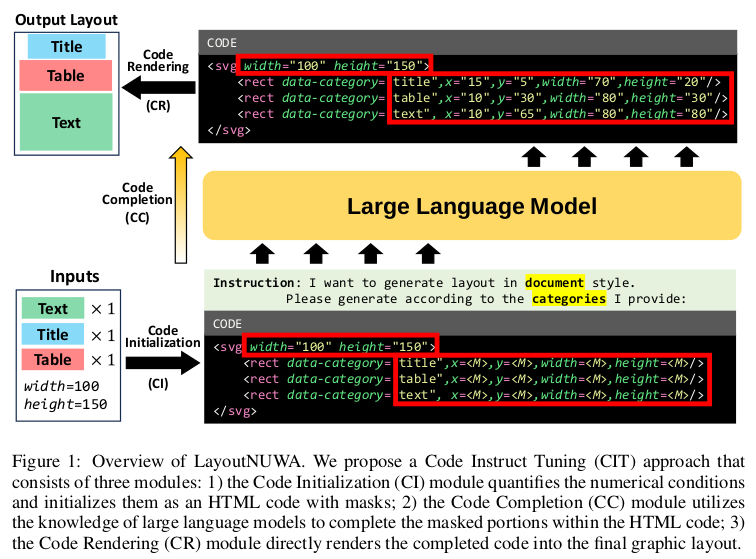
비단 numeric value를 예측하는데서 벗어나, semantic information을 학습하게 하고자, Input & Output을 Code langauge관점으로 task를 정의함
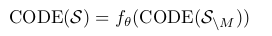
-
장점 3가지
- Semantic Insight : code language를 활용함으로 서로 다른 component간의 semantic relation을 catch하기 쉬워짐 (?)
- LLM Utilization : code language로 변환하여 LLM의 자연어 이해능력으로 semantic 정보를 이해하게됨
- Model Scalability: code language는 numerical value예측보다 풍부한 표현력이 있으므로, 더 많은 attribute를 사용하더라도 scale-up할 수 있게됨
-
-
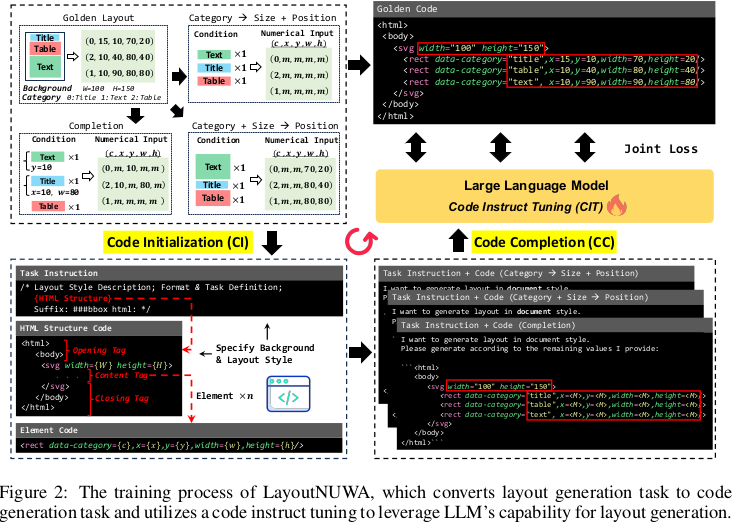
3.1 Code Instruction Tuning
- 세 가지 module로 CIT를 구성
- Code Initialization : Layout을 dynamic template를 사용한 masked code language 로 변환시켜주는 모듈
- Code Completion: Masked Code를 LLM 입력으로 주어 comple code를 생성하는 모듈
- Code Rendering: Code를 rendering하여 graphic layout으로 변환시켜주는 모듈
1. Code Initialization
-
Element Quantization: Adaptive Quantization method으로 quantify 수행 (?)
- 기존 연구와 다르게 절대 좌표계를(coodinate) 활용
-
Template Construction: HTML기반으로 template를 초기화 수행
-
Tag로 각 element가 표현됨
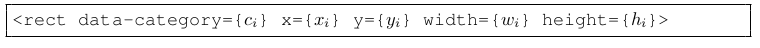
-
모든 element를 통합하고, unified layout structure를 구현하여 layout의 경계를 정의함
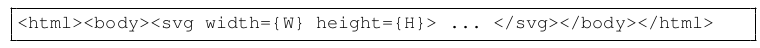
- H, W: layout의 크기
-
Domain & Task에 따라 더 잘 학습하기 위해
, 를 instruction에 추가하여 prompt를 생성함 
- Domain example: mobile UI
- Task example: remaining values
-
2. Code Completion
- 기존 연구 (LayoutDM, LayoutDiffusion) 에서 사용한 LLM token vocabulary를 사용
- AutoRegressive Manner는 순서가 정해진 반면, Layout은 순서가 없음 $\to$ Random하게 K번 permute하여 평균값을 loss에 활용
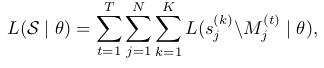
- $s_j$: j번째 layout의 element
- T: task numbers
- K: permutation time
3. Code Rendering
- 기존 연구들 (LayoutTransformer, LayoutDM, LayoutDiffusion)에서 사용한 rendering을 사용
- 단, 상대좌표로 정의된 기존 연구 결과 값에 비해, 절대좌표로 예측함으로써 즉각적 rendering이 가능하며 잠재적인 output issue를 해결함
4. Experiments
- Datasets
- RiCo : 25 element categories / 66K+ UI layout
- PubLaynet : 5 element categories / 360K+ layout
- Magazine : 6 element categories / 4K annotated layouts
- Evaluation Metrics
- FID
- mIoU
- Align.
- OverLap
- Model
- LLM: LLaMA2, CodeLLaMA
-
Quantitative Result
-
Magazine Dataset
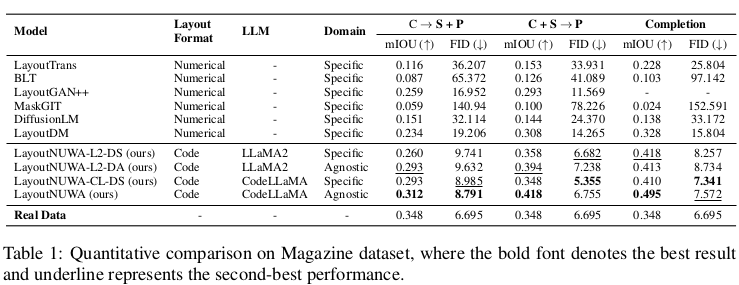
-
RiCO & PubLayNet
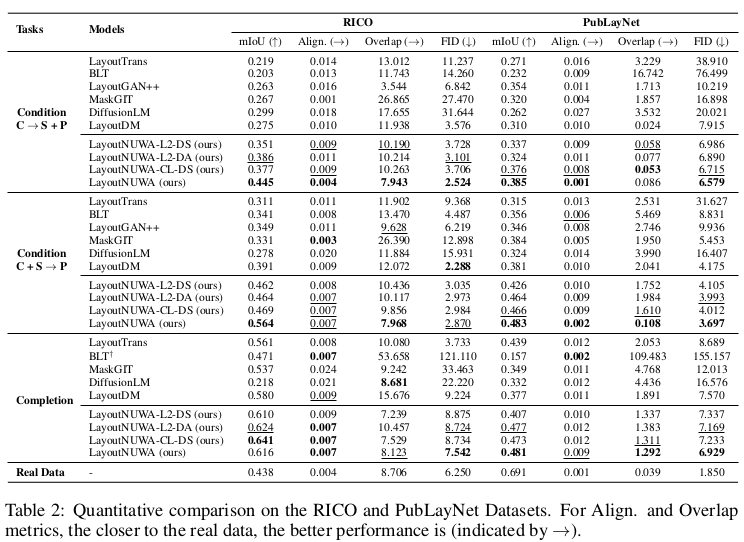
-
-
Qualitative Result (PubLayNet)

-
Task에 따른 정량적 분석
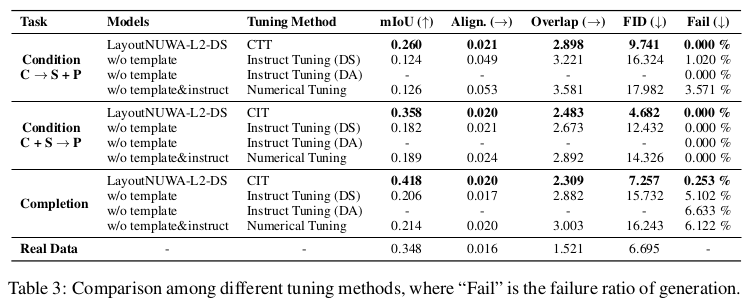
- DS: Domain Specific (데이터셋 별로 학습) $\to$ 반대는 DA (Domain Agnostic)으로, 3가지 데이터셋을 합쳐 학습이 가능함. Code generation task이기에 가능
-
LLMs와 비교
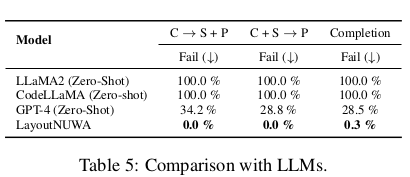
- Fail case가 줄어듦 $\to$ code기반 절대 좌표 사용