[IR] GraphFormers: GNN-nested Transformers for Representation Learning on Textual Graph
[IR] GraphFormers: GNN-nested Transformers for Representation Learning on Textual Graph
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.02605
- github: https://github.com/microsoft/GraphFormers
- NeurIPS 2021 accepted (인용수: 245회, ‘25-10-21 기준)
- downstream task: WIKI, 논문 인용 여부, Shopping 목록 link예측 task
- Motivation
-
textual graph를 이해하는 모델로 최근에 PLM (Pretrained Language Model)과 GNN (Graph Neural Network)를 cascaded하는 방식의 연구가 진행되고 있다.
-
하지만 이는 textual feature간의 독립된 모델링을 하므로 한계가 있다.
-
node간의 정보 교환이 전혀 없는 구조
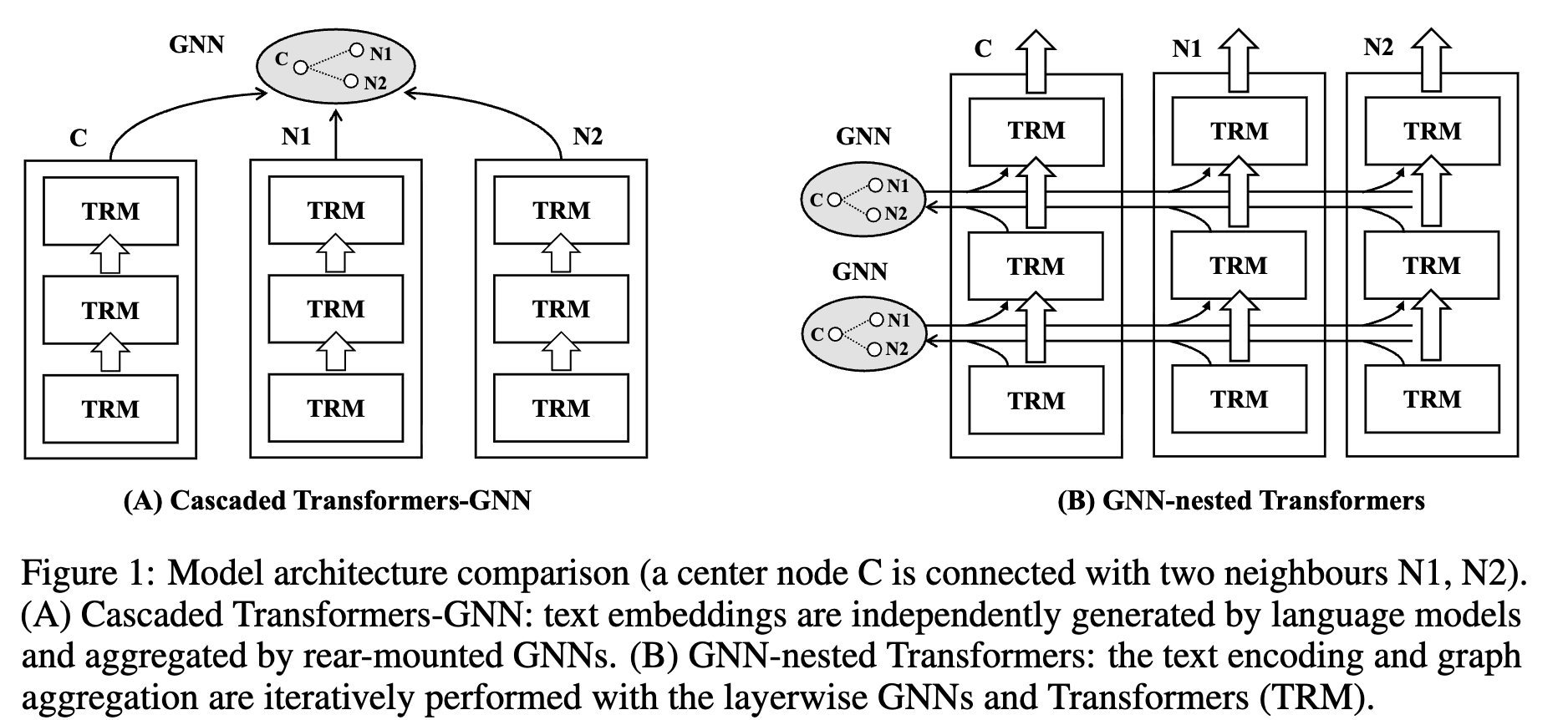
ex. “Notes on transformers” 에서 neighbor에 “tutorials on machine translation”이 있다면, 전자부품이 아닌 transformers는 AI 모델 구조임을 알수 있음.
$\to$ GNN기반으로 PLM 내부에 모델링한 component 를 nested하는 새로운 방법을 제안해보자!
-
2. Contribution
- GNN과 PLM을 fusion하기 위해 GNN component을 PLM의 중간 TRM (Transformers) alyer중간에 nested하게 넣는 GraphFormers를 제안함
- node의 text encoding된 정보간의 교환을 통해 center node embedding에 neighbor 연결 정보를 추가된 embedding을 추출할 수 있게됨
- 단순한 학습기법보다 우수한 학습기법을 제안함
- 1st iteration
- progressive learning으로 node를 초반에는 오염시킨 뒤, 학습
- 취지: center node가 neighbor에 비해 정보량이 많기에, shortcut으로만 학습될 위험이 존재하므로 이를 해결
- 2nd iteration
- unpolluted data로 학습
- 1st iteration
- 연결된 노드간의 상호 종속적인 특성으로 인해 불필요한 계산량 증가를 초래함 $\to$ 이를 해결하는 unidirectional graph attention을 제안함
- 기존재하는 neighbor node를 encoding (caching)해두어 재사용할 수 있음
- DBLP, Wiki에서 SOTA성능을 냄
3. GraphFormer
- 목표: 생성된 embedding에는 node간의 관계(relationship between the nodes)를 capture해야함
- $x_q, x_k$ 두 노드가 연결되었는가를 정확히 예측 수행해야함
3.1 GNN-nested Transformers
-
input node
- center node + neighbor nodes $\to$ sequence of tokens로 tokenize
- word embedding + positional embedding으로 구현
- center node + neighbor nodes $\to$ sequence of tokens로 tokenize
-
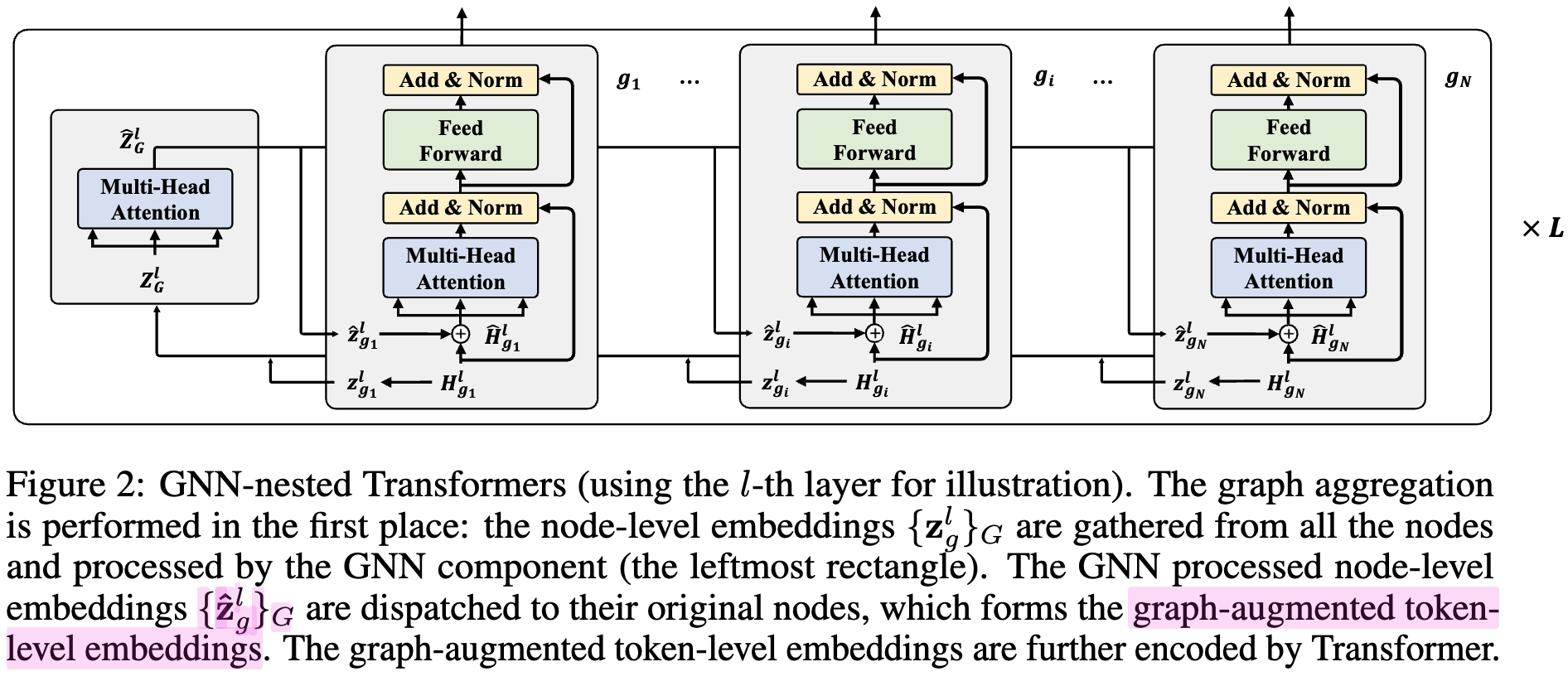
여러개의 GNN-nested Transformers multiple layers로 구성
-
Graph Aggregation in GNN
-
layerwise graph aggregation을 통해 neighborhood 정보가 개별 (center) 노드에 증강됨 (token-level embedding과 함께 concat하여 사용)
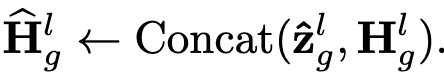
- $\hat{z_g}$: GNN-process node-level embedding
- $z_g=H_g[0]$
- $H_g$: token-level embedding
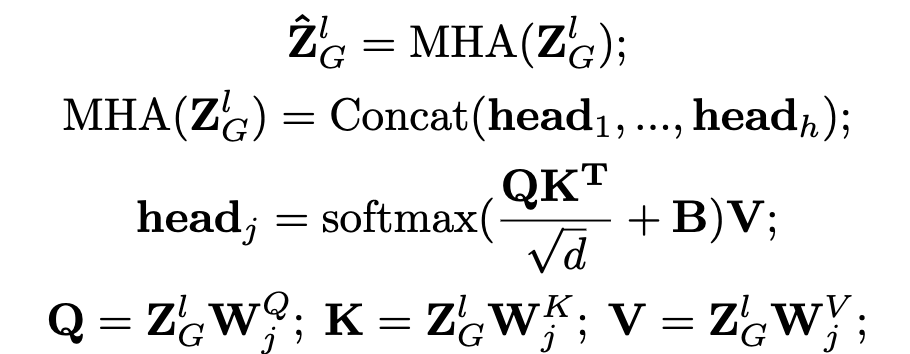
- B: learnable position bias
- center-to-center
- center-to-neighbor
- Neighbor-to-neighbor
- $\hat{z_g}$: GNN-process node-level embedding
-
-
Text Encoder in Transformer
-
TRM을 통해 token-level embedding 추출
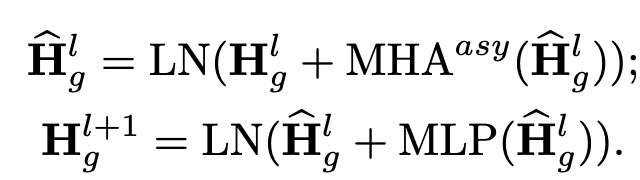
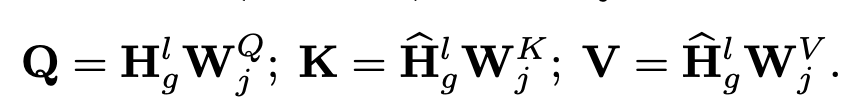
-
-
Algorithm
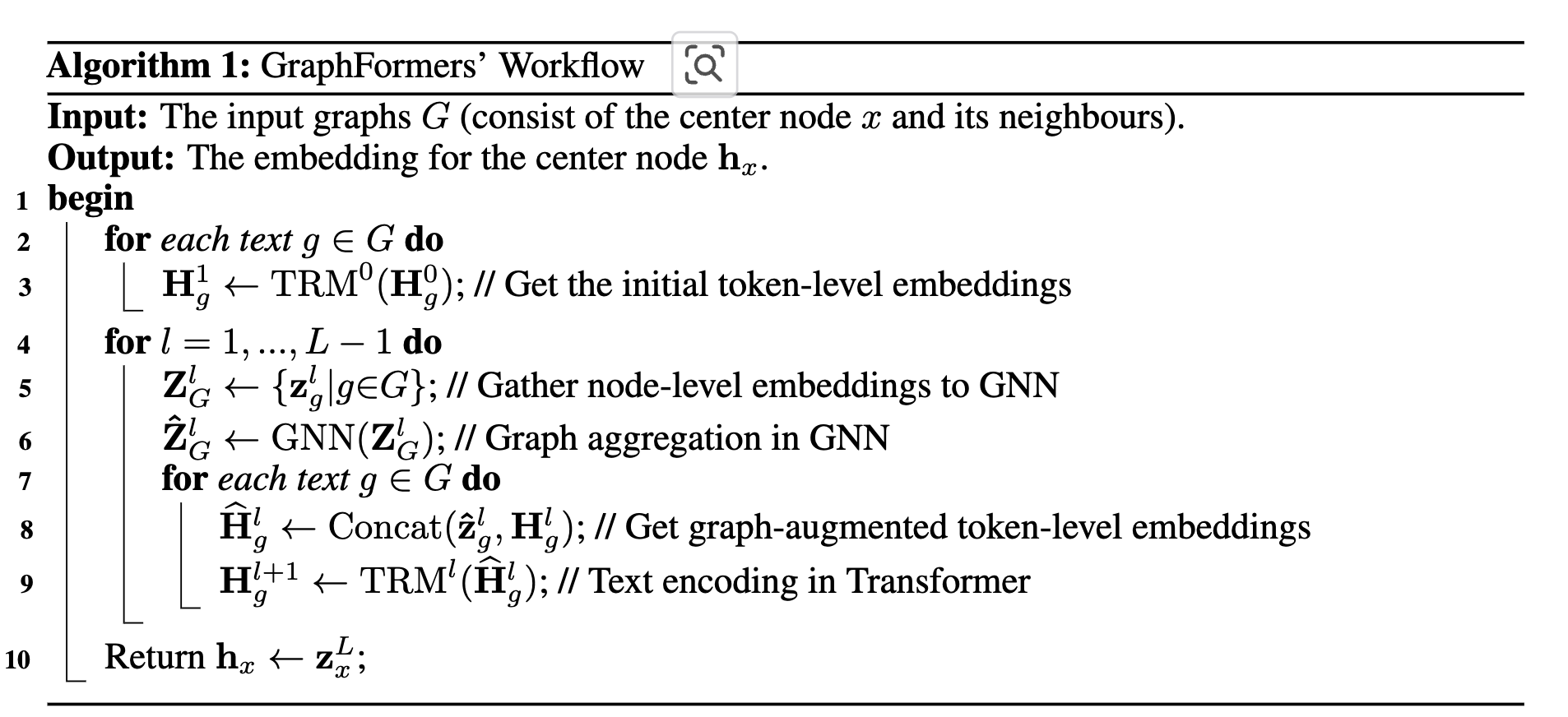
3.2 Model Simplification
-
input nodes들은 상호 종속되어 있기 때문에 매번 새롭게 계산해야하는 문제가 생김
$\to$ center node만 neighborhood node를 참조해서 encoding을 실시간으로 하고, neighborhood node는 center node와 독립적이므로 저장해보자!
-
unidirectional graph attention 적용!
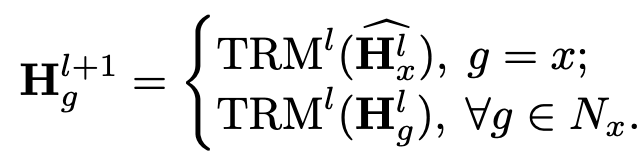
-
3.3 Model Training: Two-Stage Progressive Learning
-
학습 목적: link prediction
-
loss
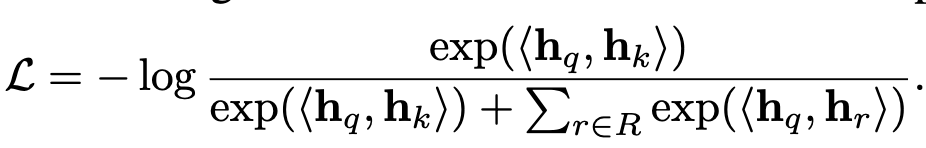
- $h_q$: query의 node embedding
- $h_k$: k개의 positive node embedding
- $h_r$: in-batch negative node sample’s embedding
-
Two-stage Training
-
naive하게 학습하면 neighborhood node와 center node간의 정보격차가 심해 center node만 가지고 shortcut 학습하게 됨
-
1st stage학습시 center node를 polluted시켜 neighborhood node를 기반으로 link를 예측하도록 함
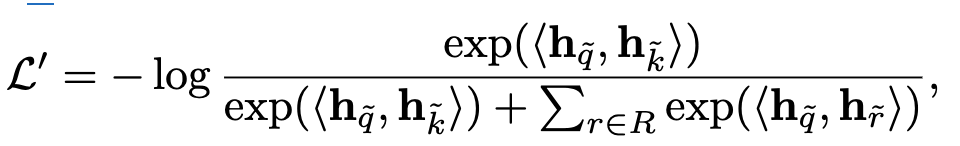
- input node의 subset token을 random masking 수행함
-
4. Experiments
4.1 Dataset
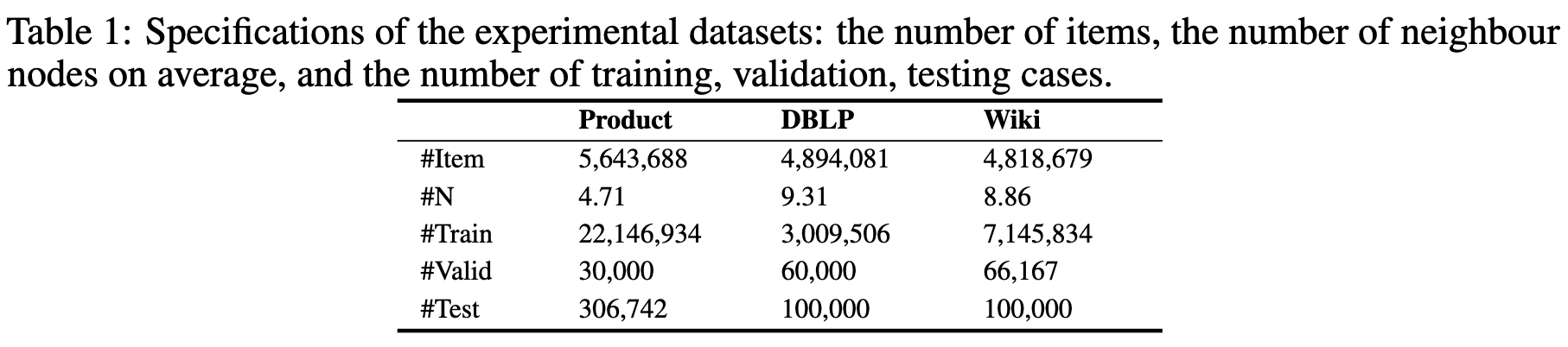
- DBLP: paper citation graph
- Wikidata5M: Wikipedia 의 첫번째 문장 기반으로 reference link
- ProductGraph: online product 데이터셋으로, 유저의 행동을 tracking하여 (Amazon, Nike shoes) 30분 내에 함께 browsing된 물건간의 graph로 연결됨
- product에는 고유 text description이 존재 (product name, brand, saler, etc)
4.2 Evaluation
-
Tokenizer = Wordpiece사용
-
5개의 neighbor를 사용
-
Precision@1, NDCG, MRR
-
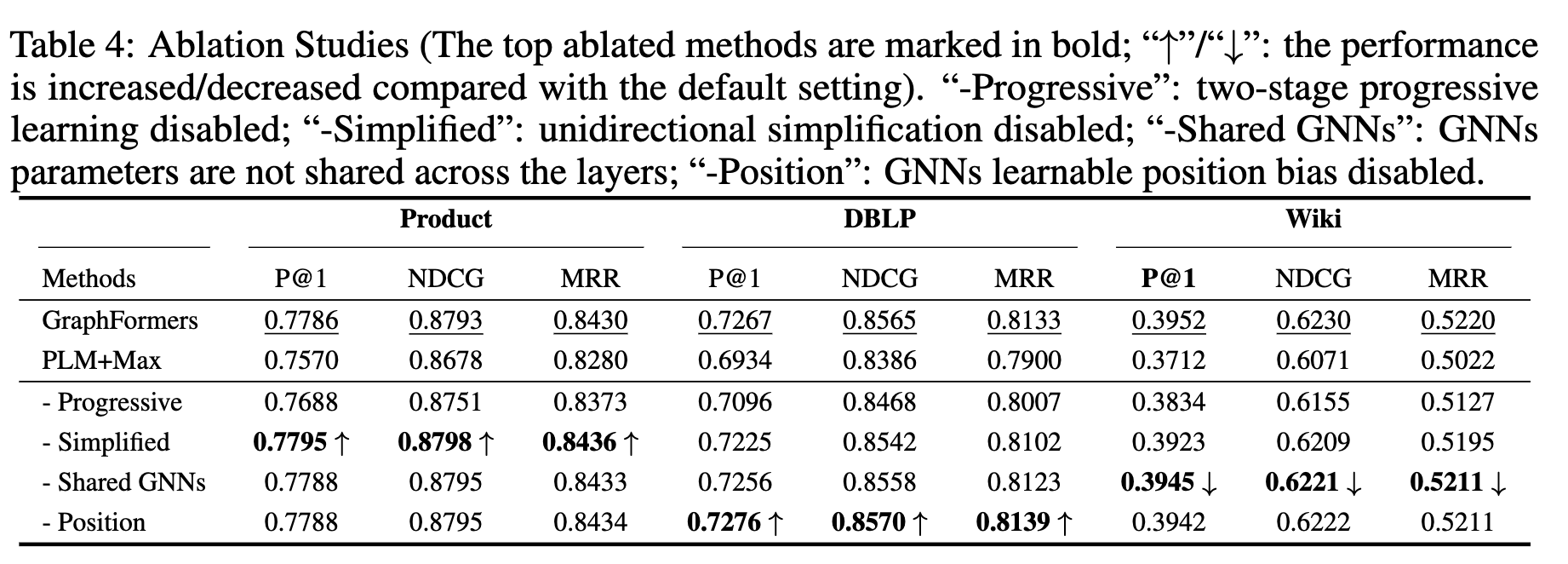
정량적 결과
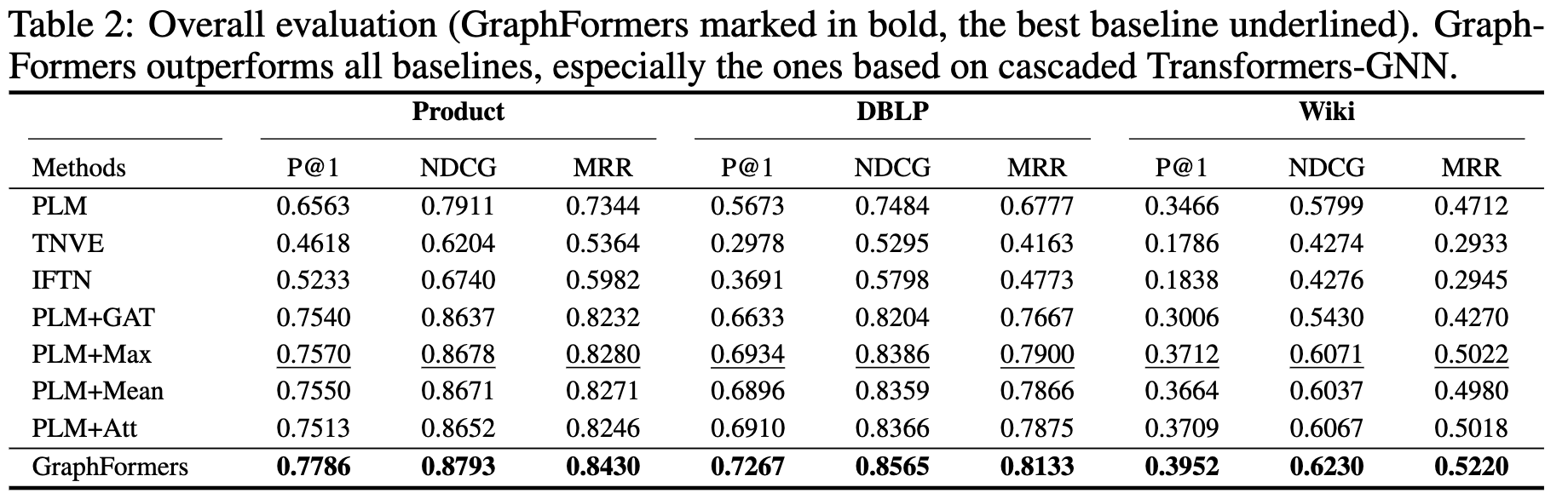
- PLM-only보다 PLM+GNN기반이 다 우수했음
-
neighborhood를 늘리면 성능은 향상됨
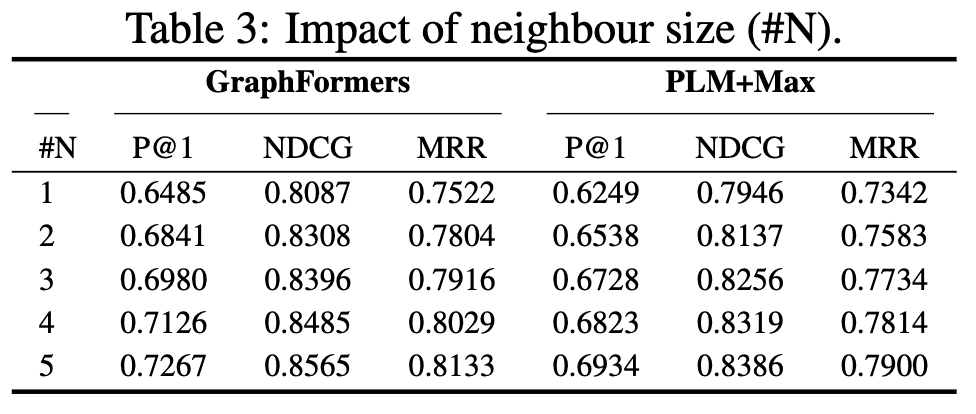
-
하지만 속도는 줄어듦고 계산량은 증가함
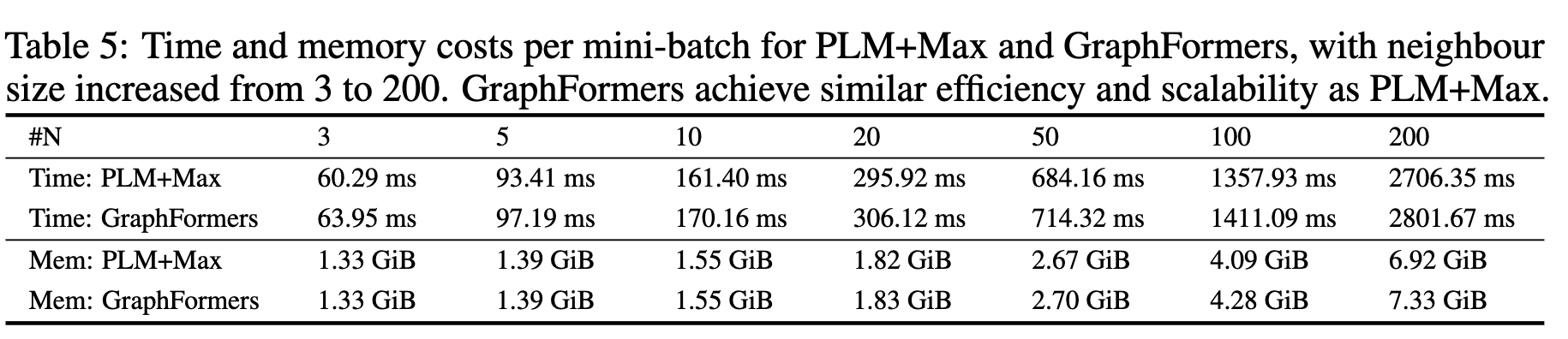
-
Ablation Studies