ColPali: Efficient Document Retrieval with Vision Language Models
[Retrieval] ColPali: Efficient Document Retrieval with Vision Language Models
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.01449
- github: https://github.com/illuin-tech/colpali
- huggingface: https://huggingface.co/vidore
- ICLR 2025 accepted (인용수: 17회, ‘25-02-15 기준)
- downstream task: (Visual-rich) Document Retrieval
1. Motivation
-
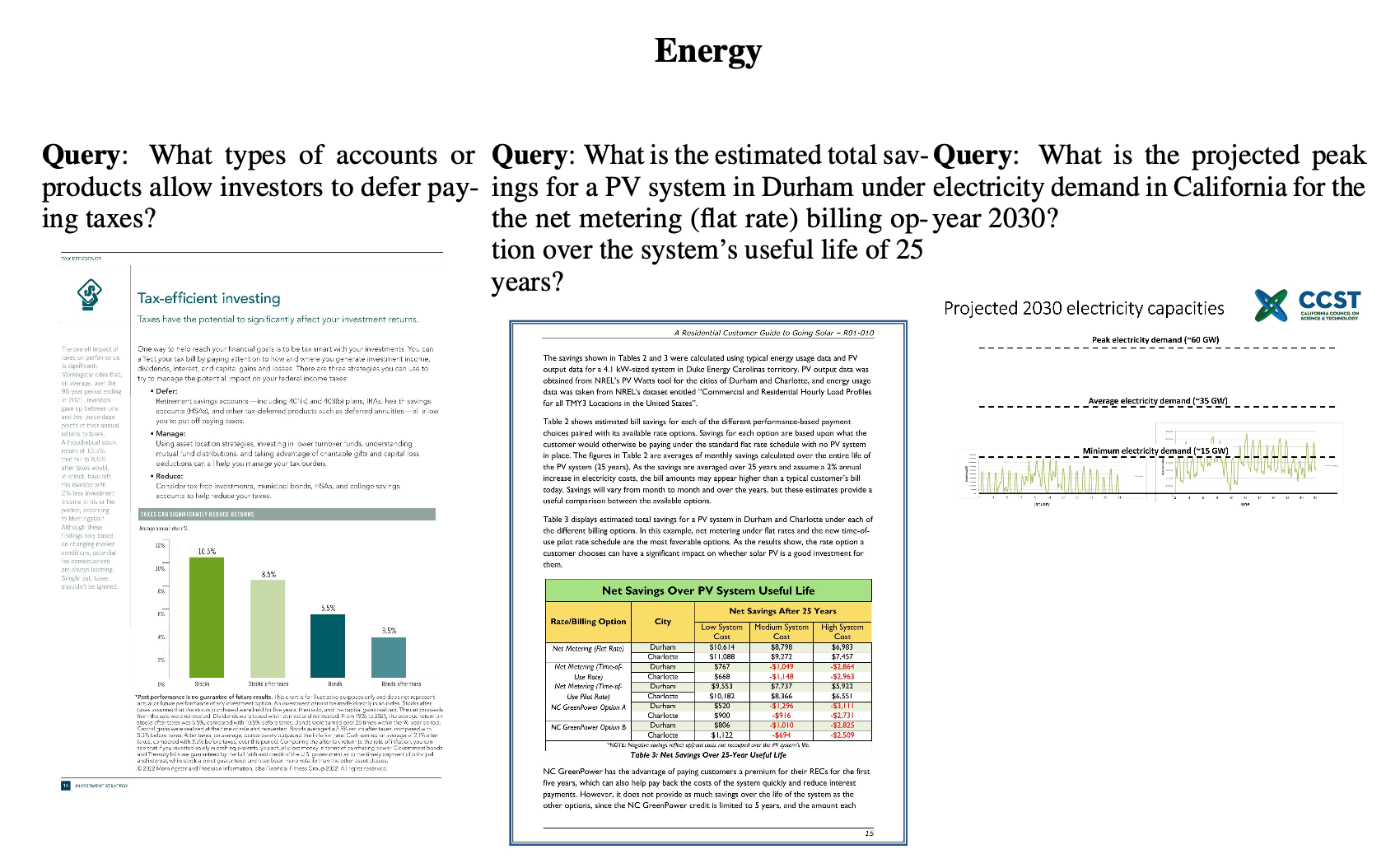
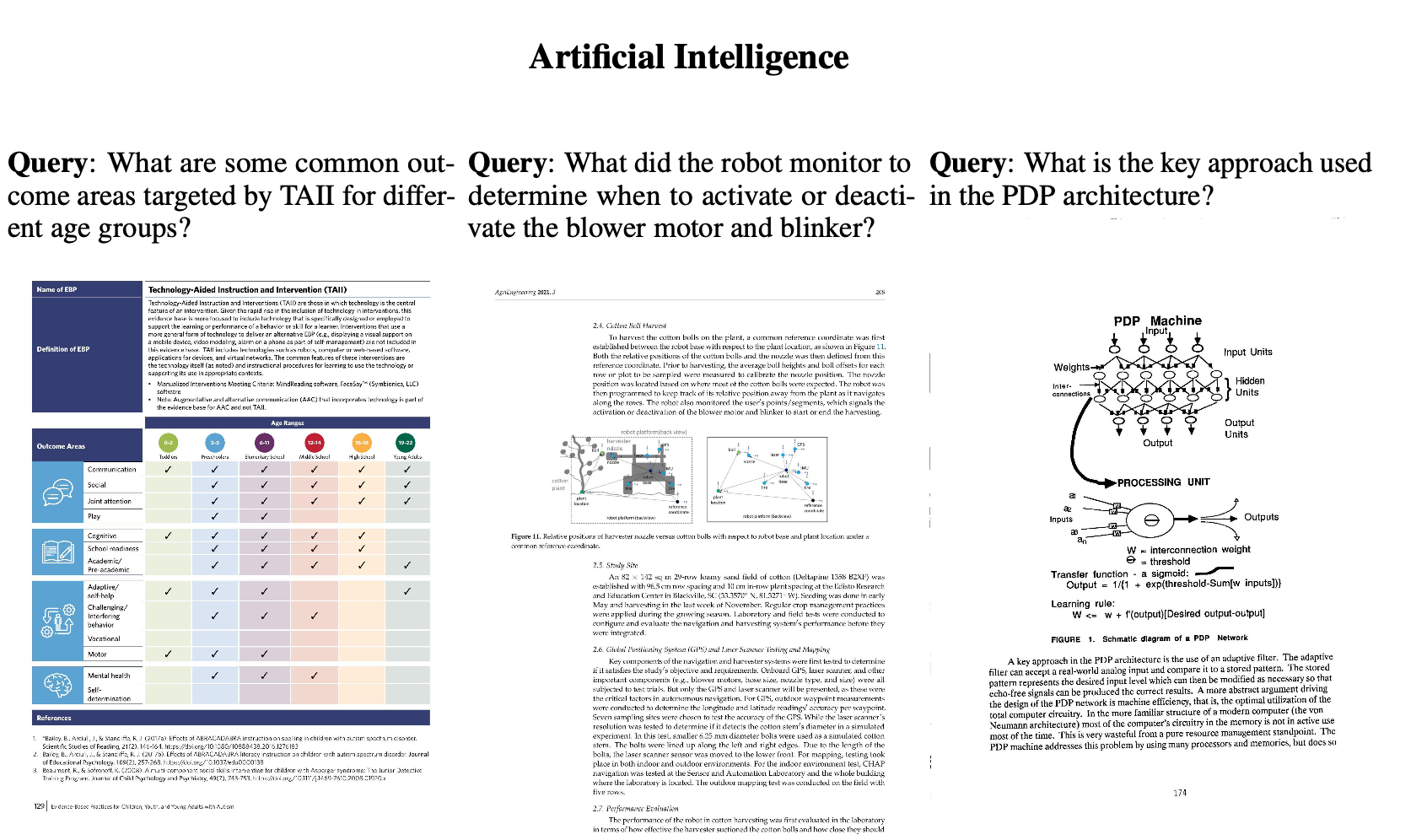
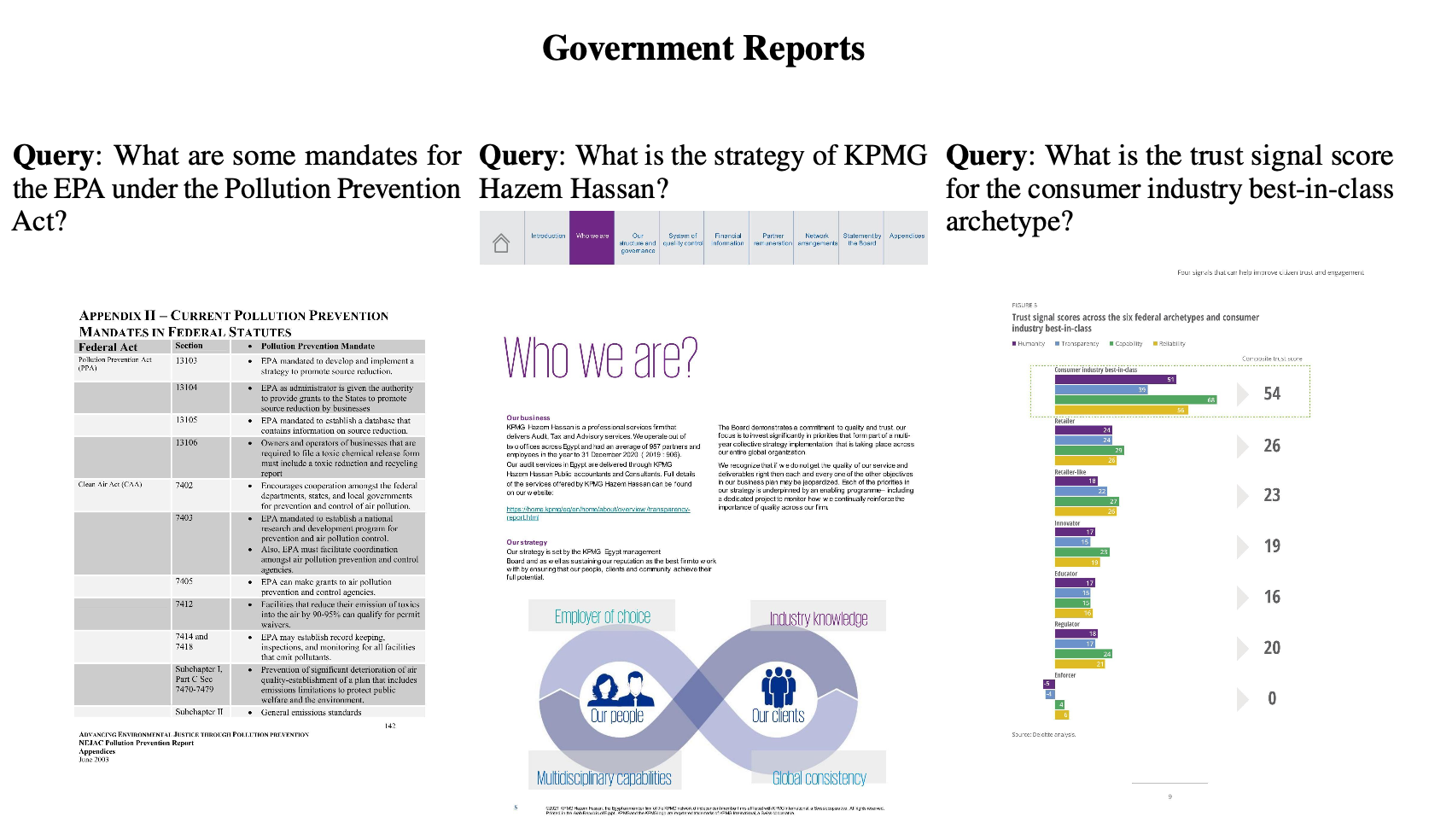
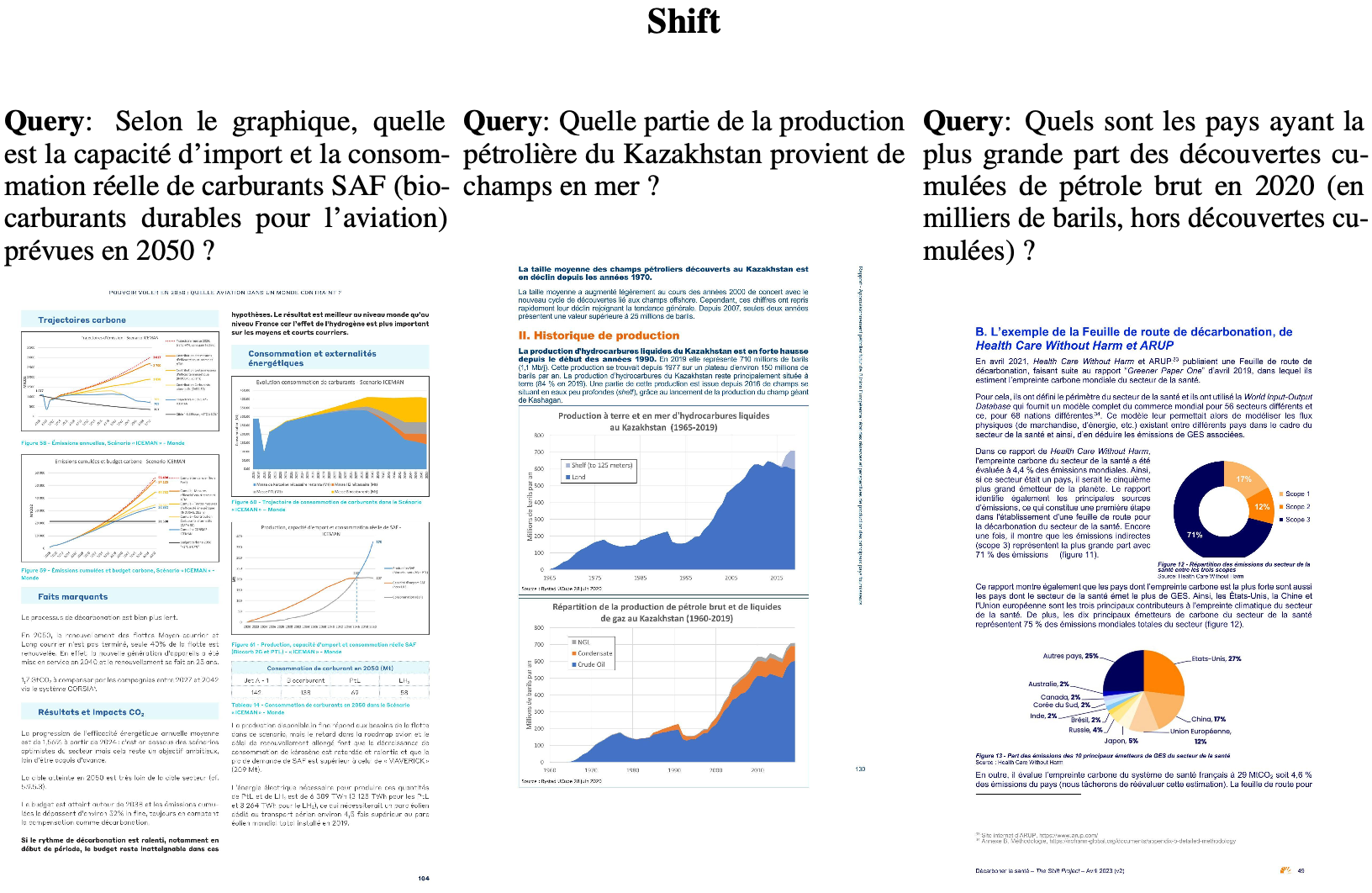
기존의 Document Retrieval task은 text-centric, text-only 검색만 다루고 있었음.
-
하지만, visually rich한 document (ex. 논문, report) 특성상 visual한 특성을 반영한 retrieval system이 필요로 함
$\to$ Document의 visual한 특성도 고려한 Document retrieval benchmark과 baseline을 제안해보자!
2. Contribution
- ViDoRe
- 기존의 text-centric system의 문제점을 지적함
- 다양한 도메인과 언어 (영어, 프랑스어)로 구성된 Page-level document retrieval용 benchmark인 ViDoRe(Visual Document Retreival) 를 제안함
- ColPali
- (Pali) VLM기반으로 document의 visual feature만 (purely)으로 retrieval하는 novel training 전략을 제안함.
- (Col) Late interaction 기반으로 빠른 query matching을 제안함.
- 제안한 benchmark에서 SOTA를 보임
3. ColPali
3.1 Problem Formulation
- Document retrieval := page-level retireval
- 목적: 산업계에서 실용적인 검색 시스템 (RAG)
- R1: retrieval performance
- R2: low latency: online querying phase에서 latency constraint 고려
- R3: high throughput: indexation 수행 시 접근성이 빨라야함
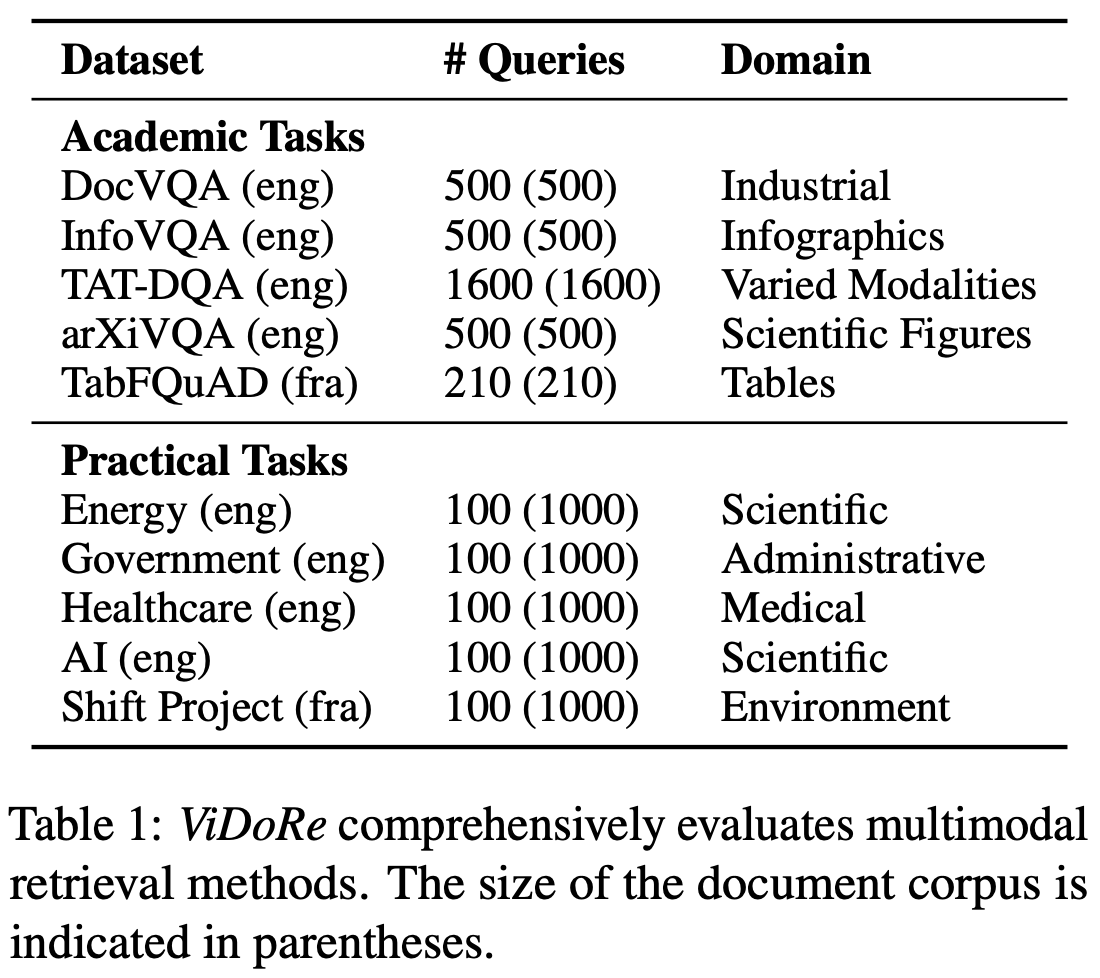
3.2 Benchmark Design
-
다양한 orthogonal subtask & modalities 로 구성시킴
-
subtasks: medical, business, administrative, languages (English, French)
-
Academic tasks
- 기존의 VQA benchmark의 triplet쌍 (question-page-answer)을 retrieval로 활용
- question $\to$ query text
- page (image) $\to$ golden answer
- 기존의 VQA benchmark의 triplet쌍 (question-page-answer)을 retrieval로 활용
-
Practical Tasks
-
Industry에 실용적인 예시로 구성하기 위해 webcrawler + GPT Turbo 3.5를 활용해서 주제당 1,000 question queries로 bencmark를 구성 $\to$ 이중, Human Labeler가 전체 맥락이 page와 유사한 100개의 query를 선별

-
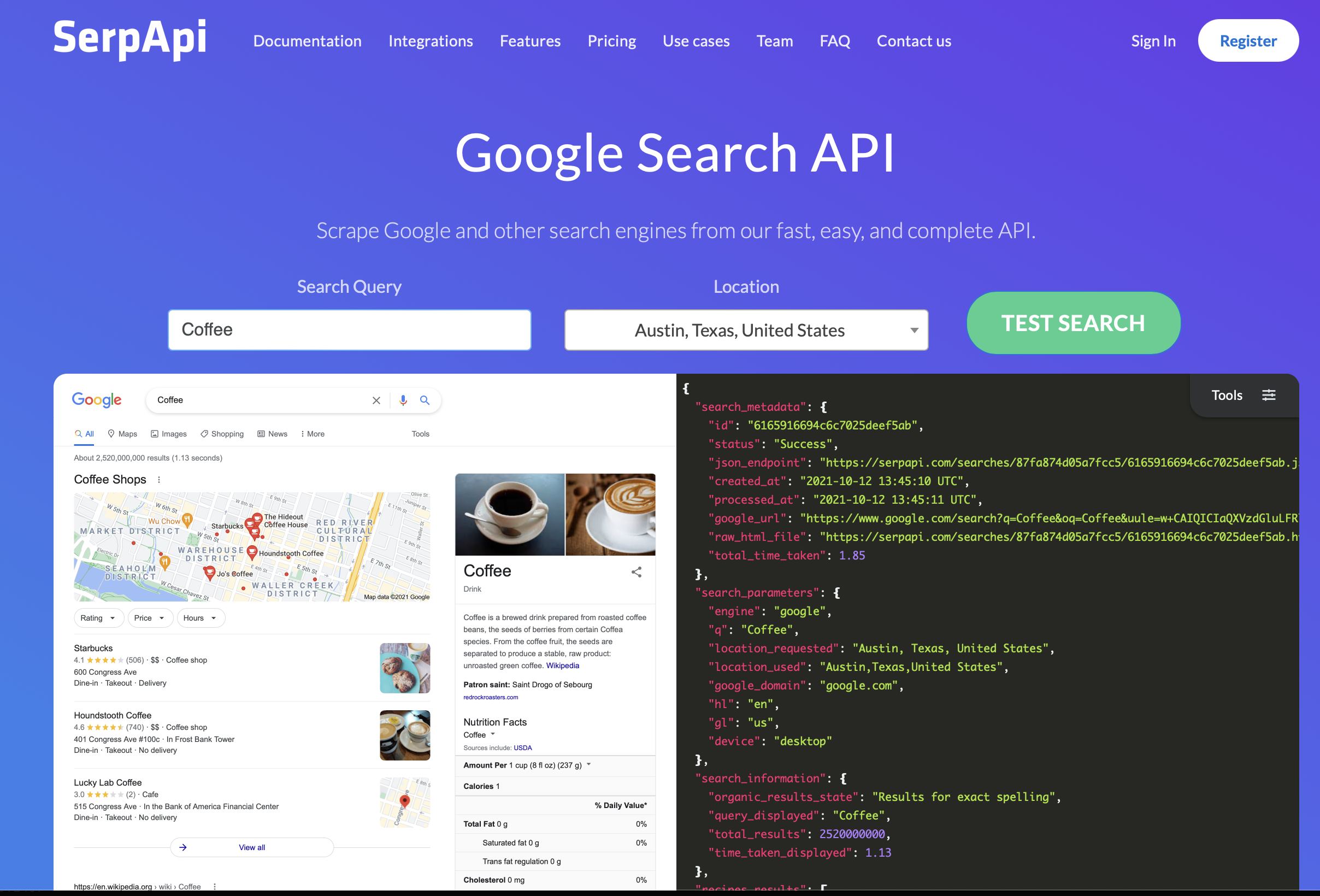
Web-Crawler
-
uer-defined query (ex. “Artifical Intelligence”)를 GPT-3.5 Turbo로 brainstorming하여 유사 subject를 생성 $\to$ search topic을 broaden + deepen하는 효과
-
SerpAPI + filetype filter를 활용해 Google search engine에다가 해당 query를 가지고, worker들은 Web에서 연관된 document pdf를 탐색
-
중복된 document search 방지를 위해 Bloom filter(?)를 활용해 SQLite database에 적재
-
-
Datamix
- 각 주제별로 private infomation 포함되거나, visually rich하지 않으면 filtering하여 1,000개의 document를 선별
-
Query Generation
-
Claud Sonet을 활용해서 이미지당 3개의 question을 다음 prompt로 생성

-
-
Human Validation: Document와 무관한 질문을 filtering하도록 지시. Topic당 100개의 queries가 최종 남게됨
-
-
-
-
modalities: text, figures, infographics, tables, etc
-
-
Evaluation Metrics: Document Retrieval에서 전형적으로 사용하는 metrics 사용
- Recall@K
- MRR
- NDCG $\to$ 이걸 기준으로 Report
3.3 Assessing Current Systems
-
Unstructured off-the-shelf tool를 활용해서 비정형 데이터를 정형화 (link: https://unstructured.io)
- Deep Learning Vision model를 활용하여 Document Layout, titles를 검출
- Chunking-strategy를 선택하면, “의미적으로 그룹”을 하여 text를 쪼갬
- ex. text-only: text외에 visual element (figures, images, tables, etc)는 noise label로 간주하여 무시
-
Unstructured + X:
- OCR-engine까지 활용하여 tables, charts, images의 text를 추출
- 해당 element 단위로 chunk
- Claud-3 Sonet를 활용해 caption을 생성 (fully-fledged captioning strategy)
-
Embedding model
- Text encoder 중 SOTA인 BGE-M3를 활용 $\to$ 검토 필요
- Chunk 단위로 max-pooling한 값을 page-level similarity score로 활용
-
Contrastive VLMs
- CLIP계열을 활용
-
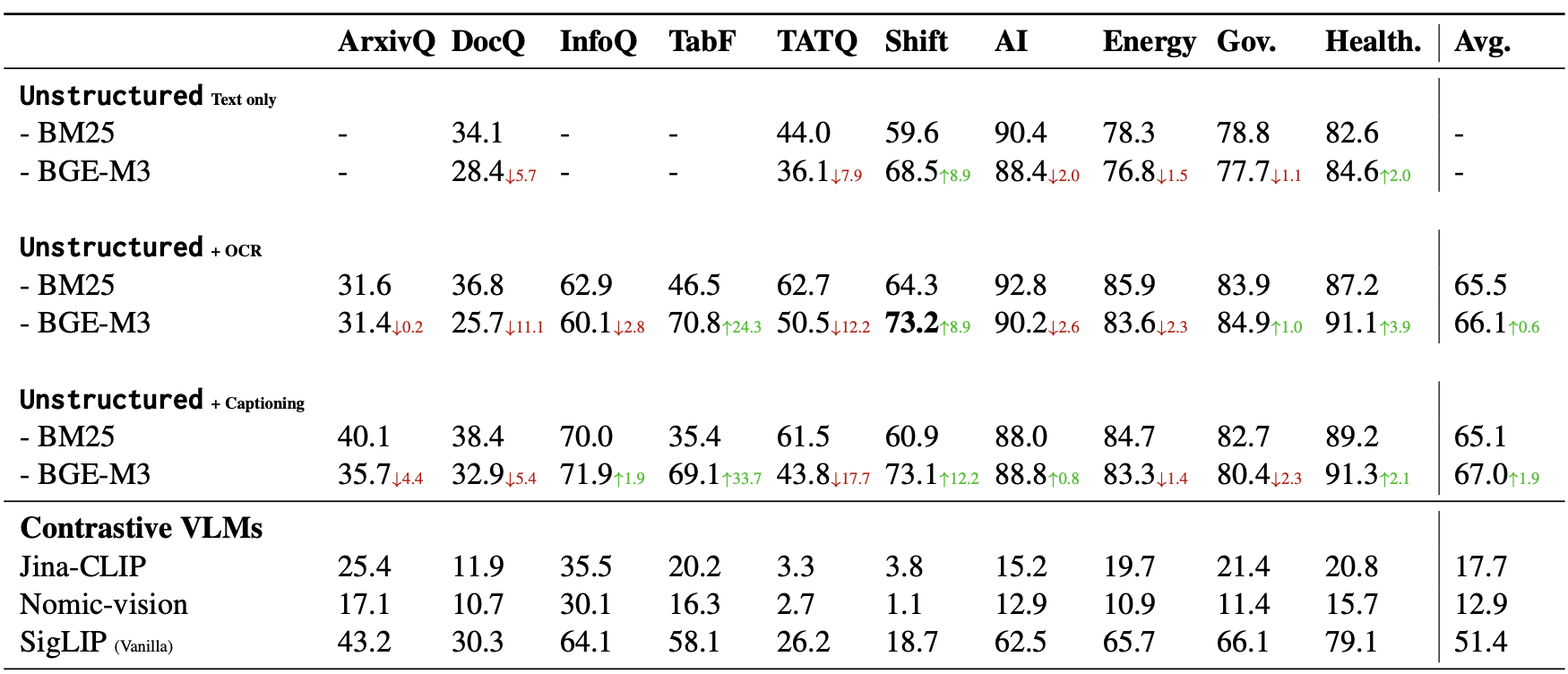
Results
-
Text Embedding 성능은 실제 Retrieval에 큰 영향이 없음 (BGE-M3 vs. BM25) $\to$ Text embedding 모델보다 chunking 등 text chunking전략이 중요하구나 (Unstructured로 text를 묶는 작업)
-
R1: Unstructured + X가 제일 좋음
-
R2: 기존 PDF parsing 방식은 lengthy함 (특히 +OCR, +Captioning이.)
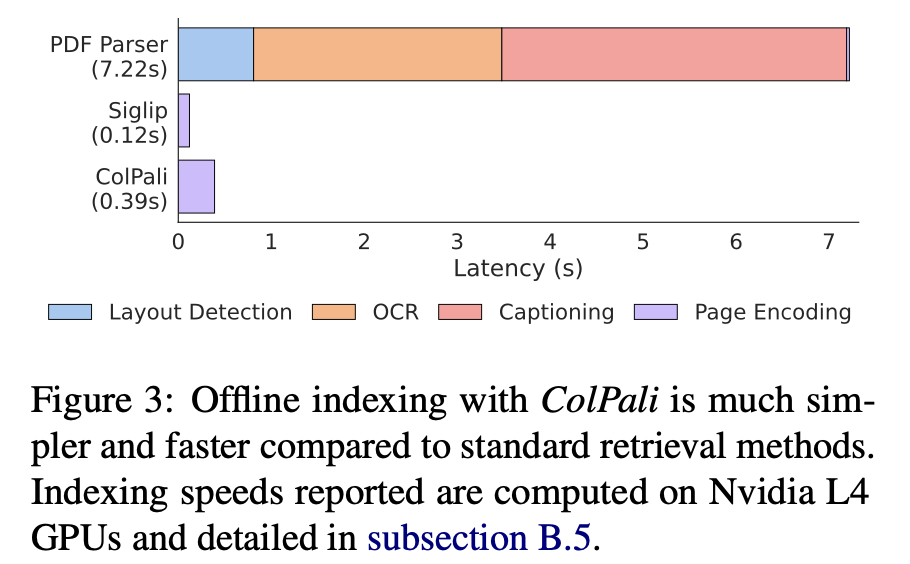
$\to$ PDF parsing (PDF throughput)의 시간이 너무 오래걸려 비실용적임.
-
3.4 Late Interaction based Vision Retrieval
-
Architecture
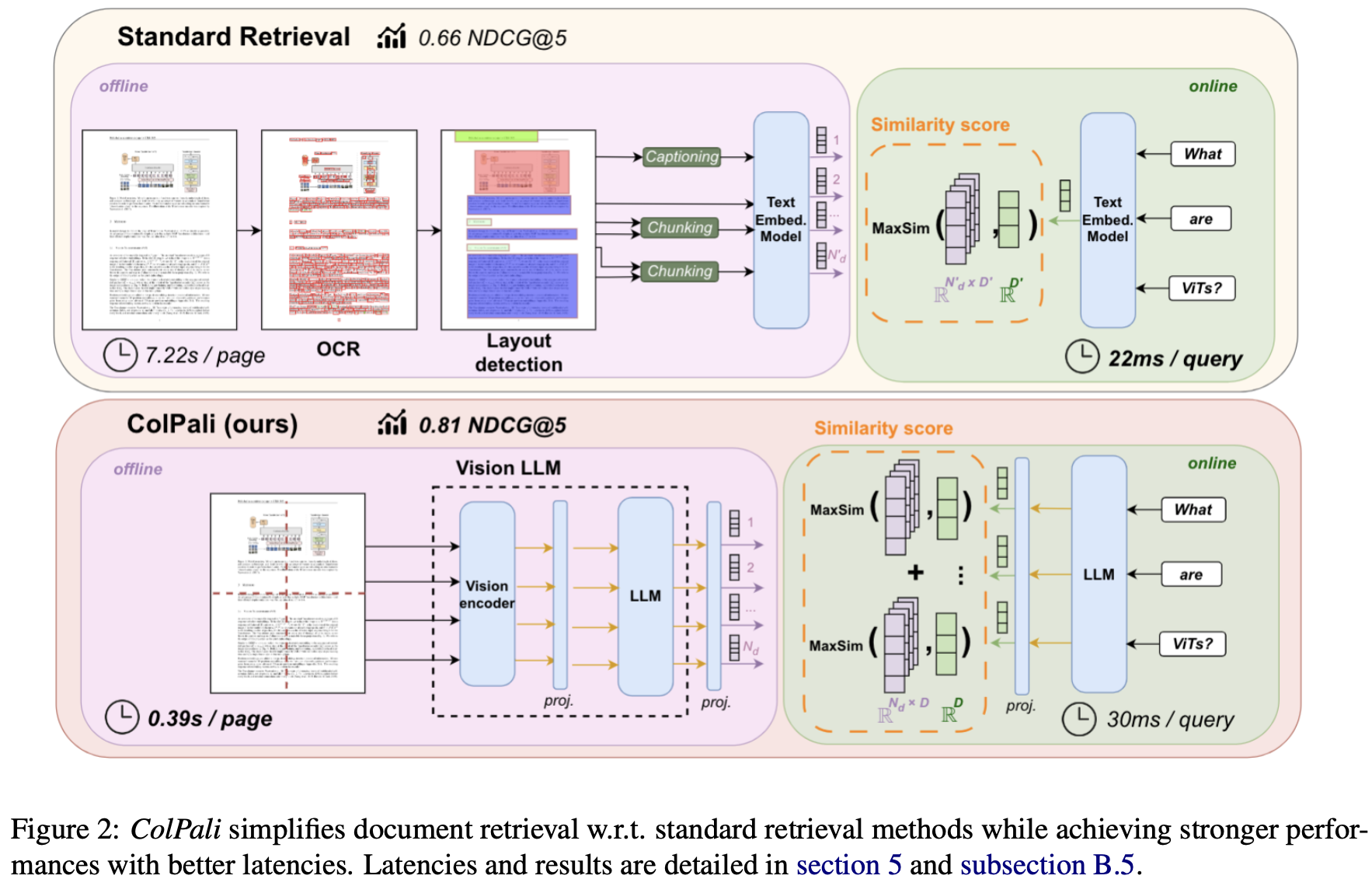
-
Baseline: Paligemma-3B
- Projection dimension: 128
-
Late Interaction
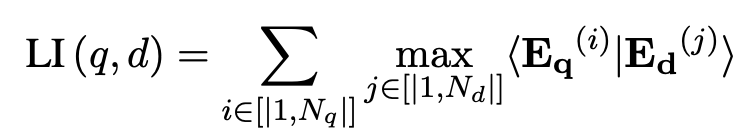
- E$_q$: query embedding $\in \mathbb{R}^{N_q \times D}$
- E$_d$: document embedding $\in \mathbb{R}^{N_d \times D}$
-
Contrastive Loss
-
In-batch contrastive loss로 구성 (maximum negative + positive)
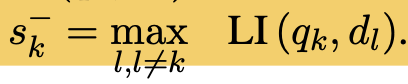
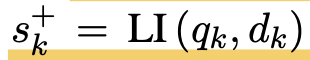
-
-
Dataset
- 127,460 query+document 데이터셋
- Academic (63%) + synthetic (37%)로 학습
- 단장의 document으로만 구성
- 2%는 validation set
- 127,460 query+document 데이터셋
-
Parameters
- projection layer는 random initialize
- 16-bit 학습
- LoRa로 학습 $\alpha=32, r=32$
-
Query augmentation
- 5개의 unused token을 할당하여 query augmentation
-
4. Experiments
-
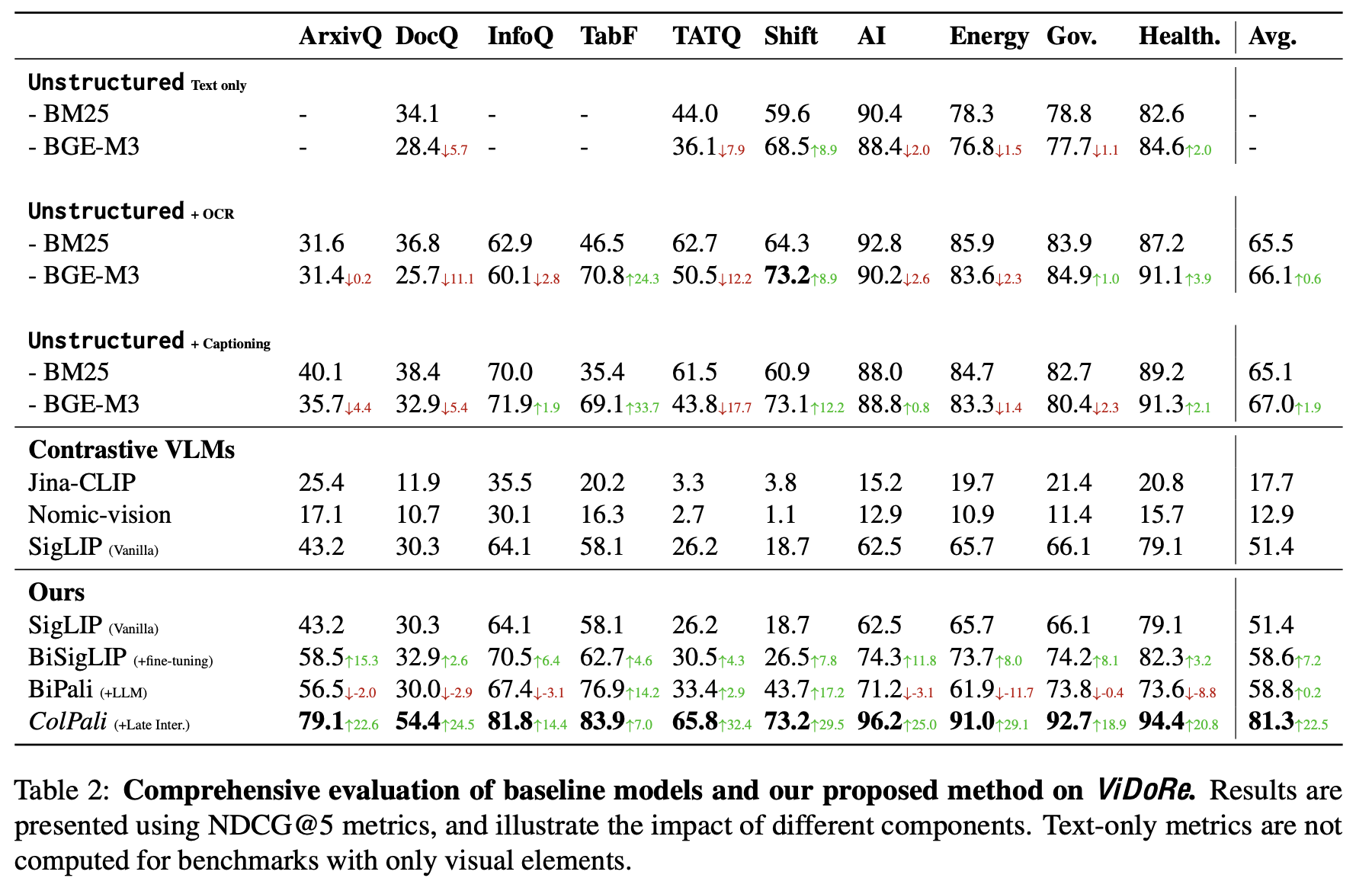
R1: Performance
-
SigLIP: WebLI로 학습된 pretrained Sigmoid CLIP
-
BiSigLIP: SigLIP의 text encoder를 ViDoRe로 finetuning한 SigLIP
-
BiPali: SigLIP의 image patch embedding을 LLM에 태우고 average pooling한 Dense vector로 retrieval하는 모델. ViDoRe로 finetuning
- English에서는 BiSigLIP에 비해 성능이 하락 $\to$ NTP로 학습한 데이터가 ViDoRe보다 5배 많았음.
-
French에서는 성능이 증가함 $\to$ LLM의 multi-lingual 때문으로 사료됨
-
ColPali: text token과 image patch 간의 interaction 덕분에 성능이 좋아짐.
-
반면, ColSigLIP은 성능이 망가짐
-
이는 SigLIP 특성상, patch embedding이 아닌, pooled token만 가지고 contrastive pretraining을 했기 때문으로 사료됨
-
-
-
R2: Latencies & Memory Footprint
- BGE-M3: embedding 추출 시 15ms
- ColPai:
- embedding 추출 시 30ms
- late interaction : 1ms
- similarity score 계산 시 < 1ms
-
R3: Offline indexing
-
BGE-M3는 text embedding 단위가 chunk이므로, chunking하는 시간이 매우 오래 걸림 (layout detection, ocr, captioning)
-
ColPali는 image로부터 직접 encode를 하므로 추가 공수 X
-
-
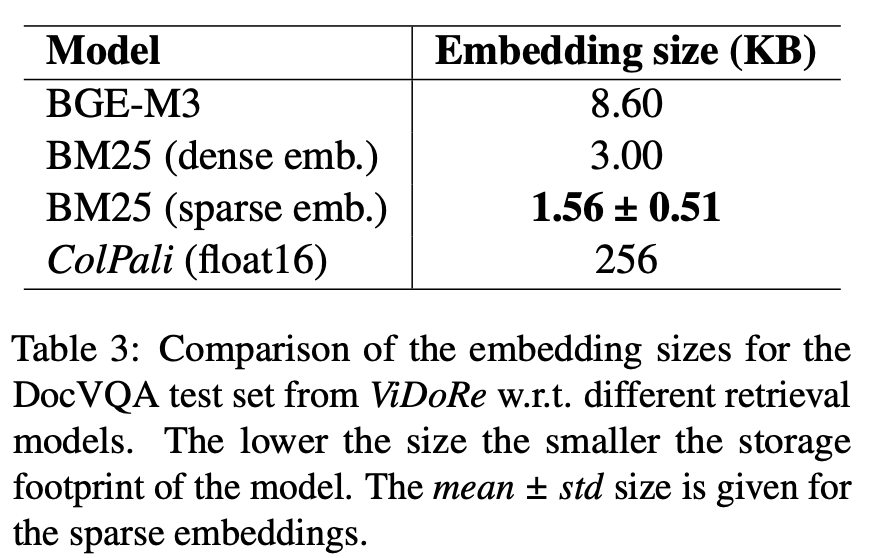
(R4): Memory
-
기존 text보다는 memory 비용이 많으 듦
-
-
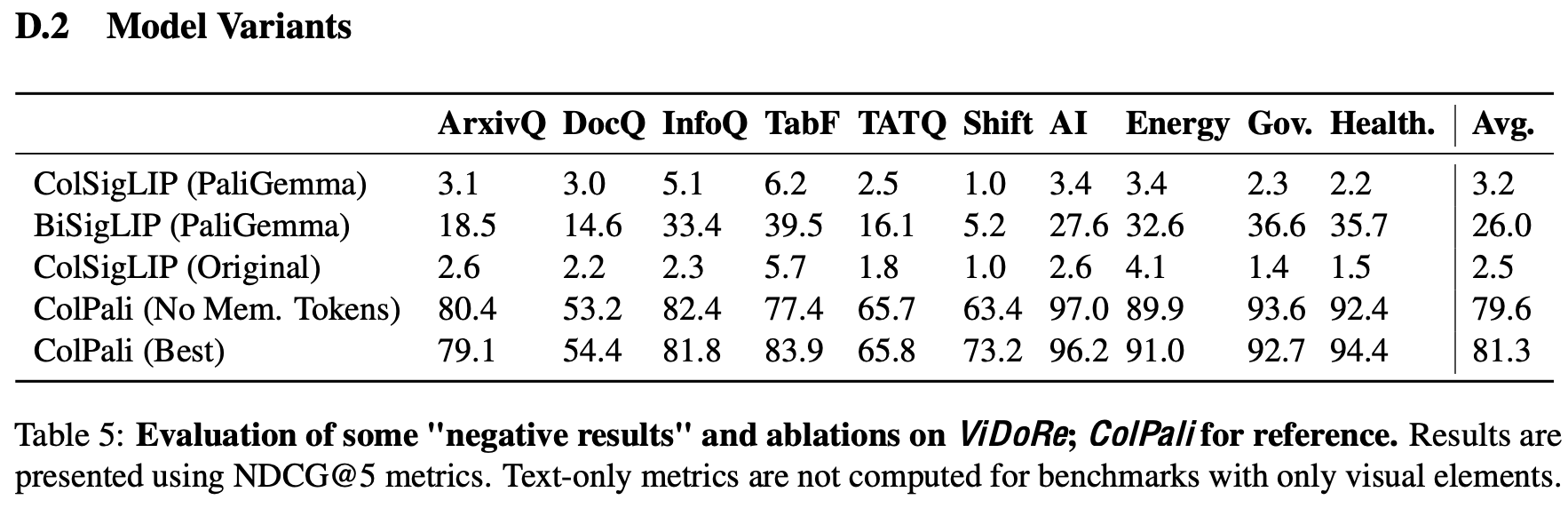
Ablation study
-
Interpretability
-
query에 가장 연관된 image patch를 알 수 있음
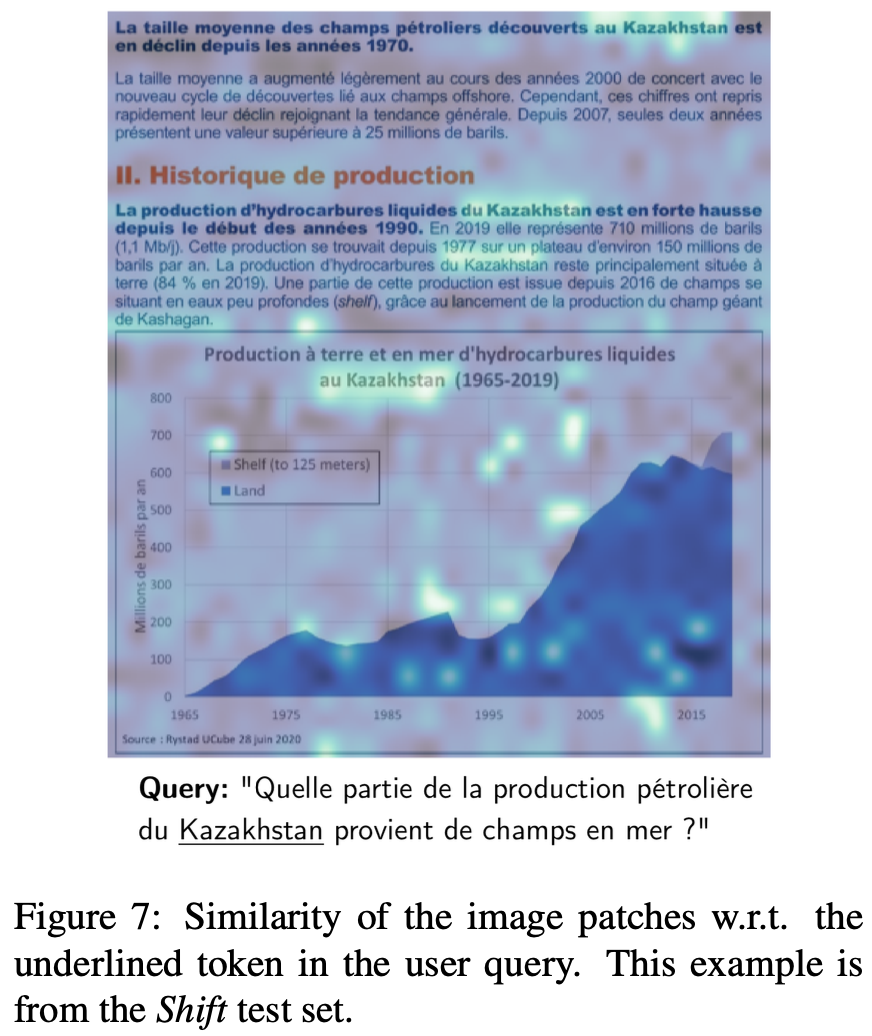
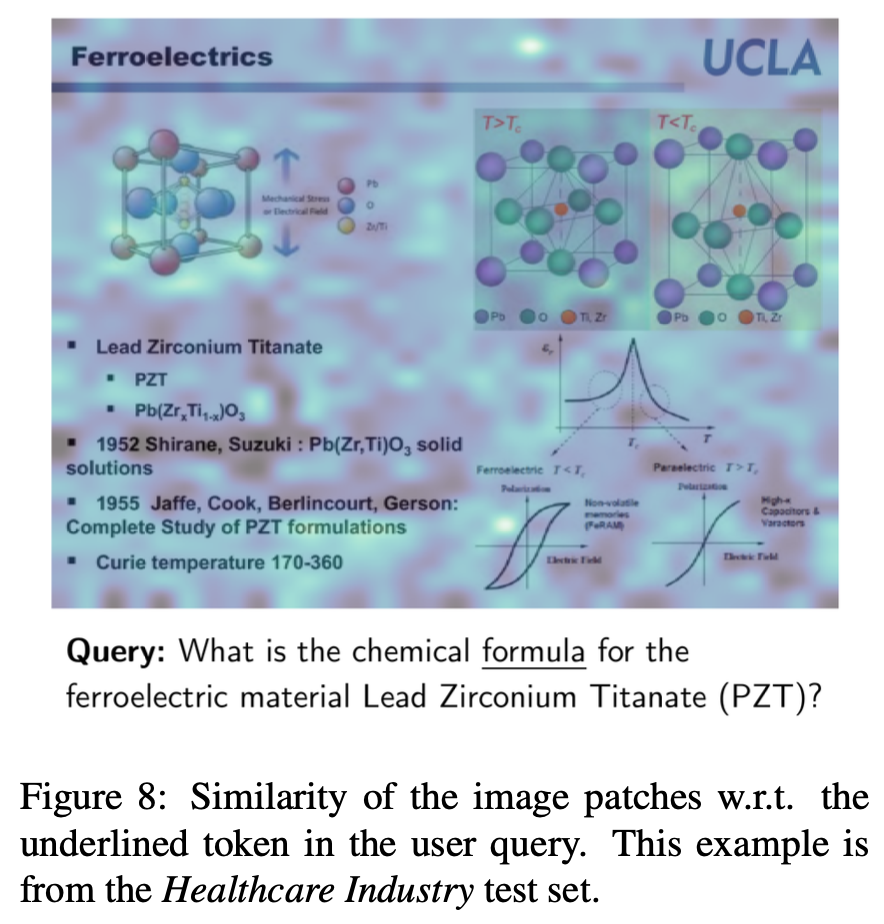
-
-
Increasing Patch token vs. Model size
- 결론: 둘다 중요
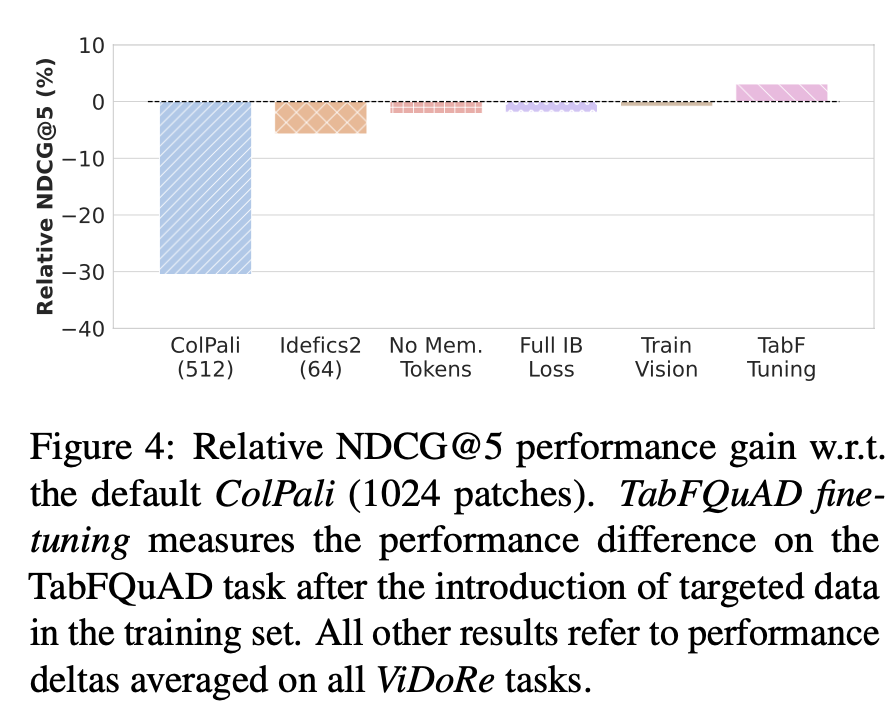
-
3B + 1024 token $\to$ 3B+ 512 token: 30% 성능 하락
-
3B + 1024 token $\to$ 8B + 62 token : 5% 성능 하락
-
Train Vision: Vision encoder까지 학습. 성능 향상 없음
-
No Mem. Tokens: Query augmentation이 English에서는 성능향상이 없었음. 하지만, French 에서는 성능향상이 있었음
(Table 5 참고)
-
Ful IB Loss: In-batch내 negative를 전부 학습하는 것. hardest negative만 학습하는 것보다 미세한 (-2.4%) 성능 하락 있었음
-
TabF Tuning: 1.5K의 French document 추가 시, 성능이 향상
-
-