[OD] CoDETR: DETRs with Collaborative Hybrid Assignments Training
[OD] CoDETR: DETRs with Collaborative Hybrid Assignments Training
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.12860v5
- github: https://github.com/Sense-X/Co-DETR
- ICCV 2023 accepted (인용수: 297회, ‘24-12-04 기준)
- downstream task: OD
1. Motivation
-
논문을 고르게 된 이유
-
꾸밈 요소 검출 문제 $\to$ “그룹” 요소를 찾고, rule-base로 보완하는 문제로 정의

-
MS-COCO leaderboard에서 SOTA
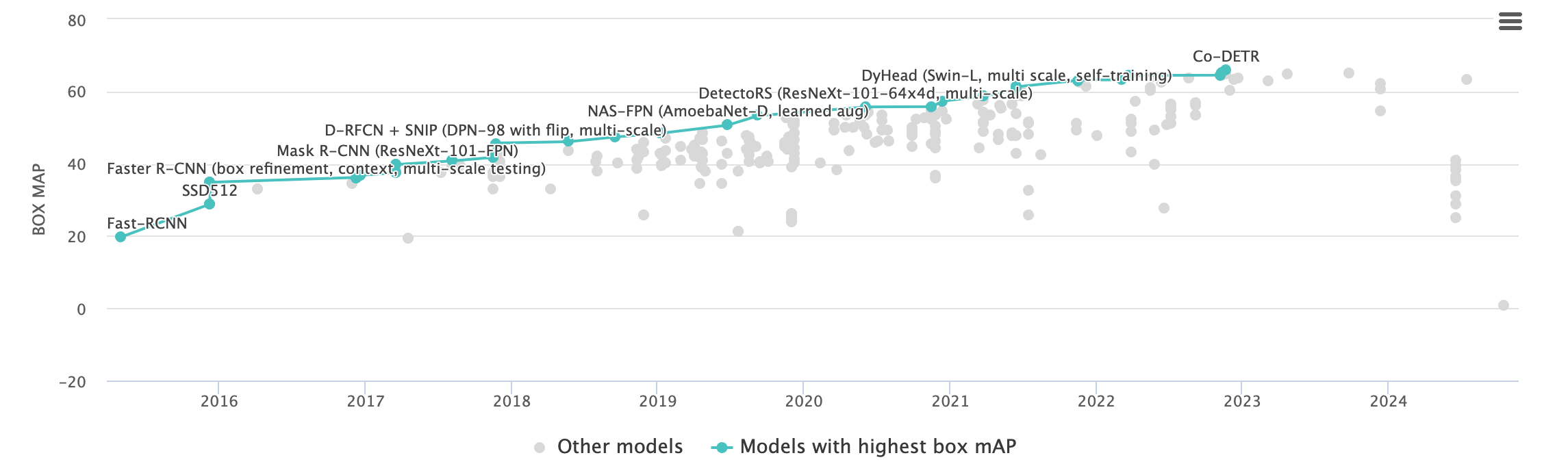
-
-
기존 DETR의 문제는 one-to-one matching으로 GT당 1개의 positive query를 가지고 학습하게 됨으로써, sparse supervision으로 encoder / decoder의 feature & attention map이 학습을 충분히 못한다는 점이다.

-
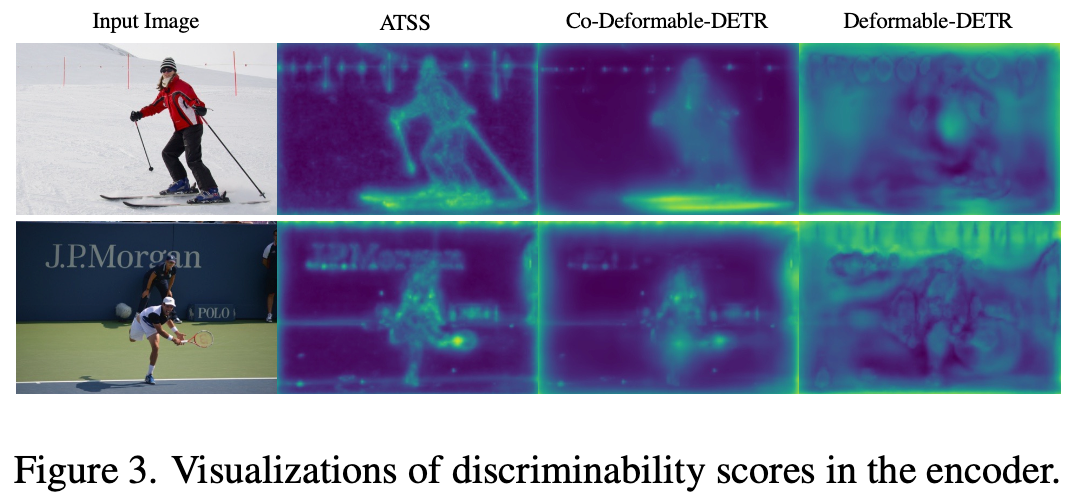
반면, ATSS와 같이 one-to-many 학습을 하면 encoder의 feature가 discriminative 능력을 잘 학습하게 된다.
$\to$ DETR의 end-to-end 장점은 유지하면서 다른 object detector의 장점을 살리는 학습방식을 고안해보자!
-
2. Contribution
-
기존 DETR의 “sparse supervision”을 개선할 새로운ㅇ collaborative hybrid assignment training 기법인 “Co-DETR”을 제안함
-
학습시에만 auxiliary decoder를 활용하여 gt당 여러개의 positive query를 할당 (one-to-many) 함으로써 이를 해결
-
customized positive query를 auxiliary head로부터 positive coordinate를 추출하여 initial positive query로 활용
$\to$ encoder의 discriminative learning ability 와 decoder의 cross attention learning을 향상
-
추가되는 parameter가 없어 Inference 속도는 동일
-
-
MS-COCO에서 SOTA (66.0 mAP)
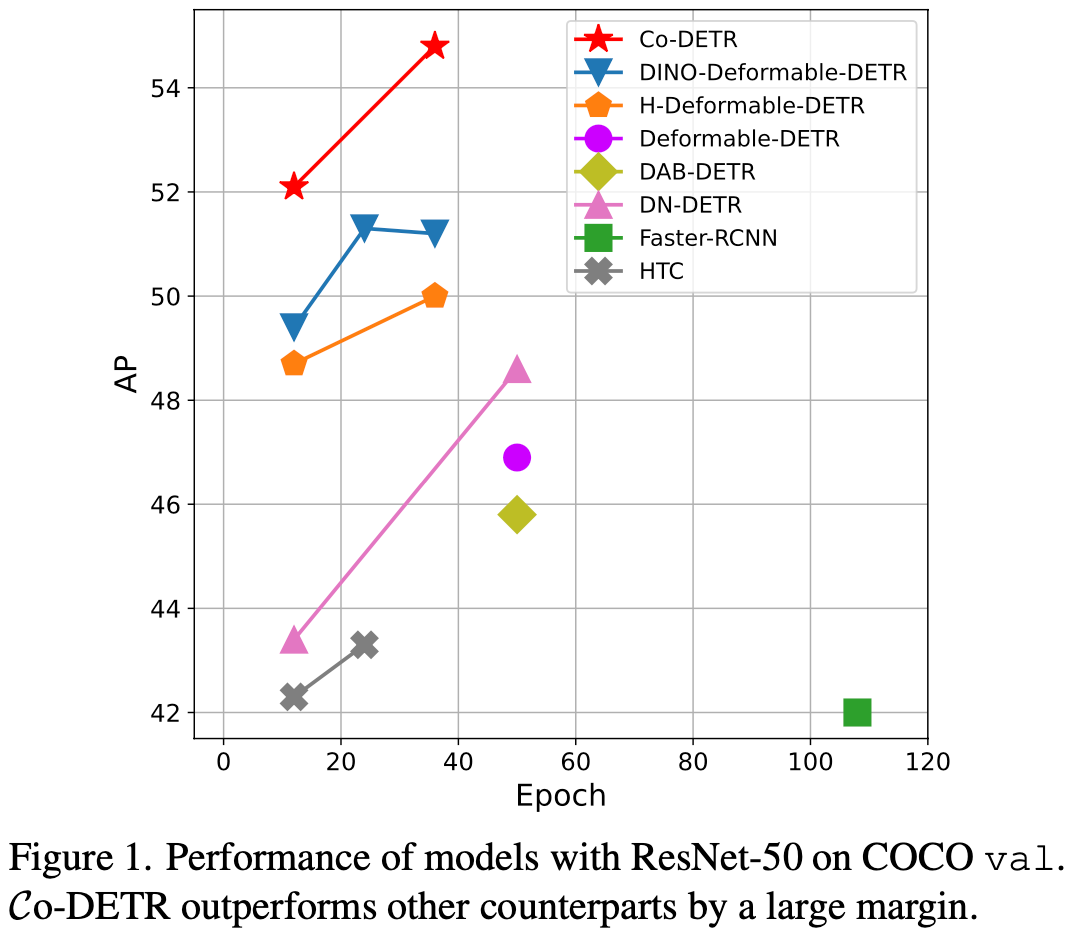
3. Co-DETR
-
기존 DETR의 문제점
-
Hungrian matching기반 one-to-one set matching
- GT 1개당 Positive query 1개만 matching $\to$ bbox regression은 1개의 query만 학습 $\to$ forground에 대한 학습이 잘 안될 것
-
실험
-
Encoder feature: $F \in \mathbb{R}^{C \times H \times W}$
-
Discriminability score map: $D \in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times H \times W}$
$\to$ D를 통해 IoF (Intersection over foreground), IoB (Intersection over Background)를 계산
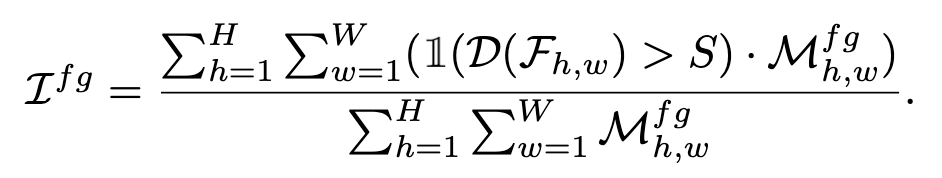
-
S: Threshold. 해당 feature grid score가 Threshold 이상이면 forground, 이하면 background로 간주
-
$M_{h,w}^{fg}$: (h,w)에 위치한 gt의 forground
-
$D(F_{h,w})$: Discriminability score. Encoder feature를 아래와 같은 공식으로 유도
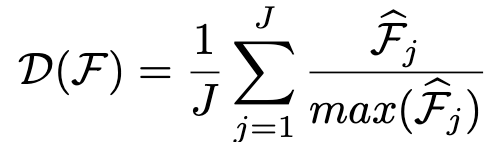
-
J: J개의 multi-level feature 갯수
-
$\hat{F}_{j}$: j번째 level feature의 l2-norm encoder feature $\in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times H_j \times W_j}$
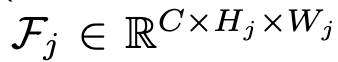
-
-
-
Cross-attention score: attention map을 기준으로 IoF, IoB를 그림
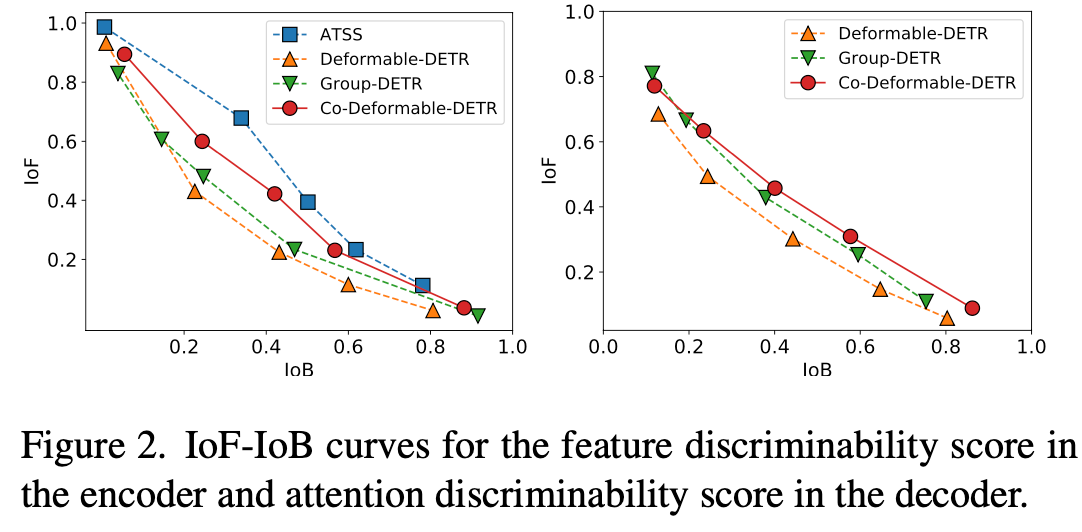
$\to$ 예상대로 동일 IoB일때 IoF가 Co-DETR > DETR(Deformable)보다 낫게 나옴 $\to$ encoder / decoder의 discriminative / cross-attention feature 향상
-
-
-
왜 Co-DETR이 좋은가?
-
GT에 matching되는 query가 stable해진다
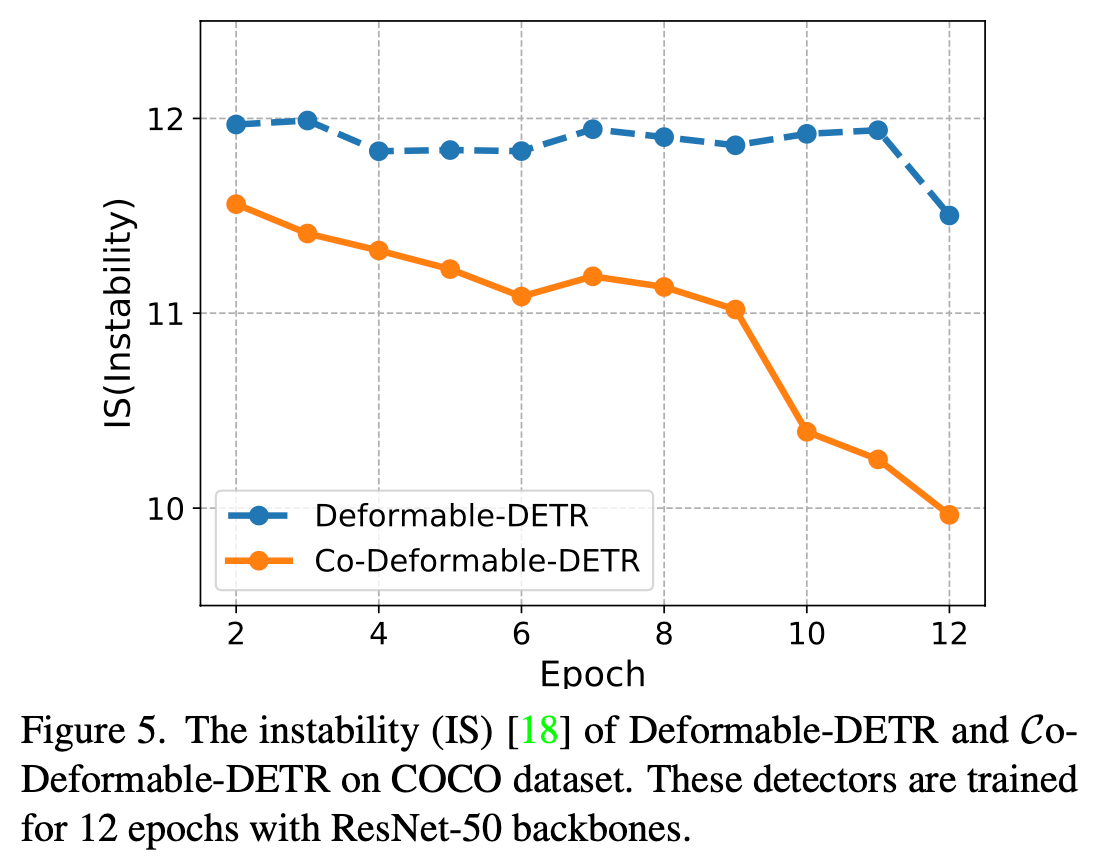
-
Auxiliary head에 negative query가 없어, memory가 합리적으로 사용된다.
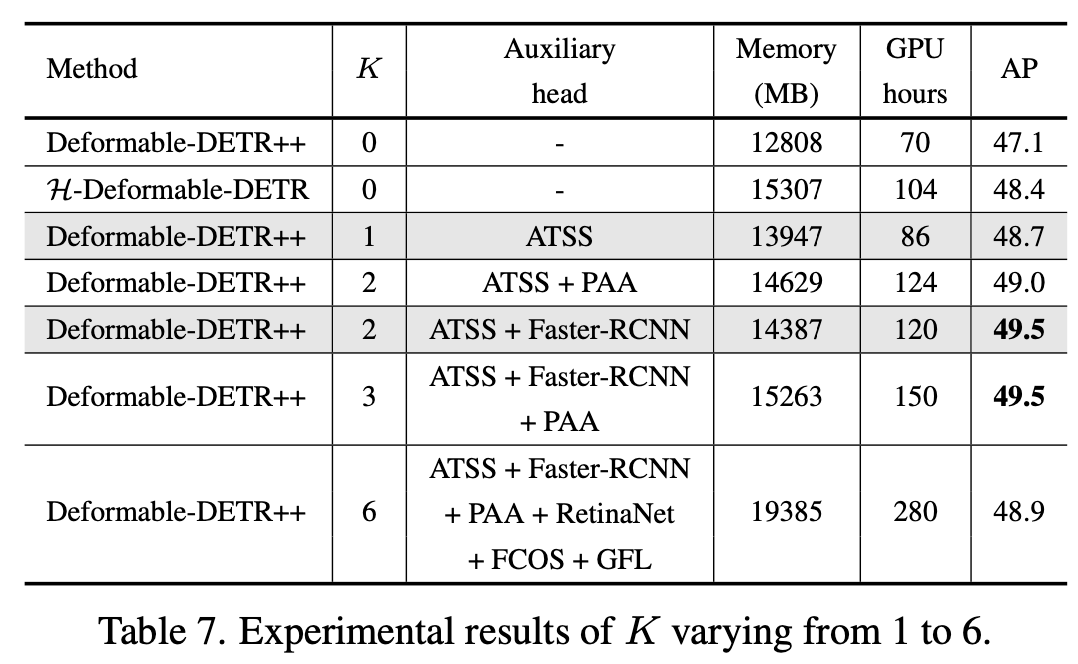
-
-
Architecture
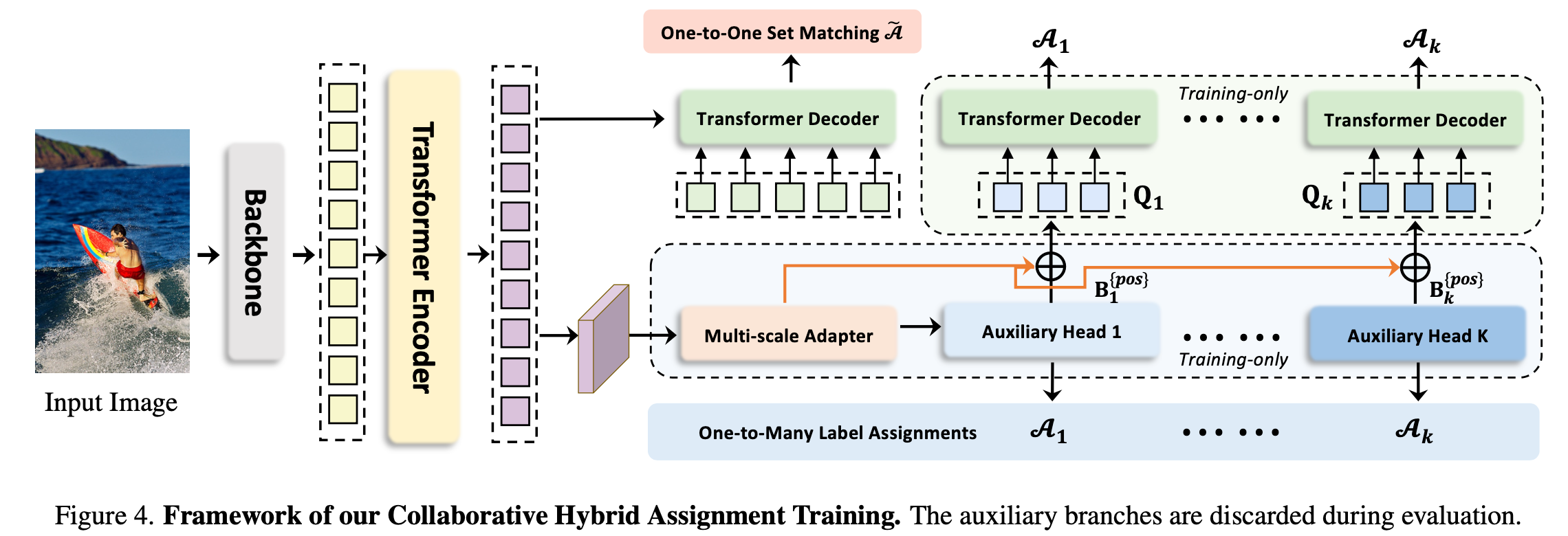
-
K개의 auxiliary decoder head를 붙이고, 각 head별 positive sample 할당 정책 (A)에 따라 positive query / negative query를 할당
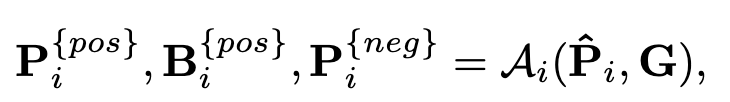
-
G: Ground Truth bbox
-
$\bold{\hat{P}}_i$: i번째 auxiliary head의 Prediction
-
$A_i$: i번째 auxiliary head의 query 할당 정책
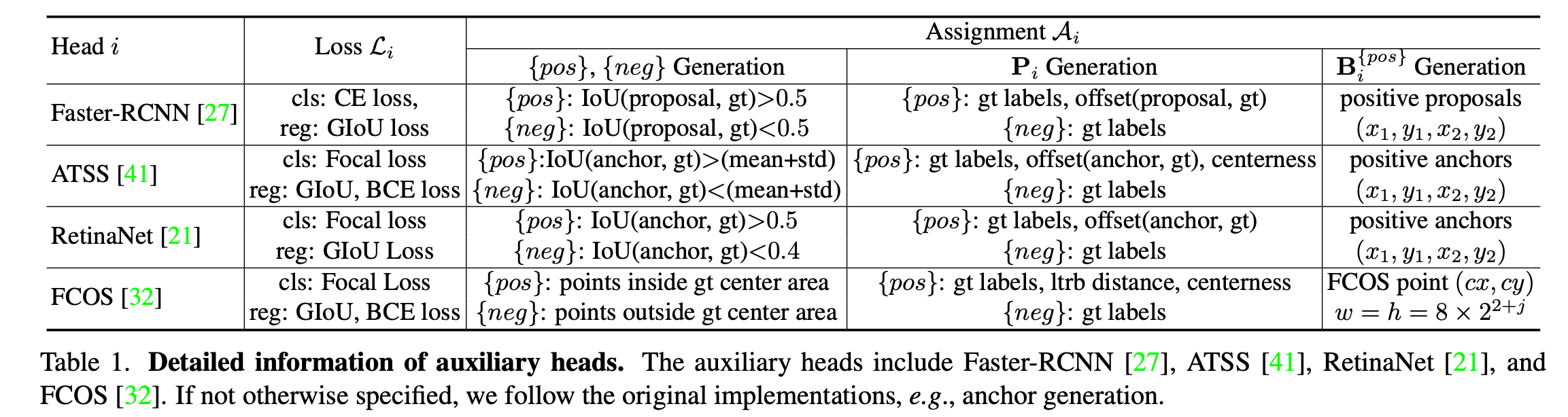
-
-
-
Loss
-
Encoder loss
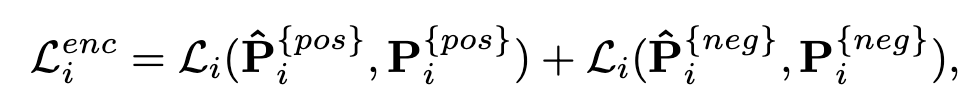
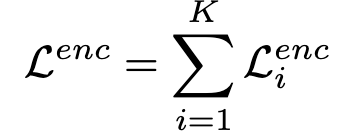
-
Decoder loss
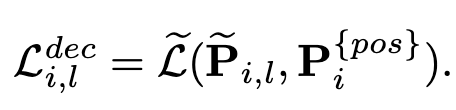
- $\tilde{\bold{P}}_{i,l}$: l번째 decoder layer의 i번째 auxiliary head의 prediction
- $\bold{P}_i^{pos}$: positive target
-
Customized Positive Query
-
One-to-many matching의 단점은, 수많은 negative query를 양산하는 것 $\to$ 여기서는 negative는 고려하지 않음
-
Auxiliary head가 예측한 positive queries의 bbox $\bold{B}_i^{pos} \in \mathbb{R}^{M_i \times 4}$를 initial query로 활용
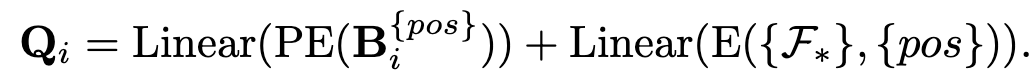
- $M_i$: i번째 auxiliary head의 positive sample 갯수
- PE: Positional Encoding
- E: ??
-
-
CoDETR Loss
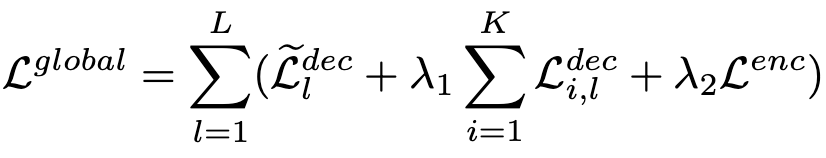
-
4. Experiments
-
MS-COCO
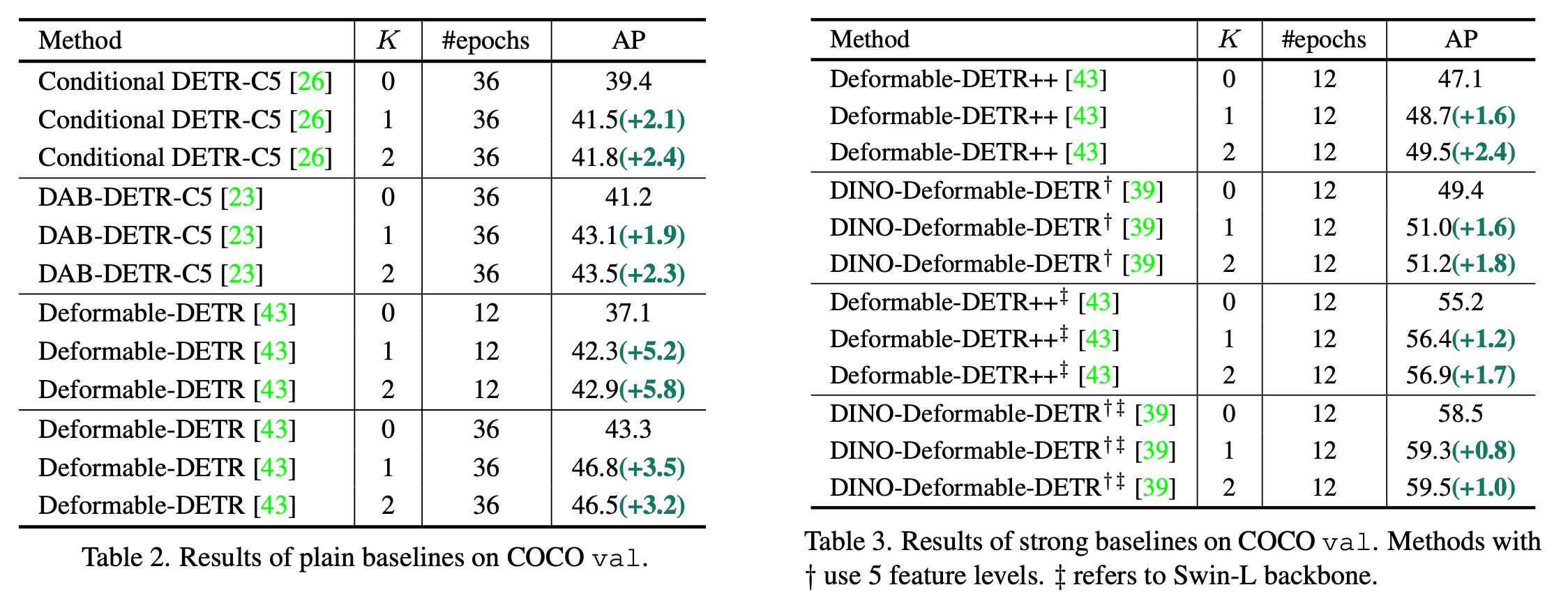
-
SOTA와 비교
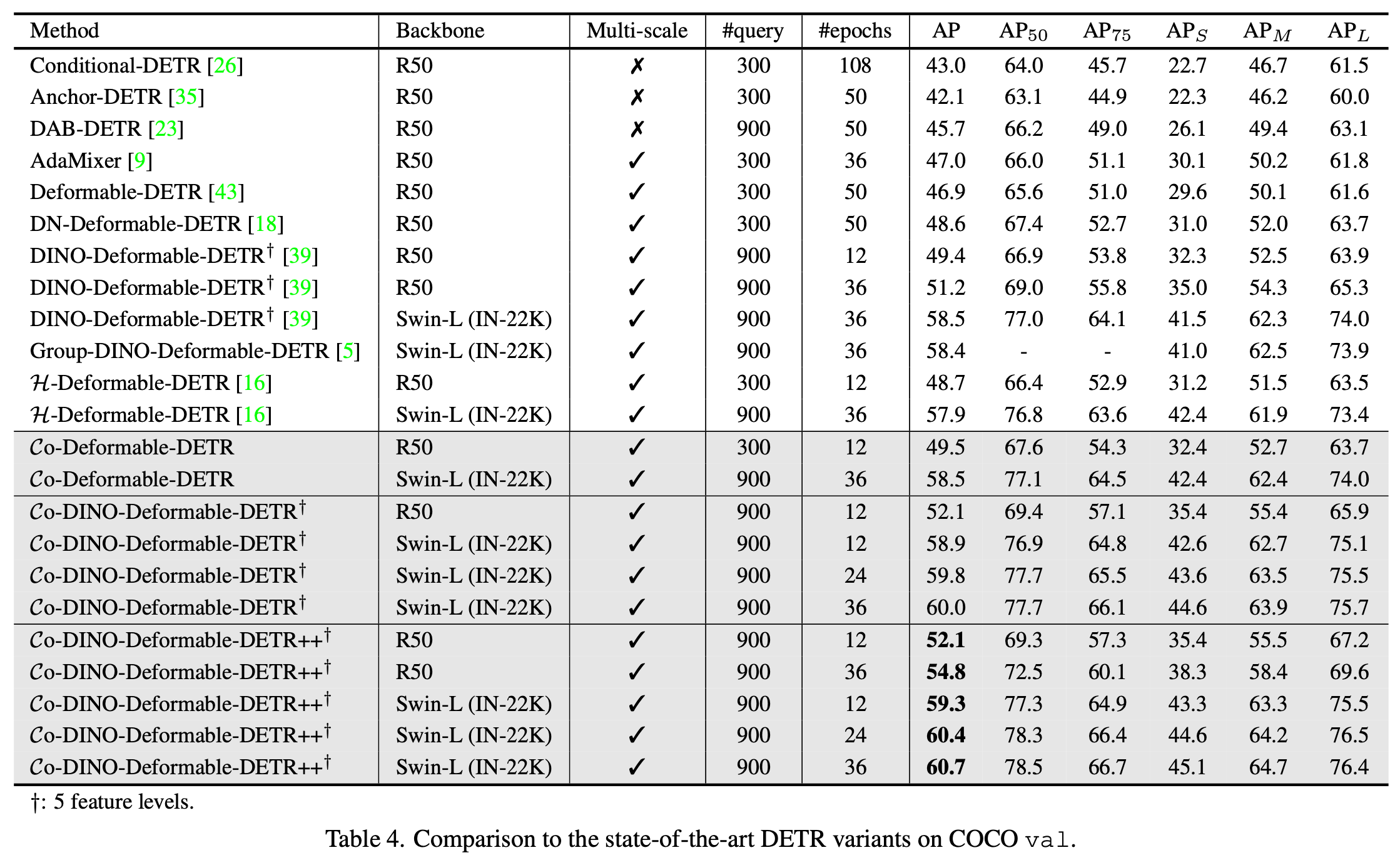
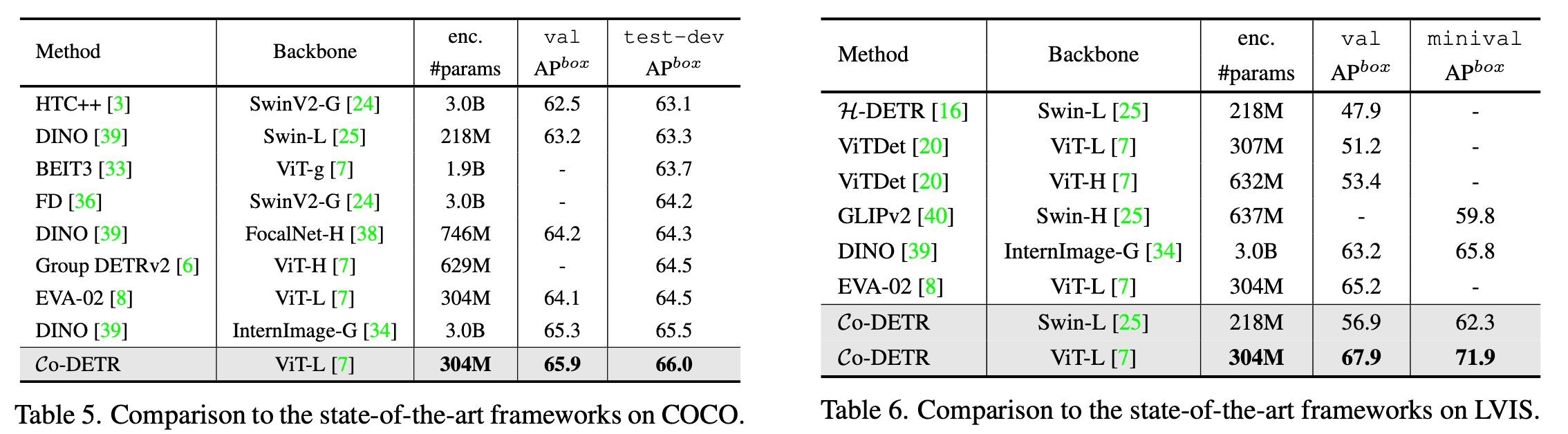
-
Ablation studies
-
임의의 auxiliary head +1 추가시 성능 향상
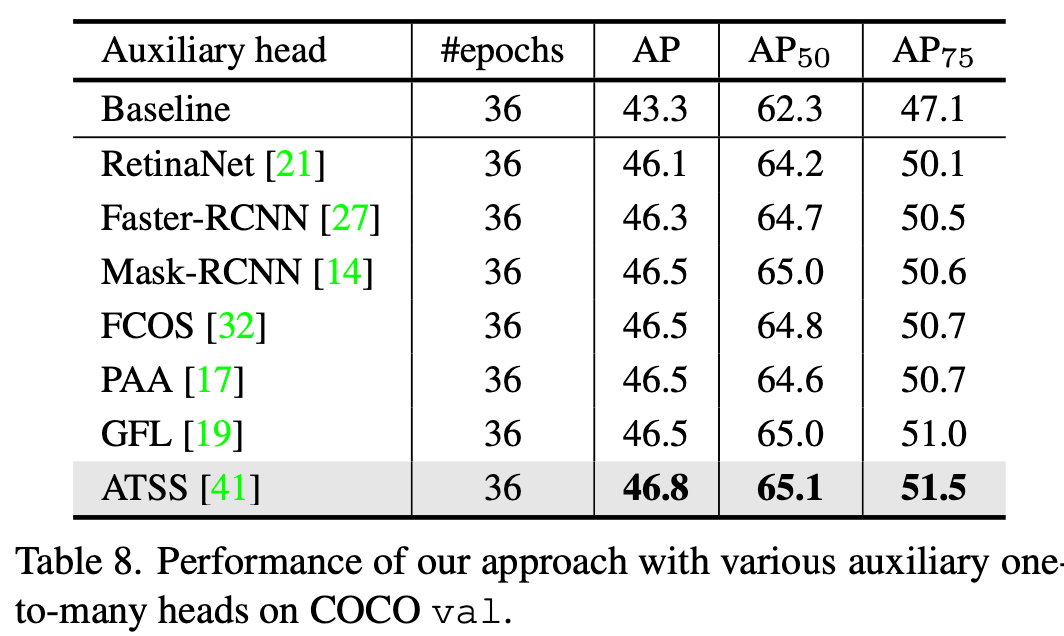
-
1~6 Auxiliary head별 성능 향상
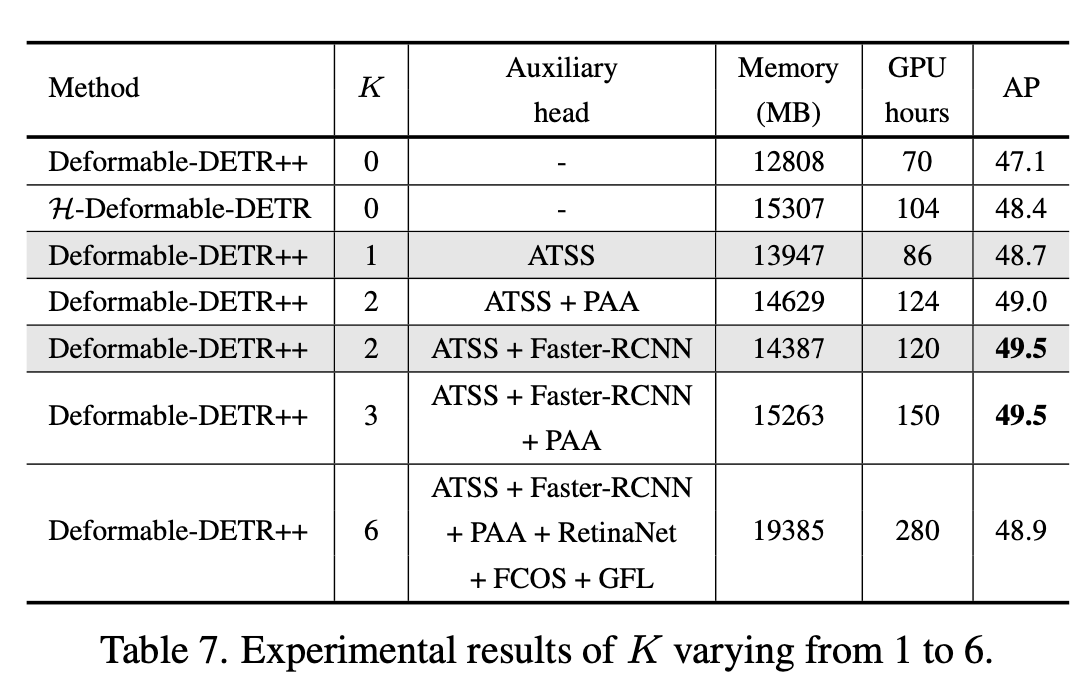
-
3개 이상부터는 auxilary head별 optimization 방향이 달라 conflict 발생하여 성능이 하락하는 걸로 짐작
-
Conflict 분석
-
Head i, j별 distance 정의
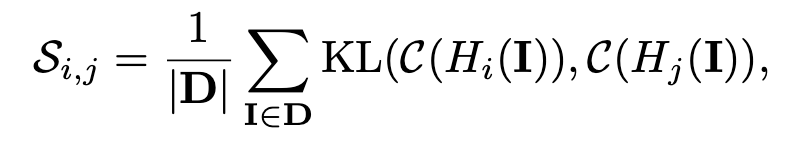
- C: CAM 결과
-
one-to-one matching DETR head와 distance를 K에 따라 비교
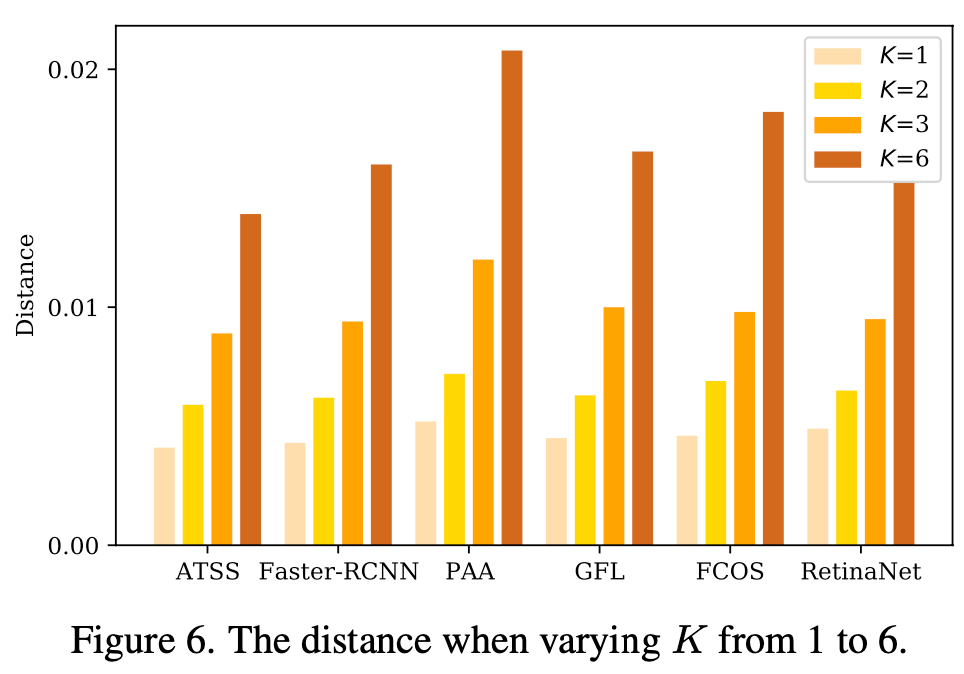
- K=1일땐 minor하나 K=3이상부터 무시불가능한 수준으로 distance가 증가
-
각 module별 성능 향상 기여
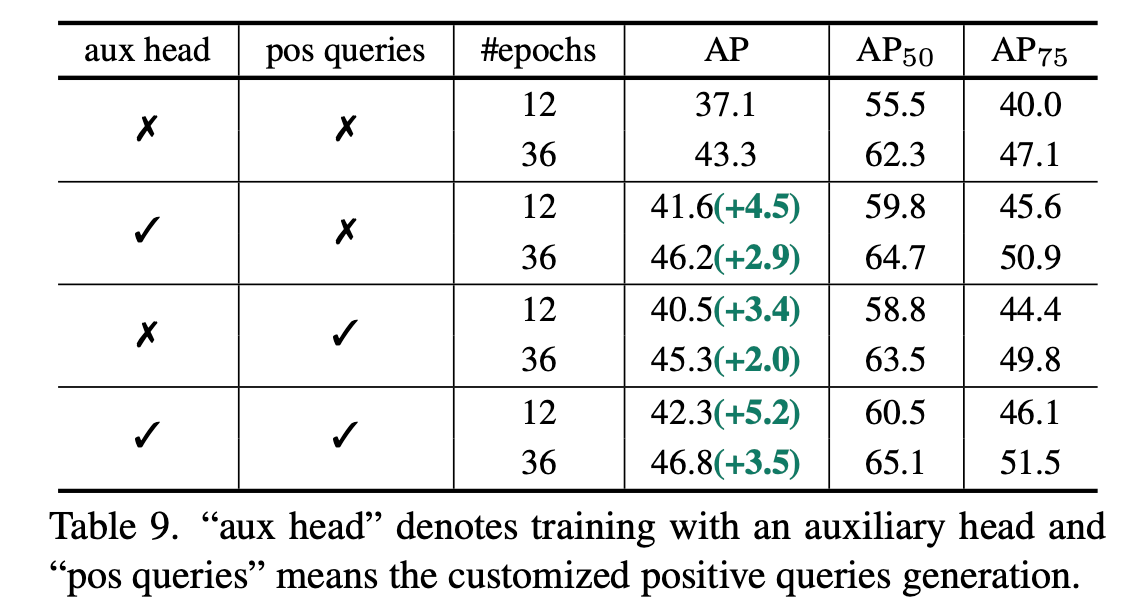
-
-
Auxiliary head의 positive query 정성적 결과 & positive / negative query와 original query간의 distance
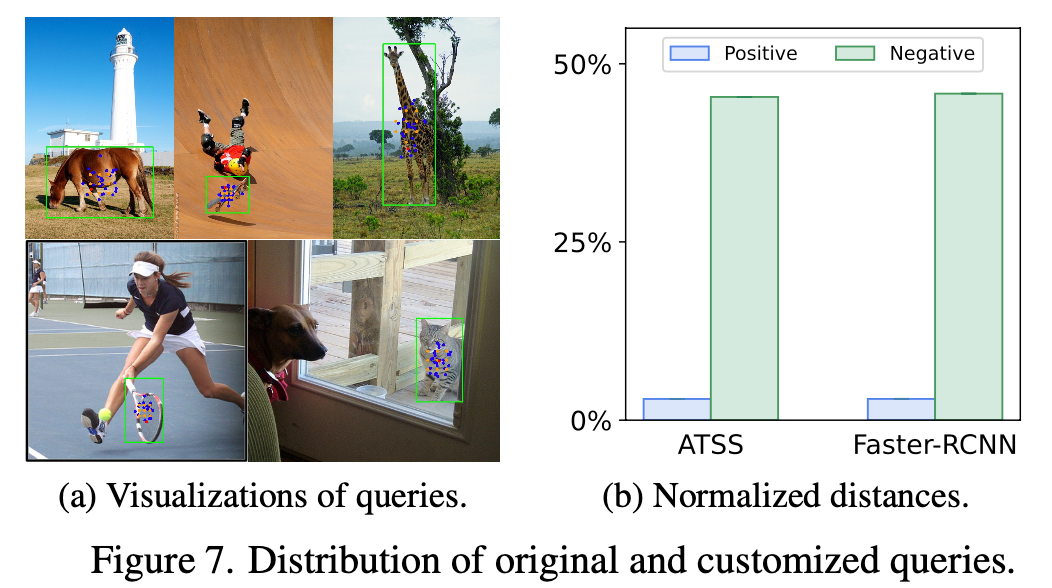
-
-
Auxiliary branch의 성능도 향상
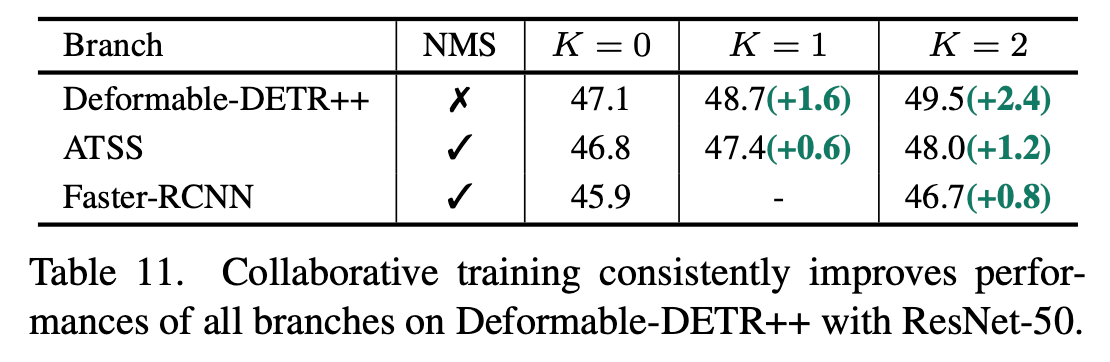
-
-