AGENT S: AN OPEN AGENTIC FRAMEWORK THAT USES COMPUTERS LIKE A HUMAN
[Agent] AGENT S: AN OPEN AGENTIC FRAMEWORK THAT USES COMPUTERS LIKE A HUMAN
- paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.08164
- github: https://github.com/simular-ai/Agent-S
- ICLR 2025 accepted (인용수: 11회, ‘25-03-31 기준)
- downstream task: MLLM for computer tasks in real-world environment
1. Motivation
-
현재 기술에서는 실제 환경에서 Computer tasks를 자동화 하기 위해 3가지 기술적 한계가 존재함
-
Domain-specific 정보 취득의 어려움
ex. 전문화된 최신 도메인 정보가 필요, 지속적으로 진화하는 app & web에 대응해야함
-
긴 작업 계획 (Long task horizons)
$\to$ multi-step planning으로 해결해야 하는 문제가 많음. 중간 목표 (intermediate subgoals) 달성 여부를 tracking해야 함
-
동적 & 비균일한 인터페이스를 다루어야 함
$\to$ visual & textual 정보를 처리하고, 광범위한 action space 안에서 작업해야 함
$\to$ 유저의 task를 잘개 쪼개어 Next action들을 planning하고, ACI (Agent-Computer Interface)를 통해 MLLM의 reasoning 능력을 끌어내는 방법은 없을까?
-
2. Contribution
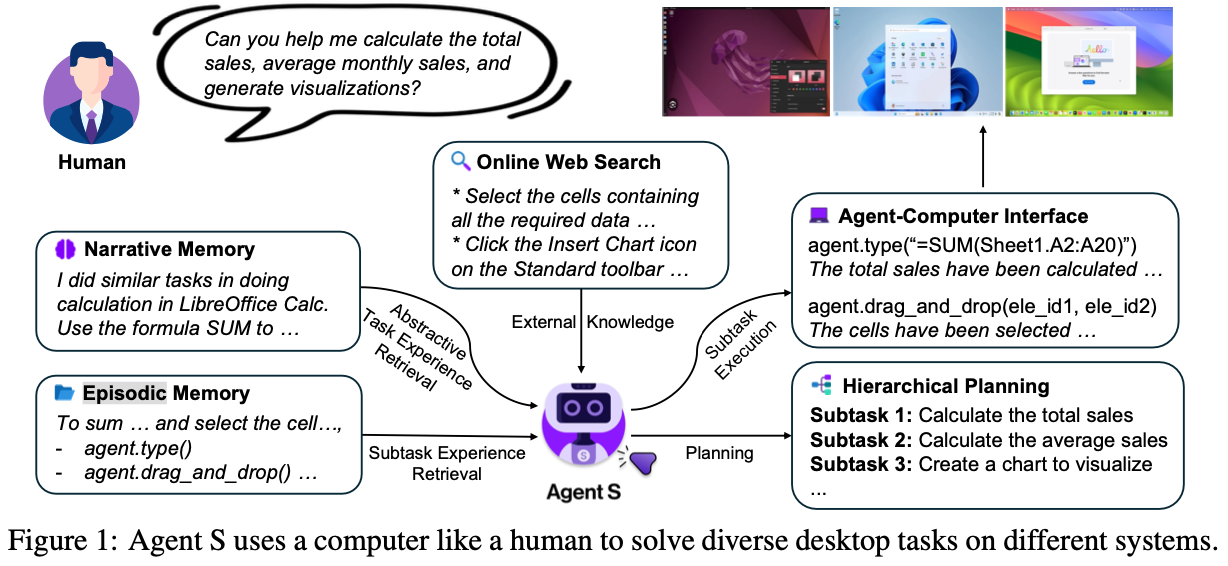
- Computer를 사람처럼 다루는 새로운 agentic framework, Agent S를 제안함
-
Experience-Augmented Hirerarchical Planning 방법을 제안함 $\to$ 유저의 complex, long-horzon task를 executable subtask로 바꾸는 역할
-
Online Web Knowledge: 최신 (Up-to-date) 지식을 모아놓은 database
-
Narrative Memory: 과거 task experience interaction data를 고차원으로 저장해 놓은 database. $\to$ Agent에게 문맥에 맞는 task planning을 하도록 돕는 역할 (RAG)
-
Episodic Memory: 매우 구체적이고, step-by-step subtask experience를 저장해 놓은 database $\to$ Agent의 Planning ability를 향상시키기 위해 사용
$\to$ task를 성공적으로 수행한 experience의 모든 데이터는 Narrative, Episodic memory에 요약 & 평가되어 지속적으로 improve되게끔 저장됨
-
- Self-supervised continual memory update방법을 제안함 $\to$ 초기 cold-start에 유용함
- MLLM기반의 GUI agent이 computer task를 수행하기 위해 필요한 Agent-Computer Interface를 제안함
- 전처리 layer (추상화 layer)로, grounding, safety, efficiency를 향상시키는 목적.
- dual-input strategy: screentshot + accessibility tree (html) 입력
- bounded action space: LLM이 이해할 함수형태로 제공 (ex. $click(element_id)$)
- 전처리 layer (추상화 layer)로, grounding, safety, efficiency를 향상시키는 목적.
-
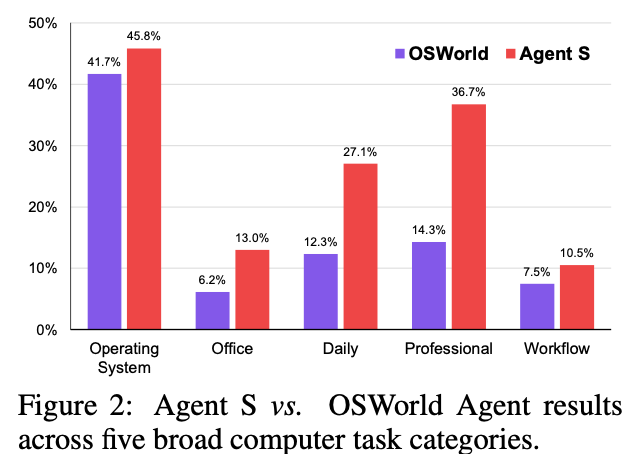
다양한 Computer use task에서 SOTA (WindowsAgentArena, OSWorld)
3. Related Work
MLLM Agents
- Agentic system에서 reasoning backbone으로 MLLM이 도입
- LLMs with Memory, Tool use, Structured Planning, Act in external environments와 증강하여 사용되곤 함
- Software Engineering의 경우, Agent-Computer Interface (ACI) for MLLM을 통해 computer를 제어함
GUI Agents
- 연구가 Web interface뿐만 아니라, mobile 환경, 그리고 OS-level environment로 이동하는 추세
- 행동 복제 (Behavioral cloning)기반 Reinforcement Learning, In-context trajectory examples, state-dependent offline experimence, 그리고 reusable skill generation 등의 연구가 진행되었음
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) fror AI Agents
- 신뢰할 만한, 최신 외장 지식을 MLLM 입력으로 사용하는 사례가 많음.
4. Agent S
-
Overall diagram
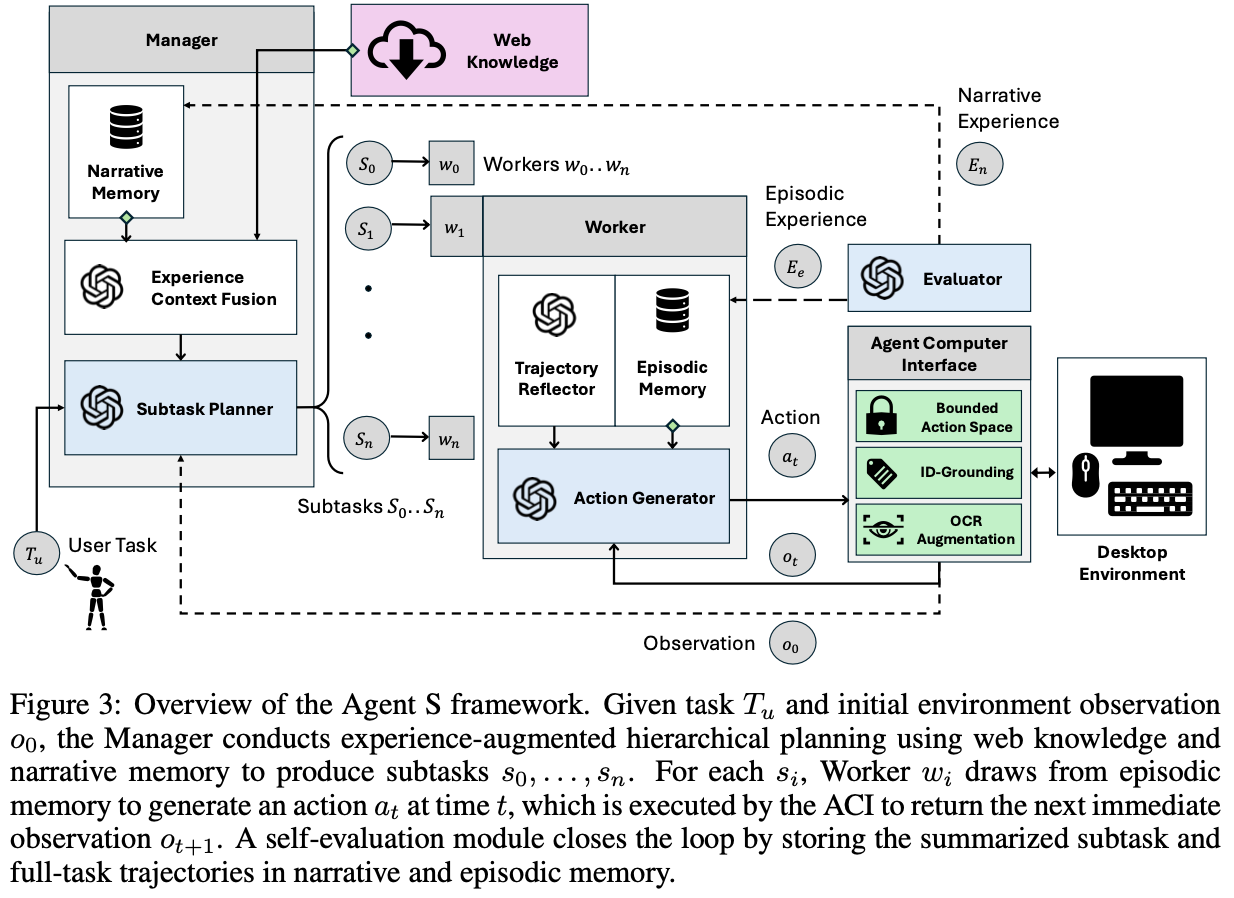
3.1 Experience-Augmented Herarcical Planning
- 복잡한 User task ($T_u$)를 executable subtask로 쪼개어, 해당 task를 달성하도록 Plan을 짜는 역할
- High-level planning + Low-level execution을 가능하도록 하기위해 2가지 data를 사용
- external web-based experience
- internal task-specific experience
Manager ($G$)
-
Plan (subtask)을 생성하는 역할
-
input
- user task $T_u$
- ACI로부터 initial environment observation $O_0$
- Annotated Accessibility Tree
- Screenshot
-
output
-
Observation-aware query $Q$
How to do {something}- 역할
- Online Web Search (Perplexica Search Engine)의 query로 활용되며, external knowledge를 검색하는데 쓰임
- Narrative Memory ($M_n$)에서 유사한 task experience를 embedding기반 similarity search로 쓰임
- success/fail은 self-evaluator $S$ module이 제공
- Successful / failed tracjectory에 대한 요약된 memory $E_{n_u}$를 제공 $\to$ No human-feedback / ground-truth required
- 역할
-
-
Experience Context Fusion module
-
Reasoning backbone: ChatGPT-4o, Claud-3.5
-
Online websearch, narrative memory에서 각각 retrieved한 정보를 취합해서 detailed subtasks를 생성
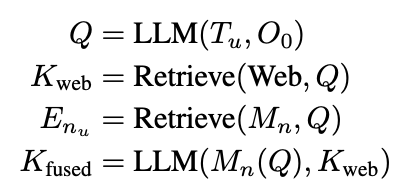
-
Subtask $s_i$별로 연관된 Contextual information $C_{s_i}$을 생성함
-
-
Worker
-
subvtask $s_i$을 sequentially 처리하는 모듈 $<w_0,…, w_n>$
-
Multi step으로 처리함
-
input: Contextual information $C_{s_i}$, subtask $s_i$, 그리고 user task $T_u$ $<C_{s_i}, s_i, T_u>$
-
output: Episodic memory $M_e$에서 embedding similarity기준으로 데이터를 추출
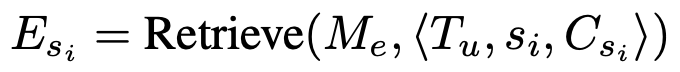
- Episodic memory $M_e$: complete plan, specific grounding actions, summaries from subtask trajectories 중에 successful만 저장
-
Trajectory Reflector ($TR_i$)
- 전체 episode $E_{s_i}$를 보고, reflective advice를 제안하여 대안이 될만한 strategies를 제공하거나 반복적인 action을 회피하도록 유도함
- Reasoning backbone: ChatGPT-4o, Claud-3.5
-
Action Generator
-
input: $TR_i$의 reflection, subtask experience $E_{s_i}$
-
output: single structured response 생성$(a_j$)
-
이전 action status check
-
observation 분석
-
semantic next action (?)
-
grounded next action (?)
$\to$ templated chain-of-thought을 제공함으로써 improved reasoning & results
-
-
-
Self-Evaluator
-
전체 experience를 observation 후에, Experience summaries를 생성하여 Manager, Worker module에게 textual reward $r$을 제공함
-
subtask에 대해 DONE signal이 생성됨 $\to$ Worker의 memory (Episodic memory $M_e$)를 complete epoisode에 대한 summary로 update
-
Complete user-provided task에 대해 DONE signal이 생성됨 (SUCCESS) OR maximum limit에 도달함 (FAIL)$\to$ Narrative memory $M_n$를 entire task competion process에 대한 summary로 update
$\to$ 지속적인 storing, retrieving self-evaluated task experience는 점차 Agent S의 성능을 향상시키는 역할
-
-
3.2 Memory Construction & Update
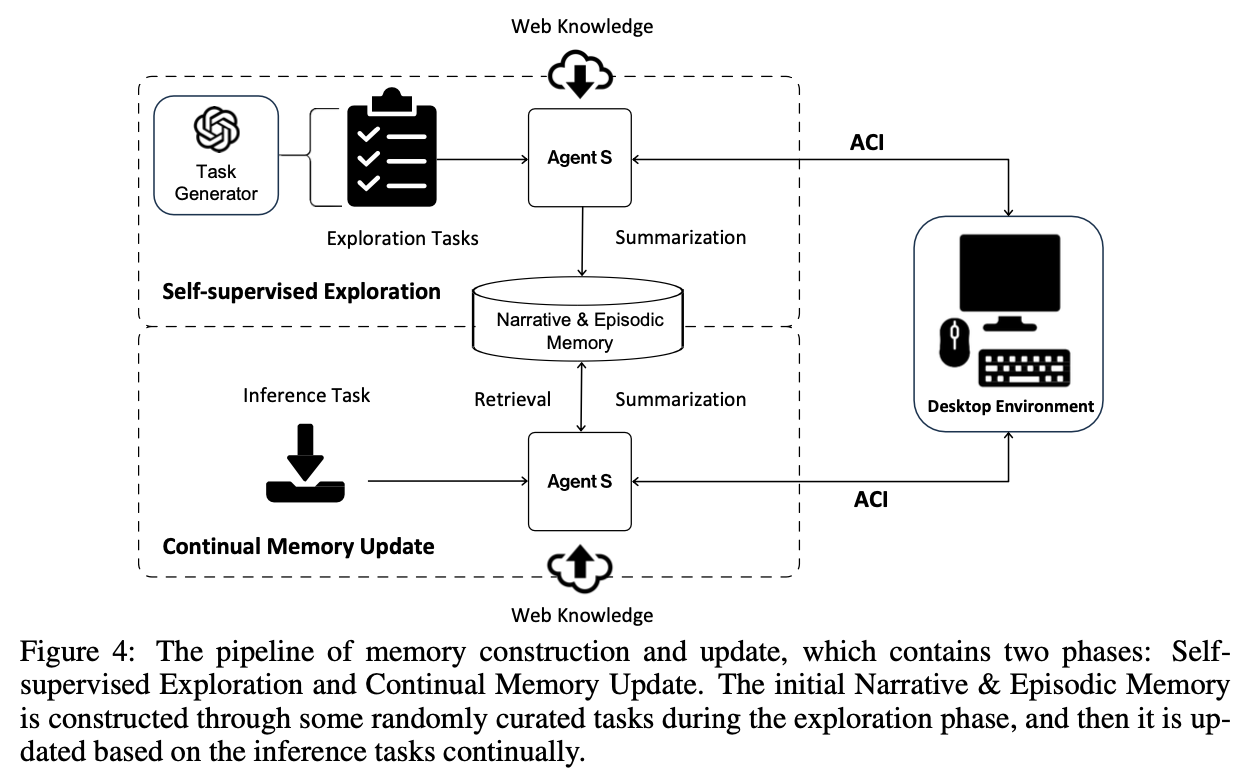
- Self-supervised Exploration기반 초기 memory construction
- Synthetically generated task를 통해 narrative memory $M_n$, Episode memory $M_e$를 구축함
- Environment independent task: task generator에게 OSWorld, WindowsAgentArena의 top-50 most common task를 생성하도록 함
- Environment dependent task: task generator에게 environment를 고려하여 OSWorld, WindowsAgentArena의 초기 셋팅값을 사용하여 new task를 생성하도록 함
- Task가 생성되었으면, Agent S에게 web knowledge $K_{web}$만 사용하여 full task에 대한 experience ($E_n$), subtask에 대한 experience($E_e$)를 취득함
- Key for $E_n$: $Q$
- Key for $E_e$: $Q, s_i, C_{s_i}$
- Synthetically generated task를 통해 narrative memory $M_n$, Episode memory $M_e$를 구축함
3.3 Agent-Computer Interface
- Vision-augmented accessibiility tree를 통해 grounding 능력을 향상시키고, agent의 action을 bound시켜 discrete valid action space을 제공하는 역할
Perception & Grounding
-
MLLM의 한계: 정확한 pixel space coordinate를 pinpoint 하는 grounding 능력이 부족함 $\to$ grounding이 매우 큰 bottleneck임
-
하지만 Desktop environment tasks를 수행하기 위해서는 해당 능력이 필수임
$\to$ 이미지 뿐 아니라, parsable Accessibility Tree를 함께 제공
- Parsable Accessibility Tree? 모든 요소의 coordinate 정보, state 정보가 index가능한 형태로 저장
- 어떻게 indexing? 모든 요소를 integer값으로 사전에 tagging하여, MLLM이 indexing가능하도록 전처리 작업을 수행함
- 추가로, accessibility tree에 없는 이미지 속 text는 OCR module로 추출한 text를 accessibility tree에 추가. - accessibility tree 존재 유무는 IoU (Intersection over Union)으로 판단
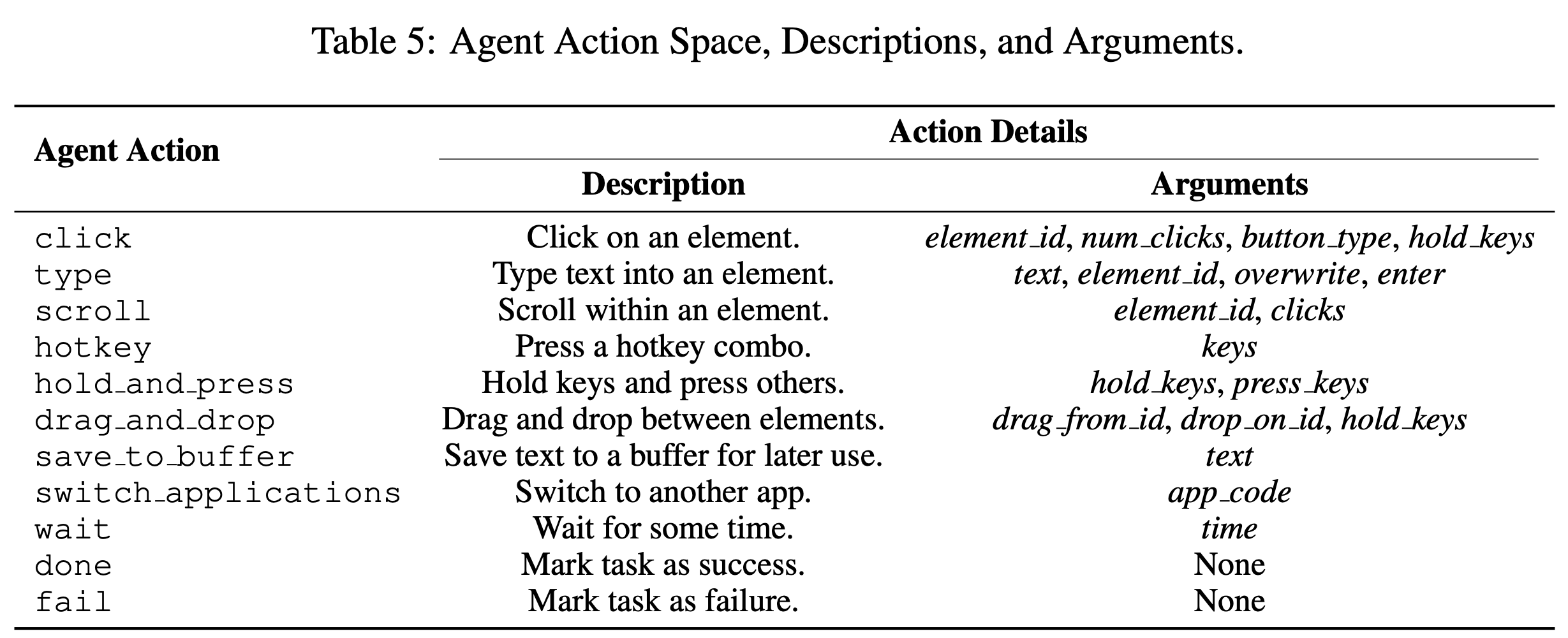
Constrained Action space with Concurrent Feedback
-
적절한 타이밍에 적절한 action을 하기 위해서는 action space를 bound해야함
-
Action spaces
5. Experiments
Benchmarks
- OSWorld
- 다양한 real-world computer tasks로 구성된 MLLM용 benchmark
- OS
- Office (LibreOffice Calc, Impress, Writer)
- Daily (Chrome, VLC Player, Thunderbird)
- Prfessional (VS Code, GIMP)
- Workflow (multiple apps)
- 다양한 real-world computer tasks로 구성된 MLLM용 benchmark
- WindowsAgentArena: Window OS에 국한된 benchmark
Baselines
- Reasoning model: GPT-4o and Claude-3-Sonnet
- OCR: PaddleOCR
- Embedding model: text-embedding-3-small
Main Results
-
정량적 결과

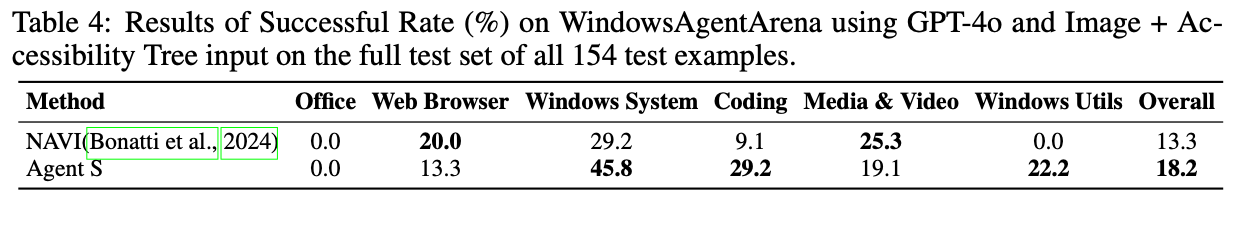
-
정성적 결과

Ablation Studies
-
Test set
- 65개의 instance로 구성함
-
각 모듈별 성능에 기여하는 정도
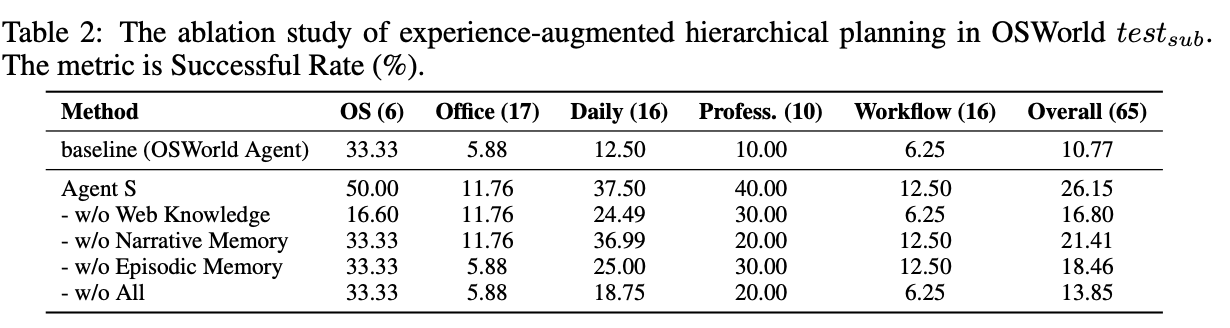
- Web Knowledge > Episodic > Narrative 가 제일 중요한 성능 향상 요인
-
ACI vs. LLM + Hirarchical Planning 여부 (Fig.6) / Self-evaluator의 성능 기여 정도 (Fig. 7)

- Fig. 6
- Baseline: GPT-4o
- Baseline + Retrieval: GPT-4o + Experiential Learning (DB의 update)
- Agent S: GPT-4o + ACI (grounding + action space bounding)
- Agent S (ACI + Retrieval): GPT-4o + ACI + Experiential Leraning (DB의 update)
- Agent S: GPT-4o + ACI + Experiential Leraning (DB의 update) + Manager (Hirarchical Planning)
- Fig. 7
- w/o Continual Memory update: Self-supervised Memory construction (Exploration) 만 하고, memory를 update안하는 경우
- w/o Self-Evaluator: Self-Evaluator의 summary를 저장하지 않고, full trajectory를 저장하는 경우
- w/o Exploration: Self-supservised Memory construction (Exploraiton)도 없는 경우
- Fig. 6
-
Error Analysis (중복 포함)
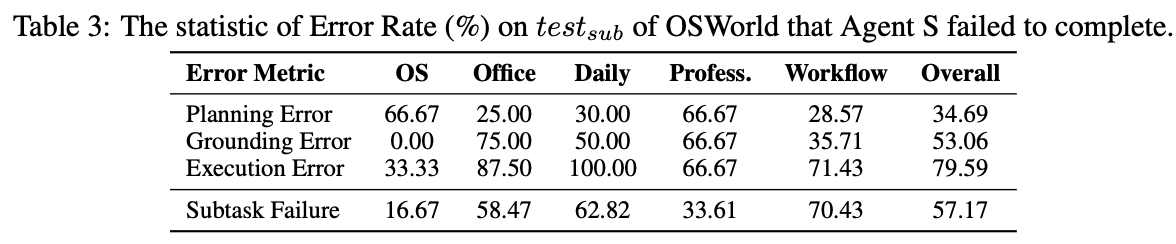
- Grounding Error: pixel좌표를 잘못 가져옴
- Grounding Error가 제일 큰 비중을 차지함. (Execution Error는 여러가지 에러에 의해 유발되기 때문)
- Planning Error: subtask를 제대로 나누지 못했다든지, subtask goal과 다른 plan을 세웠다든지, etc
- Grounding Error: pixel좌표를 잘못 가져옴